Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBE/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3640 |
3602 |
15.26 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3506 |
3469 |
12.46 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3038 |
3006 |
50.30 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3036 |
3004 |
51.40 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3012 |
2981 |
4.44 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2984 |
2953 |
24.13 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2972 |
2941 |
31.33 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2960 |
2929 |
30.82 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
2945 |
2914 |
15.69 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1735 |
1717 |
267.04 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1599 |
1583 |
101.75 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1476 |
1461 |
9.30 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1470 |
1455 |
9.94 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1460 |
1445 |
3.32 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1428 |
1413 |
8.65 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1379 |
1364 |
2.24 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1368 |
1354 |
70.46 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1326 |
1312 |
23.84 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1291 |
1277 |
40.98 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1236 |
1223 |
27.10 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1219 |
1207 |
7.79 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1110 |
1098 |
1.32 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1088 |
1077 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1054 |
1043 |
0.55 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1033 |
1023 |
2.71 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
911 |
902 |
2.78 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
864 |
855 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
824 |
815 |
4.91 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
732 |
724 |
6.13 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
662 |
656 |
5.17 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
601 |
595 |
13.31 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
508 |
502 |
7.32 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
412 |
408 |
2.15 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
334 |
331 |
2.13 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
244 |
242 |
1.09 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
205 |
203 |
211.05 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
183 |
181 |
8.32 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
91 |
90 |
1.64 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
45 |
45 |
4.05 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27990.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9896) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27699.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
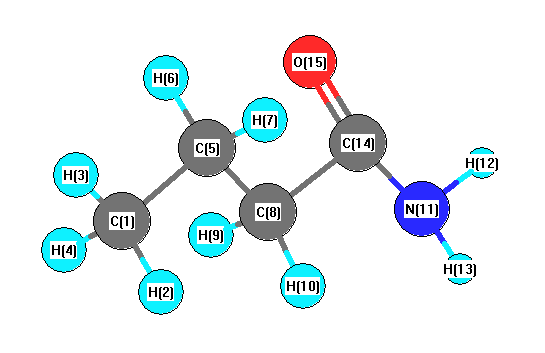
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBE/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.640 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.212 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.221 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.426 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.216 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.236 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.544 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.210 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.237 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
N |
-0.759 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.343 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.344 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.478 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
O |
-0.336 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.472 |
-3.463 |
-0.034 |
3.495 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.948 |
-6.251 |
-0.289 |
| y |
-6.251 |
-39.061 |
-0.187 |
| z |
-0.289 |
-0.187 |
-38.362 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.763 |
-6.251 |
-0.289 |
| y |
-6.251 |
-3.406 |
-0.187 |
| z |
-0.289 |
-0.187 |
-2.357 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.714 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.113 |
|---|
| xy | -6.251 |
|---|
| xz | -0.289 |
|---|
| yz | -0.187 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.371 |
-0.432 |
-0.219 |
| y |
-0.432 |
8.650 |
0.048 |
| z |
-0.219 |
0.048 |
6.456 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
219.052 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.800 |