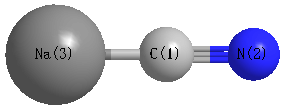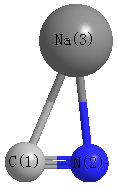Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD=FULL/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -254.500986 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -254.500415 |
| HF Energy | -254.188602 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 46.158092 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD=FULL/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.686 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.870 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.564 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1837 | 2.2507 |
N2 | 1.1837 | | 3.4344 | Na3 | 2.2507 | 3.4344 | |
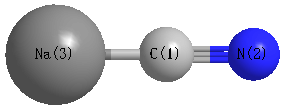 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at CCSD=FULL/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -254.504931 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -254.504626 |
| HF Energy | -254.195963 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 51.471591 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD=FULL/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.125 |
0.669 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.067 |
0.000 |
| Na3 |
-0.614 |
-1.044 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1932 | 2.4412 |
N2 | 1.1932 | | 2.1979 | Na3 | 2.4412 | 2.1979 | |
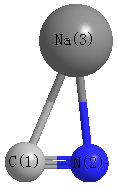 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
86.773 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
29.210 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
64.016 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at CCSD=FULL/aug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -254.505596 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -254.505103 |
| HF Energy | -254.195590 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 48.758072 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at CCSD=FULL/aug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.853 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.661 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.431 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1915 | 3.2842 |
N2 | 1.1915 | | 2.0927 | Na3 | 3.2842 | 2.0927 | |
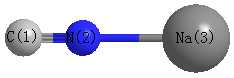 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability