Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -167.398336 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -167.402110 |
| HF Energy | -167.398336 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 67.701698 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3609 |
3297 |
13.47 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3382 |
3090 |
14.02 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3168 |
2894 |
6.44 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1737 |
1587 |
57.19 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1473 |
1345 |
24.43 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1345 |
1229 |
30.70 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1256 |
1147 |
63.64 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1098 |
1004 |
99.35 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
547 |
499 |
1.63 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
995 |
909 |
3.02 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
765 |
699 |
39.36 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
424 |
388 |
23.98 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9899.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9136) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9044.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.409 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.042 |
-0.555 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.245 |
-0.054 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.343 |
1.478 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.891 |
0.039 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.849 |
0.845 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.4195 | 1.3285 | 1.1229 | 1.9267 | 1.8996 |
O2 | 1.4195 | | 2.3411 | 2.1504 | 1.0362 | 3.2118 | N3 | 1.3285 | 2.3411 | | 2.2068 | 3.1373 | 1.0826 | H4 | 1.1229 | 2.1504 | 2.2068 | | 2.1140 | 2.2817 | H5 | 1.9267 | 1.0362 | 3.1373 | 2.1140 | | 3.8257 | H6 | 1.8996 | 3.2118 | 1.0826 | 2.2817 | 3.8257 | |
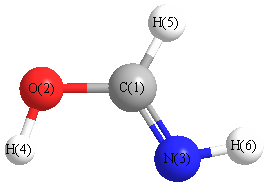 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
102.236 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
103.501 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
116.807 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
115.016 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
128.177 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.056 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.173 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.298 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.066 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.201 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.004 |
2.677 |
0.000 |
3.344 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-13.877 |
0.975 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.975 |
-16.065 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-16.664 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.487 |
0.975 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.975 |
-0.794 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.693 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.386 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.188 |
|---|
| xy | 0.975 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.715 |
0.222 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.222 |
1.604 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.440 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
42.740 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.538 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -167.409733 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -167.413666 |
| HF Energy | -167.409733 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 68.284678 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3539 |
3233 |
12.73 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3391 |
3098 |
9.56 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3265 |
2983 |
0.78 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1716 |
1568 |
88.72 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1487 |
1358 |
13.68 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1363 |
1245 |
17.66 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1205 |
1101 |
16.36 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1113 |
1017 |
71.16 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
498 |
455 |
31.91 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1015 |
927 |
4.29 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
778 |
711 |
58.15 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
695 |
635 |
68.10 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10031.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9136) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9165.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.457 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.156 |
-0.344 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.191 |
-0.131 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.280 |
1.538 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.718 |
-1.289 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.907 |
0.678 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.4060 | 1.3285 | 1.1172 | 1.8874 | 1.9197 |
O2 | 1.4060 | | 2.3569 | 2.0760 | 1.0415 | 3.2289 | N3 | 1.3285 | 2.3569 | | 2.2253 | 2.2329 | 1.0806 | H4 | 1.1172 | 2.0760 | 2.2253 | | 2.8608 | 2.3496 | H5 | 1.8874 | 1.0415 | 2.2329 | 2.8608 | | 3.2804 | H6 | 1.9197 | 3.2289 | 1.0806 | 2.3496 | 3.2804 | |
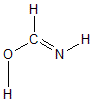 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
99.848 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
105.195 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
119.030 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.197 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
130.774 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.058 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.181 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.325 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.084 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.213 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.199 |
0.755 |
0.000 |
0.781 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.905 |
2.620 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.620 |
-13.453 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-16.659 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.849 |
2.620 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.620 |
3.829 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.980 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.960 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.452 |
|---|
| xy | 2.620 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.980 |
0.325 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.325 |
2.120 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.442 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.656 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.454 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -167.406993 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -167.410891 |
| HF Energy | -167.406993 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 67.669486 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3547 |
3241 |
24.92 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3347 |
3058 |
1.46 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3297 |
3012 |
40.39 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1699 |
1552 |
68.26 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1462 |
1336 |
12.70 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1439 |
1315 |
4.80 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1211 |
1106 |
61.74 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1080 |
987 |
47.89 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
522 |
477 |
28.02 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1083 |
989 |
48.25 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
768 |
702 |
1.72 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
586 |
536 |
57.89 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10020.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9136) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9154.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBE/STO-3G
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.453 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.160 |
-0.362 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.290 |
0.134 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.300 |
1.524 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.754 |
-1.321 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.309 |
-0.957 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.4177 | 1.3285 | 1.1129 | 1.9275 | 1.9235 |
O2 | 1.4177 | | 2.4995 | 2.0733 | 1.0414 | 2.5401 | N3 | 1.3285 | 2.4995 | | 2.1120 | 2.5087 | 1.0903 | H4 | 1.1129 | 2.0733 | 2.1120 | | 2.8815 | 2.9571 | H5 | 1.9275 | 1.0414 | 2.5087 | 2.8815 | | 2.0956 | H6 | 1.9235 | 2.5401 | 1.0903 | 2.9571 | 2.0956 | |
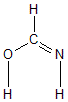 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
102.132 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
104.933 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
131.029 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.442 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
119.530 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.051 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.175 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.293 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.097 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.193 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.126 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.172 |
-1.746 |
0.000 |
2.103 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-20.982 |
-1.500 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.500 |
-12.810 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-16.692 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.231 |
-1.500 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.500 |
6.027 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.203 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.407 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -8.172 |
|---|
| xy | -1.500 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.631 |
-0.105 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.105 |
2.385 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.481 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
42.682 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.533 |


