Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2613.391706 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2613.395657 |
| HF Energy | -2613.391706 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 80.597986 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3211 |
3211 |
6.97 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1416 |
1416 |
18.48 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
719 |
719 |
23.58 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
388 |
388 |
73.23 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
3363 |
3363 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
964 |
964 |
2.76 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5030.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 5030.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.007 |
1.489 |
0.000 |
| Br2 |
-0.007 |
-0.368 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.150 |
1.978 |
0.948 |
| H4 |
0.150 |
1.978 |
-0.948 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| C1 | | 1.8578 | 1.0779 | 1.0779 |
Br2 | 1.8578 | | 2.5355 | 2.5355 | H3 | 1.0779 | 2.5355 | | 1.8956 | H4 | 1.0779 | 2.5355 | 1.8956 | |
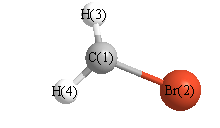 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
116.958 |
|
Br2 |
C1 |
H4 |
116.958 |
| H3 |
C1 |
H4 |
123.126 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.560 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.019 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.270 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.270 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.293 |
1.147 |
0.000 |
1.184 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.583 |
0.621 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.621 |
-21.836 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.500 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.415 |
0.621 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.621 |
3.706 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.291 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.582 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.747 |
|---|
| xy | 0.621 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.245 |
0.047 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.047 |
5.543 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.819 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
42.909 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.551 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2613.391648 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -2613.391648 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 80.664402 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3213 |
3213 |
5.17 |
110.63 |
0.14 |
0.24 |
| 2 |
A1 |
1409 |
1409 |
19.98 |
0.98 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 3 |
A1 |
716 |
716 |
21.93 |
7.41 |
0.25 |
0.41 |
| 4 |
B1 |
256i |
256i |
86.32 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B2 |
3371 |
3371 |
0.35 |
54.83 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
950 |
950 |
2.76 |
4.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4701.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 1) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4701.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at M06-2X/6-311G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.486 |
| Br2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.368 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.952 |
-1.988 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-0.952 |
-1.988 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
Br2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| C1 | | 1.8547 | 1.0766 | 1.0766 |
Br2 | 1.8547 | | 2.5420 | 2.5420 | H3 | 1.0766 | 2.5420 | | 1.9047 | H4 | 1.0766 | 2.5420 | 1.9047 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br2 |
C1 |
H3 |
117.799 |
|
Br2 |
C1 |
H4 |
117.799 |
| H3 |
C1 |
H4 |
124.402 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at M06-2X/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.568 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Br |
0.023 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.273 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.273 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.148 |
1.148 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.653 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-24.447 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.738 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.561 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.252 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.813 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.625 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.206 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.243 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.836 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.551 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
42.891 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.549 |
