Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -151.181495 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -151.189467 |
| HF Energy | -151.181495 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 83.171105 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3558 |
3388 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
3088 |
2941 |
37.53 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1679 |
1599 |
71.99 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
1496 |
1424 |
0.85 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A1 |
1099 |
1046 |
43.30 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A1 |
846 |
806 |
14.11 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A1 |
466 |
444 |
1.92 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A2 |
3659 |
3484 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A2 |
1409 |
1342 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A2 |
1077 |
1026 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A2 |
256 |
244 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B1 |
3657 |
3482 |
4.21 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B1 |
3140 |
2991 |
28.22 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B1 |
1369 |
1304 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B1 |
853 |
813 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B1 |
391 |
373 |
103.91 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B2 |
3559 |
3390 |
0.85 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B2 |
1670 |
1590 |
8.13 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B2 |
1412 |
1344 |
22.88 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B2 |
1112 |
1059 |
118.16 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B2 |
750 |
714 |
446.18 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 18272.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9523) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 17401.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.538 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.283 |
-0.181 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
-1.283 |
-0.181 |
| H4 |
0.882 |
0.000 |
1.182 |
| H5 |
-0.882 |
0.000 |
1.182 |
| H6 |
0.821 |
1.381 |
-0.766 |
| H7 |
-0.821 |
1.381 |
-0.766 |
| H8 |
-0.821 |
-1.381 |
-0.766 |
| H9 |
0.821 |
-1.381 |
-0.766 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.4706 | 1.4706 | 1.0919 | 1.0919 | 2.0697 | 2.0697 | 2.0697 | 2.0697 |
N2 | 1.4706 | | 2.5653 | 2.0689 | 2.0689 | 1.0133 | 1.0133 | 2.8484 | 2.8484 | N3 | 1.4706 | 2.5653 | | 2.0689 | 2.0689 | 2.8484 | 2.8484 | 1.0133 | 1.0133 | H4 | 1.0919 | 2.0689 | 2.0689 | | 1.7647 | 2.3884 | 2.9332 | 2.9332 | 2.3884 | H5 | 1.0919 | 2.0689 | 2.0689 | 1.7647 | | 2.9332 | 2.3884 | 2.3884 | 2.9332 | H6 | 2.0697 | 1.0133 | 2.8484 | 2.3884 | 2.9332 | | 1.6430 | 3.2143 | 2.7626 | H7 | 2.0697 | 1.0133 | 2.8484 | 2.9332 | 2.3884 | 1.6430 | | 2.7626 | 3.2143 | H8 | 2.0697 | 2.8484 | 1.0133 | 2.9332 | 2.3884 | 3.2143 | 2.7626 | | 1.6430 | H9 | 2.0697 | 2.8484 | 1.0133 | 2.3884 | 2.9332 | 2.7626 | 3.2143 | 1.6430 | |
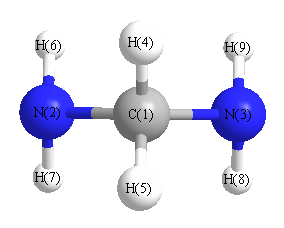 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
H6 |
111.548 |
|
C1 |
N2 |
H7 |
111.548 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H8 |
111.548 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H9 |
111.548 |
| N2 |
C1 |
N3 |
121.434 |
|
N2 |
C1 |
H4 |
106.747 |
| N2 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.747 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
106.747 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.747 |
|
H4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.815 |
| H6 |
N2 |
H7 |
108.336 |
|
H8 |
N3 |
H9 |
108.336 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.188 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.646 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.646 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.156 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.156 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.292 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.292 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.292 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.292 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.991 |
1.991 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-16.701 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-26.951 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-18.563 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.055 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-9.318 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.263 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 6.526 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 10.249 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.226 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.254 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.492 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
54.126 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.357 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -151.179608 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -151.187602 |
| HF Energy | -151.179608 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 83.665850 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3666 |
3491 |
3.36 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3561 |
3391 |
0.90 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2983 |
2841 |
113.38 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1660 |
1581 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1540 |
1466 |
1.39 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1370 |
1305 |
4.64 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1232 |
1173 |
4.15 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
997 |
949 |
13.15 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
844 |
804 |
190.50 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
494 |
470 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
315 |
300 |
25.41 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B |
3667 |
3492 |
5.93 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B |
3562 |
3392 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B |
3010 |
2866 |
84.32 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B |
1654 |
1575 |
111.67 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B |
1470 |
1400 |
38.32 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B |
1253 |
1193 |
17.59 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B |
1162 |
1106 |
38.09 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
987 |
940 |
16.20 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
816 |
778 |
165.39 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
276 |
263 |
87.32 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 18259.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9523) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 17388.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.547 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.174 |
-0.311 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
-1.174 |
-0.311 |
| H4 |
0.884 |
-0.077 |
1.201 |
| H5 |
-0.884 |
0.077 |
1.201 |
| H6 |
-0.040 |
2.034 |
0.225 |
| H7 |
0.833 |
1.185 |
-0.892 |
| H8 |
0.040 |
-2.034 |
0.225 |
| H9 |
-0.833 |
-1.185 |
-0.892 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.4540 | 1.4540 | 1.1020 | 1.1020 | 2.0597 | 2.0417 | 2.0597 | 2.0417 |
N2 | 1.4540 | | 2.3481 | 2.1522 | 2.0662 | 1.0141 | 1.0155 | 3.2528 | 2.5686 | N3 | 1.4540 | 2.3481 | | 2.0662 | 2.1522 | 3.2528 | 2.5686 | 1.0141 | 1.0155 | H4 | 1.1020 | 2.1522 | 2.0662 | | 1.7739 | 2.5024 | 2.4446 | 2.3438 | 2.9247 | H5 | 1.1020 | 2.0662 | 2.1522 | 1.7739 | | 2.3438 | 2.9247 | 2.5024 | 2.4446 | H6 | 2.0597 | 1.0141 | 3.2528 | 2.5024 | 2.3438 | | 1.6521 | 4.0688 | 3.4987 | H7 | 2.0417 | 1.0155 | 2.5686 | 2.4446 | 2.9247 | 1.6521 | | 3.4987 | 2.8973 | H8 | 2.0597 | 3.2528 | 1.0141 | 2.3438 | 2.5024 | 4.0688 | 3.4987 | | 1.6521 | H9 | 2.0417 | 2.5686 | 1.0155 | 2.9247 | 2.4446 | 3.4987 | 2.8973 | 1.6521 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
H6 |
111.894 |
|
C1 |
N2 |
H7 |
110.270 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H8 |
111.894 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H9 |
110.270 |
| N2 |
C1 |
N3 |
107.698 |
|
N2 |
C1 |
H4 |
113.999 |
| N2 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.069 |
|
N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
107.069 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H5 |
113.999 |
|
H4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.188 |
| H6 |
N2 |
H7 |
108.969 |
|
H8 |
N3 |
H9 |
108.969 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at wB97X-D/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.134 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.649 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.649 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.289 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.304 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.289 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.304 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.622 |
1.622 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-20.419 |
3.114 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.114 |
-16.741 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-20.907 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.595 |
3.114 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.114 |
3.922 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.326 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.653 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.678 |
|---|
| xy | 3.114 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.291 |
-0.046 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.046 |
4.916 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.604 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
53.069 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.285 |
