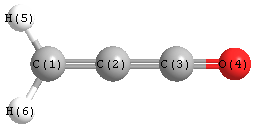Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.506916 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.506916 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 87.950822 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
2989 |
2968 |
35.26 |
246.61 |
0.12 |
0.21 |
| 2 |
A1 |
2263 |
2247 |
740.02 |
26.38 |
0.42 |
0.59 |
| 3 |
A1 |
1743 |
1731 |
24.95 |
2.64 |
0.53 |
0.69 |
| 4 |
A1 |
1432 |
1422 |
2.69 |
16.77 |
0.51 |
0.68 |
| 5 |
A1 |
906 |
900 |
6.19 |
40.22 |
0.24 |
0.38 |
| 6 |
B1 |
974 |
967 |
23.62 |
0.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 7 |
B1 |
622 |
618 |
15.54 |
0.44 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
B1 |
216 |
215 |
0.34 |
3.13 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
B2 |
3049 |
3028 |
11.45 |
155.18 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 10 |
B2 |
1029 |
1022 |
1.22 |
0.31 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
B2 |
429 |
426 |
6.72 |
2.24 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
B2 |
148i |
147i |
14.47 |
0.04 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7752.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9931) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7699.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.880 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.559 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.721 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.906 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.929 |
-2.465 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-0.929 |
-2.465 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3212 | 2.6013 | 3.7860 | 1.0978 | 1.0978 |
C2 | 1.3212 | | 1.2801 | 2.4648 | 2.1204 | 2.1204 | C3 | 2.6013 | 1.2801 | | 1.1847 | 3.3189 | 3.3189 | O4 | 3.7860 | 2.4648 | 1.1847 | | 4.4685 | 4.4685 | H5 | 1.0978 | 2.1204 | 3.3189 | 4.4685 | | 1.8580 | H6 | 1.0978 | 2.1204 | 3.3189 | 4.4685 | 1.8580 | |
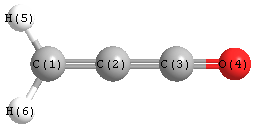 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
180.000 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.194 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
122.194 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
180.000 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.613 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.229 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.135 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.262 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.164 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.133 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.133 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.563 |
2.563 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.691 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.549 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.597 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.618 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.405 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.023 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.046 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.142 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.916 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.579 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.949 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
83.057 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.114 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.508087 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.508087 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 88.182044 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3074 |
3053 |
9.16 |
133.31 |
0.69 |
0.82 |
| 2 |
A' |
3002 |
2982 |
31.80 |
195.15 |
0.13 |
0.23 |
| 3 |
A' |
2174 |
2159 |
728.66 |
34.02 |
0.44 |
0.61 |
| 4 |
A' |
1713 |
1701 |
8.43 |
1.52 |
0.67 |
0.80 |
| 5 |
A' |
1433 |
1423 |
0.89 |
16.06 |
0.54 |
0.71 |
| 6 |
A' |
1038 |
1031 |
13.37 |
4.19 |
0.11 |
0.19 |
| 7 |
A' |
928 |
922 |
3.71 |
33.02 |
0.17 |
0.29 |
| 8 |
A' |
482 |
478 |
8.99 |
4.63 |
0.71 |
0.83 |
| 9 |
A' |
168 |
167 |
18.14 |
6.21 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 10 |
A" |
981 |
974 |
23.50 |
0.43 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A" |
681 |
676 |
10.34 |
0.81 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
A" |
263 |
261 |
1.21 |
3.82 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7968.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9931) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7913.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.978 |
-1.549 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
-0.648 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.329 |
0.612 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
-0.837 |
1.676 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.041 |
-1.277 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.761 |
-2.623 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3298 | 2.5256 | 3.7007 | 1.0973 | 1.0953 |
C2 | 1.3298 | | 1.3022 | 2.4700 | 2.1355 | 2.1168 | C3 | 2.5256 | 1.3022 | | 1.1790 | 3.0305 | 3.4139 | O4 | 3.7007 | 2.4700 | 1.1790 | | 4.1233 | 4.5865 | H5 | 1.0973 | 2.1355 | 3.0305 | 4.1233 | | 1.8568 | H6 | 1.0953 | 2.1168 | 3.4139 | 4.5865 | 1.8568 | |
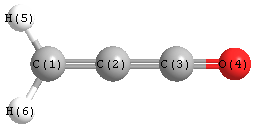 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
147.310 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.965 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.292 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
169.108 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.743 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBEultrafine/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.186 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.131 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.189 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.133 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.131 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.130 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.706 |
-1.575 |
0.000 |
2.322 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-21.948 |
-0.960 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.960 |
-22.545 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.802 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.725 |
-0.960 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.960 |
-0.170 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.555 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.110 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.596 |
|---|
| xy | -0.960 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.506 |
-2.700 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.700 |
9.004 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.961 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
80.893 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.994 |