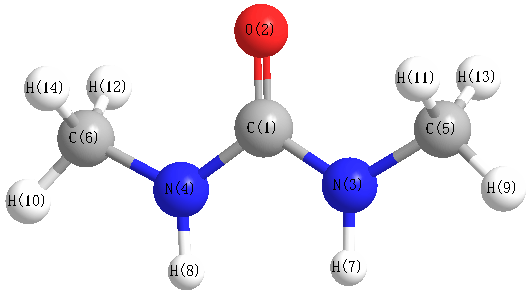
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3533 |
3484 |
7.03 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3103 |
3060 |
2.55 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3033 |
2991 |
4.25 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2956 |
2916 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1750 |
1726 |
191.30 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1492 |
1472 |
20.77 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1461 |
1441 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1438 |
1419 |
4.63 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1392 |
1373 |
17.24 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1175 |
1159 |
0.50 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1145 |
1129 |
3.32 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1111 |
1096 |
5.75 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
903 |
891 |
2.57 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
512 |
505 |
28.39 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
400 |
394 |
46.11 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
229 |
226 |
1.94 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
171 |
168 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
93 |
92 |
0.79 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
3528 |
3480 |
7.06 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3102 |
3060 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3033 |
2991 |
69.59 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
2955 |
2914 |
157.30 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1531 |
1510 |
256.97 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
1467 |
1447 |
19.81 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1453 |
1433 |
133.67 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1398 |
1379 |
3.46 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1215 |
1199 |
236.88 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1123 |
1107 |
8.76 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1104 |
1089 |
31.36 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1042 |
1028 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
723 |
713 |
2.16 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
699 |
690 |
28.17 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
488 |
481 |
132.28 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
333 |
328 |
52.63 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
123 |
121 |
9.27 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
93 |
92 |
1.47 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25652.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9863) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25301.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.693 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.502 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.531 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.531 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.235 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.235 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.251 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.251 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.171 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.171 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.125 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.519 |
3.519 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-37.349 |
-1.787 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.787 |
-30.542 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-36.177 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.989 |
-1.787 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.787 |
6.220 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.231 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.463 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -6.806 |
|---|
| xy | -1.787 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.166 |
-0.517 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.517 |
10.447 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.315 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
194.312 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.940 |