Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -233.659529 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -233.670575 |
| HF Energy | -233.659529 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 185.296328 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3930 |
3759 |
31.03 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3128 |
2992 |
40.34 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3049 |
2917 |
58.81 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3046 |
2914 |
17.03 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3034 |
2902 |
26.78 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
2981 |
2852 |
59.66 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1524 |
1457 |
3.11 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1506 |
1440 |
6.60 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1496 |
1431 |
1.68 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1490 |
1425 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1475 |
1411 |
3.88 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1422 |
1360 |
4.18 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1404 |
1343 |
4.02 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1326 |
1268 |
30.48 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1264 |
1209 |
40.01 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1133 |
1084 |
9.41 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1100 |
1052 |
70.59 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1081 |
1034 |
12.70 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1022 |
978 |
0.76 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
920 |
880 |
13.42 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
448 |
429 |
13.17 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
403 |
385 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
188 |
180 |
2.49 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
3120 |
2985 |
67.33 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
3097 |
2962 |
41.72 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
3064 |
2931 |
4.81 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
3014 |
2883 |
52.81 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1505 |
1439 |
8.78 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1333 |
1275 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1329 |
1271 |
0.67 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
1255 |
1200 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
1188 |
1137 |
2.31 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
962 |
920 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
823 |
788 |
1.39 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
743 |
711 |
2.29 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
271 |
259 |
121.49 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
231 |
221 |
1.37 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
106 |
102 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
60 |
58 |
5.89 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30235.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9565) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28920.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.353 |
-0.339 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.340 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-1.158 |
-0.654 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-2.520 |
0.034 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
2.343 |
0.677 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.446 |
-0.979 |
0.889 |
| H7 |
1.446 |
-0.979 |
-0.889 |
| H8 |
-0.062 |
0.990 |
0.879 |
| H9 |
-0.062 |
0.990 |
-0.879 |
| H10 |
-1.079 |
-1.306 |
0.877 |
| H11 |
-1.079 |
-1.306 |
-0.877 |
| H12 |
-3.332 |
-0.697 |
0.000 |
| H13 |
-2.638 |
0.668 |
0.883 |
| H14 |
-2.638 |
0.668 |
-0.883 |
| H15 |
3.198 |
0.247 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
| C1 | | 1.5137 | 2.5308 | 3.8907 | 1.4185 | 1.0996 | 1.0996 | 2.1310 | 2.1310 | 2.7611 | 2.7611 | 4.6991 | 4.2097 | 4.2097 | 1.9354 |
C2 | 1.5137 | | 1.5257 | 2.5382 | 2.3675 | 2.1495 | 2.1495 | 1.0953 | 1.0953 | 2.1551 | 2.1551 | 3.4898 | 2.8010 | 2.8010 | 3.1991 | C3 | 2.5308 | 1.5257 | | 1.5253 | 3.7457 | 2.7707 | 2.7707 | 2.1622 | 2.1622 | 1.0964 | 1.0964 | 2.1747 | 2.1719 | 2.1719 | 4.4479 | C4 | 3.8907 | 2.5382 | 1.5253 | | 4.9054 | 4.1883 | 4.1883 | 2.7797 | 2.7797 | 2.1540 | 2.1540 | 1.0928 | 1.0939 | 1.0939 | 5.7214 | O5 | 1.4185 | 2.3675 | 3.7457 | 4.9054 | | 2.0829 | 2.0829 | 2.5802 | 2.5802 | 4.0520 | 4.0520 | 5.8396 | 5.0589 | 5.0589 | 0.9565 | H6 | 1.0996 | 2.1495 | 2.7707 | 4.1883 | 2.0829 | | 1.7783 | 2.4800 | 3.0460 | 2.5465 | 3.0992 | 4.8684 | 4.4034 | 4.7467 | 2.3158 | H7 | 1.0996 | 2.1495 | 2.7707 | 4.1883 | 2.0829 | 1.7783 | | 3.0460 | 2.4800 | 3.0992 | 2.5465 | 4.8684 | 4.7467 | 4.4034 | 2.3158 | H8 | 2.1310 | 1.0953 | 2.1622 | 2.7797 | 2.5802 | 2.4800 | 3.0460 | | 1.7587 | 2.5114 | 3.0648 | 3.7831 | 2.5957 | 3.1375 | 3.4571 | H9 | 2.1310 | 1.0953 | 2.1622 | 2.7797 | 2.5802 | 3.0460 | 2.4800 | 1.7587 | | 3.0648 | 2.5114 | 3.7831 | 3.1375 | 2.5957 | 3.4571 | H10 | 2.7611 | 2.1551 | 1.0964 | 2.1540 | 4.0520 | 2.5465 | 3.0992 | 2.5114 | 3.0648 | | 1.7549 | 2.4933 | 2.5154 | 3.0704 | 4.6343 | H11 | 2.7611 | 2.1551 | 1.0964 | 2.1540 | 4.0520 | 3.0992 | 2.5465 | 3.0648 | 2.5114 | 1.7549 | | 2.4933 | 3.0704 | 2.5154 | 4.6343 | H12 | 4.6991 | 3.4898 | 2.1747 | 1.0928 | 5.8396 | 4.8684 | 4.8684 | 3.7831 | 3.7831 | 2.4933 | 2.4933 | | 1.7681 | 1.7681 | 6.5979 | H13 | 4.2097 | 2.8010 | 2.1719 | 1.0939 | 5.0589 | 4.4034 | 4.7467 | 2.5957 | 3.1375 | 2.5154 | 3.0704 | 1.7681 | | 1.7665 | 5.9170 | H14 | 4.2097 | 2.8010 | 2.1719 | 1.0939 | 5.0589 | 4.7467 | 4.4034 | 3.1375 | 2.5957 | 3.0704 | 2.5154 | 1.7681 | 1.7665 | | 5.9170 | H15 | 1.9354 | 3.1991 | 4.4479 | 5.7214 | 0.9565 | 2.3158 | 2.3158 | 3.4571 | 3.4571 | 4.6343 | 4.6343 | 6.5979 | 5.9170 | 5.9170 | |
