Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.747969 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.751942 |
| HF Energy | -169.747969 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.407659 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3714 |
3690 |
60.69 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3443 |
3420 |
10.99 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2944 |
2925 |
62.10 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1695 |
1684 |
204.98 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1354 |
1345 |
11.91 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1281 |
1273 |
155.41 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1149 |
1142 |
29.61 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1015 |
1009 |
220.69 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
597 |
593 |
1.83 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
983 |
977 |
1.47 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
795 |
790 |
68.42 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
426 |
423 |
55.72 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9698.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9935) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9635.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.380 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.007 |
-0.538 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.203 |
-0.016 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.347 |
1.428 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.858 |
-0.070 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.840 |
0.784 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3626 | 1.2665 | 1.1045 | 1.9115 | 1.8839 |
O2 | 1.3626 | | 2.2707 | 2.0744 | 0.9714 | 3.1391 | N3 | 1.2665 | 2.2707 | | 2.1188 | 3.0613 | 1.0233 | H4 | 1.1045 | 2.0744 | 2.1188 | | 2.1278 | 2.2796 | H5 | 1.9115 | 0.9714 | 3.0613 | 2.1278 | | 3.7952 | H6 | 1.8839 | 3.1391 | 1.0233 | 2.2796 | 3.7952 | |
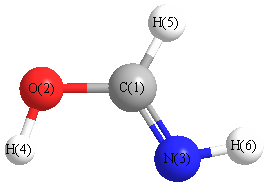 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
108.810 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
110.269 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
119.418 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
114.051 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
126.531 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.022 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.226 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.405 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.371 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.118 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.020 |
2.964 |
0.000 |
3.587 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.481 |
1.245 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.245 |
-18.398 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.285 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.360 |
1.245 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.245 |
-1.515 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.846 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.691 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.917 |
|---|
| xy | 1.245 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.041 |
-0.020 |
-0.001 |
| y |
-0.020 |
4.212 |
-0.000 |
| z |
-0.001 |
-0.000 |
3.150 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.904 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.473 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.755935 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.760042 |
| HF Energy | -169.755935 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.753819 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3592 |
3568 |
34.58 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3439 |
3417 |
7.78 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3023 |
3003 |
30.35 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1665 |
1654 |
265.88 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1337 |
1328 |
18.01 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1329 |
1320 |
1.14 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1145 |
1138 |
93.63 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1032 |
1025 |
168.80 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
567 |
563 |
45.45 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
999 |
993 |
1.97 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
799 |
794 |
29.99 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
625 |
621 |
152.08 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9776.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9935) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9712.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.420 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.118 |
-0.340 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.163 |
-0.093 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.267 |
1.487 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.813 |
-1.271 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.887 |
0.630 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3520 | 1.2709 | 1.0991 | 1.8763 | 1.8986 |
O2 | 1.3520 | | 2.2941 | 2.0149 | 0.9799 | 3.1577 | N3 | 1.2709 | 2.2941 | | 2.1304 | 2.2999 | 1.0233 | H4 | 1.0991 | 2.0149 | 2.1304 | | 2.8109 | 2.3180 | H5 | 1.8763 | 0.9799 | 2.2999 | 2.8109 | | 3.3017 | H6 | 1.8986 | 3.1577 | 1.0233 | 2.3180 | 3.3017 | |
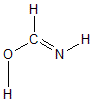 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
106.049 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
111.239 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
121.975 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.155 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
127.870 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.052 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.252 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.427 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.442 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.188 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.100 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.045 |
0.949 |
0.000 |
0.950 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.852 |
3.210 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.210 |
-14.740 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.276 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.844 |
3.210 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.210 |
4.824 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.980 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.960 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.112 |
|---|
| xy | 3.210 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.567 |
0.094 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.094 |
4.490 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.133 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.237 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.422 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.750590 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.754631 |
| HF Energy | -169.750590 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.284942 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3635 |
3611 |
25.42 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3350 |
3329 |
9.35 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3078 |
3058 |
9.48 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1666 |
1656 |
262.06 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1357 |
1349 |
0.79 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1296 |
1288 |
32.10 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1076 |
1069 |
249.87 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1036 |
1029 |
45.52 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
564 |
560 |
27.80 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1022 |
1015 |
65.89 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
813 |
807 |
40.83 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
526 |
522 |
60.39 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9709.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9935) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9646.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.439 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.109 |
-0.357 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.231 |
0.130 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.309 |
1.490 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.825 |
-1.292 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.390 |
-0.887 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3659 | 1.2695 | 1.0954 | 1.9178 | 1.9216 |
O2 | 1.3659 | | 2.3907 | 2.0136 | 0.9765 | 2.5547 | N3 | 1.2695 | 2.3907 | | 2.0550 | 2.5002 | 1.0300 | H4 | 1.0954 | 2.0136 | 2.0550 | | 2.8295 | 2.9225 | H5 | 1.9178 | 0.9765 | 2.5002 | 2.8295 | | 2.2517 | H6 | 1.9216 | 2.5547 | 1.0300 | 2.9225 | 2.2517 | |
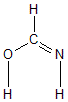 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
108.787 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
112.961 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
130.204 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.301 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.496 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.056 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.247 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.398 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.448 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.147 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.105 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.979 |
-1.728 |
0.000 |
1.986 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.143 |
-1.970 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.970 |
-13.615 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.229 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.721 |
-1.970 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.970 |
7.571 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.850 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.700 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -9.528 |
|---|
| xy | -1.970 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.475 |
0.068 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.068 |
4.539 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.117 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.796 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.465 |


