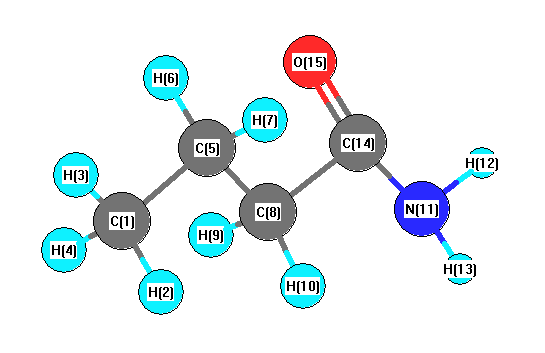
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3662 |
3612 |
24.36 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3518 |
3470 |
19.36 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3062 |
3020 |
32.04 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3057 |
3015 |
48.57 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3035 |
2993 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3002 |
2961 |
18.62 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2989 |
2948 |
26.29 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2976 |
2935 |
26.07 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2958 |
2917 |
13.95 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1753 |
1729 |
234.51 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1568 |
1547 |
110.80 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1473 |
1453 |
5.15 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1465 |
1445 |
6.77 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1457 |
1437 |
2.39 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1427 |
1407 |
6.07 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1378 |
1359 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1369 |
1350 |
70.05 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1324 |
1306 |
22.75 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1281 |
1264 |
34.40 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1228 |
1211 |
28.91 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1212 |
1195 |
5.40 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1106 |
1091 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1081 |
1066 |
2.57 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1051 |
1037 |
1.03 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1030 |
1016 |
1.72 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
910 |
898 |
2.50 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
860 |
848 |
0.80 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
823 |
812 |
5.07 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
732 |
722 |
6.42 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
658 |
649 |
5.77 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
598 |
590 |
12.64 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
505 |
498 |
6.76 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
412 |
406 |
1.98 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
334 |
330 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
247 |
244 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
183 |
180 |
7.90 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
149 |
147 |
200.87 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
92 |
91 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
51 |
50 |
4.15 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28006.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9863) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27623.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.372 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.119 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.122 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.115 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.209 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.120 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.145 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.293 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.106 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.592 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.275 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.266 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.527 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.472 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.439 |
-3.400 |
-0.029 |
3.428 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.068 |
-6.016 |
-0.357 |
| y |
-6.016 |
-38.235 |
-0.256 |
| z |
-0.357 |
-0.256 |
-37.581 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.840 |
-6.016 |
-0.357 |
| y |
-6.016 |
-3.411 |
-0.256 |
| z |
-0.357 |
-0.256 |
-2.429 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.858 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.167 |
|---|
| xy | -6.016 |
|---|
| xz | -0.357 |
|---|
| yz | -0.256 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.792 |
-0.421 |
-0.218 |
| y |
-0.421 |
8.221 |
0.104 |
| z |
-0.218 |
0.104 |
5.944 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
218.766 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.791 |