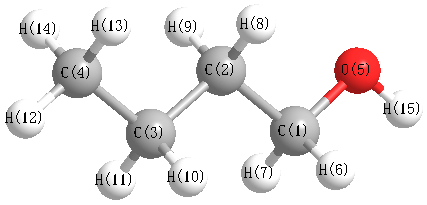 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
112.746 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.462 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H9 |
108.462 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
H15 |
107.562 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.646 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.659 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.659 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
112.591 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.464 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.464 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.085 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
110.085 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
111.258 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
110.962 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H14 |
110.962 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.403 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
109.403 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.979 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.979 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.914 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H9 |
106.804 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
106.321 |
| H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.911 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.911 |
| H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.686 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.002 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.259 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.264 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.315 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.407 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.092 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.117 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.243 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.326 |
-1.540 |
0.000 |
1.574 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.235 |
-3.468 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.468 |
-34.961 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.036 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.764 |
-3.468 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.468 |
-3.825 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.939 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.878 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.726 |
|---|
| xy | -3.468 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.841 |
0.023 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.023 |
7.161 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.686 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
186.211 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.646 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -233.660184 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -233.671471 |
| HF Energy | -233.660184 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 188.356892 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3935 |
3764 |
34.26 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3122 |
2986 |
66.66 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3119 |
2983 |
50.52 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3100 |
2965 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3083 |
2949 |
29.22 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3047 |
2914 |
83.18 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3041 |
2909 |
15.40 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3039 |
2907 |
25.12 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3023 |
2891 |
41.84 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
2987 |
2857 |
67.68 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1528 |
1461 |
4.26 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1515 |
1449 |
7.20 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1505 |
1439 |
7.91 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1502 |
1437 |
2.26 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1479 |
1414 |
5.06 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1462 |
1399 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1418 |
1356 |
2.45 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1411 |
1350 |
1.75 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1343 |
1285 |
6.58 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1332 |
1274 |
4.64 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1313 |
1255 |
32.72 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1269 |
1214 |
9.02 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1245 |
1191 |
19.40 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1167 |
1117 |
5.07 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1146 |
1096 |
12.92 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1101 |
1053 |
53.68 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1060 |
1014 |
15.52 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
985 |
942 |
4.09 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
982 |
939 |
1.55 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
865 |
827 |
6.54 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
846 |
810 |
3.60 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
752 |
719 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
517 |
494 |
10.42 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
353 |
338 |
2.25 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
287 |
274 |
64.65 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
252 |
241 |
7.36 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
235 |
225 |
50.70 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
152 |
145 |
