Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3388 |
3368 |
4.08 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3049 |
3030 |
31.52 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2964 |
2946 |
51.96 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
2957 |
2938 |
51.07 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
2947 |
2929 |
5.05 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1591 |
1582 |
19.37 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1432 |
1423 |
5.65 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1418 |
1409 |
0.99 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1409 |
1400 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1338 |
1330 |
3.80 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1329 |
1321 |
4.93 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1257 |
1250 |
4.63 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1101 |
1094 |
2.78 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1068 |
1062 |
15.82 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1021 |
1014 |
0.18 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
877 |
872 |
62.30 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
803 |
798 |
104.41 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
434 |
432 |
3.32 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
258 |
256 |
3.85 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
3472 |
3451 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3038 |
3019 |
52.53 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3006 |
2987 |
39.24 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
2979 |
2961 |
0.52 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1423 |
1415 |
7.41 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1331 |
1323 |
0.25 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1265 |
1257 |
0.67 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1185 |
1178 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
994 |
988 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
825 |
820 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
715 |
711 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
266 |
265 |
32.90 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
212 |
211 |
8.17 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
124 |
123 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25736.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9939) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25579.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
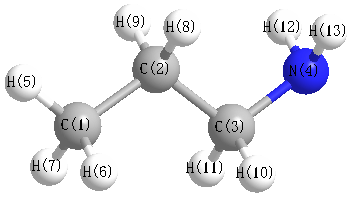
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBEultrafine/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.559 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.819 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.824 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.224 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.226 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.188 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
-0.188 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
-0.311 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.311 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
-0.333 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.333 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
-0.045 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
-0.045 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.097 |
1.361 |
0.000 |
1.365 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.079 |
-1.887 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.887 |
-33.292 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-26.250 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.692 |
-1.887 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.887 |
-6.628 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.936 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.872 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 6.213 |
|---|
| xy | -1.887 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.574 |
0.805 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.805 |
8.402 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.065 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
114.584 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.704 |