Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.808561 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.812568 |
| HF Energy | -169.610256 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.874229 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3855 |
3699 |
78.53 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3545 |
3401 |
8.67 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3063 |
2939 |
58.22 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1751 |
1679 |
180.78 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1423 |
1366 |
14.24 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1335 |
1281 |
161.07 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1195 |
1147 |
45.60 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1061 |
1018 |
212.14 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
618 |
593 |
1.29 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1043 |
1001 |
3.25 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
833 |
799 |
60.97 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
405 |
389 |
64.89 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10063.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9594) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9655.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.375 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.002 |
-0.535 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.198 |
-0.013 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.340 |
1.413 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.846 |
-0.076 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.820 |
0.787 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3541 | 1.2592 | 1.0921 | 1.9006 | 1.8663 |
O2 | 1.3541 | | 2.2614 | 2.0579 | 0.9607 | 3.1171 | N3 | 1.2592 | 2.2614 | | 2.0973 | 3.0448 | 1.0140 | H4 | 1.0921 | 2.0579 | 2.0973 | | 2.1181 | 2.2489 | H5 | 1.9006 | 0.9607 | 3.0448 | 2.1181 | | 3.7667 | H6 | 1.8663 | 3.1171 | 1.0140 | 2.2489 | 3.7667 | |
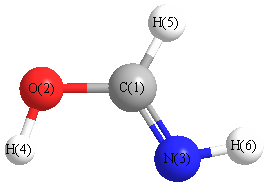 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
109.196 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
109.900 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
119.794 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
114.115 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
126.091 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.072 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.216 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.254 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.035 |
3.107 |
0.000 |
3.714 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.145 |
1.189 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.189 |
-17.944 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.839 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.246 |
1.189 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.189 |
-1.452 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.794 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.589 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.799 |
|---|
| xy | 1.189 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.128 |
0.011 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.011 |
3.333 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.225 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.283 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.425 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.808561 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.812568 |
| HF Energy | -169.610256 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.874229 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.812337 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.816435 |
| HF Energy | -169.613669 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.818171 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3783 |
3630 |
37.63 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3459 |
3319 |
6.57 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3190 |
3061 |
10.52 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1718 |
1648 |
248.12 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1417 |
1359 |
1.27 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1356 |
1301 |
33.52 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1128 |
1082 |
251.52 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1083 |
1039 |
56.36 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
591 |
567 |
32.54 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1080 |
1036 |
64.97 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
853 |
819 |
51.70 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
523 |
502 |
70.30 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10090.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9594) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9680.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.440 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.100 |
-0.355 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.222 |
0.125 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.302 |
1.481 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.821 |
-1.279 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.365 |
-0.885 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3570 | 1.2623 | 1.0835 | 1.9051 | 1.9027 |
O2 | 1.3570 | | 2.3712 | 2.0015 | 0.9654 | 2.5214 | N3 | 1.2623 | 2.3712 | | 2.0400 | 2.4791 | 1.0201 | H4 | 1.0835 | 2.0015 | 2.0400 | | 2.8082 | 2.8942 | H5 | 1.9051 | 0.9654 | 2.4791 | 2.8082 | | 2.2213 | H6 | 1.9027 | 2.5214 | 1.0201 | 2.8942 | 2.2213 | |
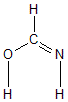 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
109.069 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
112.515 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
129.678 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.681 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.641 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.262 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.309 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.205 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.130 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.957 |
-1.762 |
0.000 |
2.005 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.924 |
-1.933 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.933 |
-13.240 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.817 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.895 |
-1.933 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.933 |
7.630 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.735 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.470 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -9.684 |
|---|
| xy | -1.933 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.503 |
-0.101 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.101 |
3.793 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.253 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.101 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.411 |