6.39 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
89 |
85 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30302.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9565) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28984.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.442 |
0.515 |
0.224 |
| C2 |
0.005 |
0.706 |
-0.223 |
| C3 |
-0.951 |
-0.334 |
0.357 |
| C4 |
-2.385 |
-0.150 |
-0.134 |
| O5 |
1.891 |
-0.737 |
-0.257 |
| H6 |
2.057 |
1.337 |
-0.169 |
| H7 |
1.488 |
0.559 |
1.323 |
| H8 |
-0.320 |
1.712 |
0.065 |
| H9 |
-0.023 |
0.661 |
-1.318 |
| H10 |
-0.924 |
-0.273 |
1.451 |
| H11 |
-0.589 |
-1.331 |
0.090 |
| H12 |
-3.051 |
-0.905 |
0.293 |
| H13 |
-2.775 |
0.835 |
0.143 |
| H14 |
-2.440 |
-0.235 |
-1.223 |
| H15 |
2.784 |
-0.881 |
0.053 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
H15 |
| C1 | | 1.5168 | 2.5423 | 3.9006 | 1.4154 | 1.0996 | 1.1010 | 2.1356 | 2.1317 | 2.7796 | 2.7476 | 4.7120 | 4.2290 | 4.2103 | 1.9445 |
C2 | 1.5168 | | 1.5269 | 2.5402 | 2.3751 | 2.1477 | 2.1477 | 1.0966 | 1.0957 | 2.1510 | 2.1443 | 3.4925 | 2.8065 | 2.8041 | 3.2118 | C3 | 2.5423 | 1.5269 | | 1.5269 | 2.9352 | 3.4811 | 2.7712 | 2.1614 | 2.1580 | 1.0966 | 1.0930 | 2.1769 | 2.1768 | 2.1733 | 3.7863 | C4 | 3.9006 | 2.5402 | 1.5269 | | 4.3181 | 4.6846 | 4.1981 | 2.7880 | 2.7643 | 2.1587 | 2.1611 | 1.0930 | 1.0946 | 1.0942 | 5.2234 | O5 | 1.4154 | 2.3751 | 2.9352 | 4.3181 | | 2.0833 | 2.0837 | 3.3157 | 2.5971 | 3.3257 | 2.5735 | 4.9752 | 4.9396 | 4.4660 | 0.9557 | H6 | 1.0996 | 2.1477 | 3.4811 | 4.6846 | 2.0833 | | 1.7770 | 2.4177 | 2.4701 | 3.7562 | 3.7665 | 5.5972 | 4.8676 | 4.8793 | 2.3453 | H7 | 1.1010 | 2.1477 | 2.7712 | 4.1981 | 2.0837 | 1.7770 | | 2.4858 | 3.0444 | 2.5550 | 3.0668 | 4.8787 | 4.4312 | 4.7480 | 2.3170 | H8 | 2.1356 | 1.0966 | 2.1614 | 2.7880 | 3.3157 | 2.4177 | 2.4858 | | 1.7626 | 2.4957 | 3.0551 | 3.7891 | 2.6079 | 3.1542 | 4.0447 | H9 | 2.1317 | 1.0957 | 2.1580 | 2.7643 | 2.5971 | 2.4701 | 3.0444 | 1.7626 | | 3.0586 | 2.5043 | 3.7705 | 3.1204 | 2.5801 | 3.4836 | H10 | 2.7796 | 2.1510 | 1.0966 | 2.1587 | 3.3257 | 3.7562 | 2.5550 | 2.4957 | 3.0586 | | 1.7559 | 2.5021 | 2.5223 | 3.0742 | 4.0091 | H11 | 2.7476 | 2.1443 | 1.0930 | 2.1611 | 2.5735 | 3.7665 | 3.0668 | 3.0551 | 2.5043 | 1.7559 | | 2.5067 | 3.0772 | 2.5202 | 3.4024 | H12 | 4.7120 | 3.4925 | 2.1769 | 1.0930 | 4.9752 | 5.5972 | 4.8787 | 3.7891 | 3.7705 | 2.5021 | 2.5067 | | 1.7675 | 1.7664 | 5.8392 | H13 | 4.2290 | 2.8065 | 2.1768 | 1.0946 | 4.9396 | 4.8676 | 4.4312 | 2.6079 | 3.1204 | 2.5223 | 3.0772 | 1.7675 | | 1.7672 | 5.8177 | H14 | 4.2103 | 2.8041 | 2.1733 | 1.0942 | 4.4660 | 4.8793 | 4.7480 | 3.1542 | 2.5801 | 3.0742 | 2.5202 | 1.7664 | 1.7672 | | 5.4160 | H15 | 1.9445 | 3.2118 | 3.7863 | 5.2234 | 0.9557 | 2.3453 | 2.3170 | 4.0447 | 3.4836 | 4.0091 | 3.4024 | 5.8392 | 5.8177 | 5.4160 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
113.285 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.539 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H9 |
108.284 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
H15 |
108.635 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
108.145 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.307 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.224 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
112.567 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.044 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
108.725 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.860 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H9 |
109.639 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H12 |
111.308 |
|
C3 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.205 |
| C3 |
C4 |
H14 |
110.951 |
|
C4 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.651 |
| C4 |
C3 |
H11 |
110.045 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.243 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.189 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.706 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H9 |
107.029 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
106.624 |
| H12 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.800 |
|
H12 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.722 |
| H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.687 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.021 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.263 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.251 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.317 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.407 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.102 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.094 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.112 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.107 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.137 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.117 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.107 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.114 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.246 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.002 |
0.801 |
0.920 |
1.579 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.367 |
0.184 |
1.912 |
| y |
0.184 |
-33.560 |
-0.595 |
| z |
1.912 |
-0.595 |
-33.575 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.201 |
0.184 |
1.912 |
| y |
0.184 |
-2.589 |
-0.595 |
| z |
1.912 |
-0.595 |
-2.612 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.224 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.194 |
|---|
| xy | 0.184 |
|---|
| xz | 1.912 |
|---|
| yz | -0.595 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.649 |
0.088 |
0.168 |
| y |
0.088 |
7.165 |
-0.035 |
| z |
0.168 |
-0.035 |
6.896 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
167.808 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.954 |
