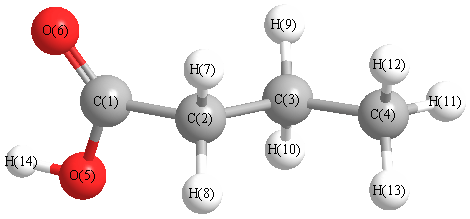Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBEPBEultrafine/6-311G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3593 |
3556 |
18.89 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3053 |
3021 |
39.75 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3041 |
3009 |
35.44 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3034 |
3003 |
29.40 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3007 |
2976 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2984 |
2953 |
30.41 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
2969 |
2938 |
12.30 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
2965 |
2934 |
23.51 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1778 |
1760 |
294.48 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1476 |
1461 |
9.77 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1469 |
1454 |
10.65 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1461 |
1446 |
2.26 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1438 |
1423 |
6.04 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1377 |
1362 |
3.89 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1341 |
1327 |
29.92 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1335 |
1321 |
10.47 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1296 |
1283 |
1.60 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1255 |
1242 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1233 |
1220 |
29.58 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1172 |
1160 |
134.92 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1087 |
1075 |
8.15 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1049 |
1038 |
82.67 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1033 |
1022 |
19.67 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
902 |
893 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
870 |
861 |
2.89 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
848 |
840 |
11.85 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
741 |
733 |
26.96 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
721 |
713 |
37.01 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
625 |
619 |
67.12 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
568 |
562 |
41.55 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
418 |
414 |
2.87 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
324 |
320 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
243 |
240 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
181 |
179 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
93 |
92 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
26 |
25 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25502.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9896) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25236.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBEPBEultrafine/6-311G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.368 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.489 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.436 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.639 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.468 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.300 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.239 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.235 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.223 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.230 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.222 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.218 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.216 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.381 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.995 |
1.253 |
0.208 |
1.613 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.011 |
5.196 |
0.116 |
| y |
5.196 |
-39.423 |
-1.427 |
| z |
0.116 |
-1.427 |
-36.543 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.973 |
5.196 |
0.116 |
| y |
5.196 |
-3.146 |
-1.427 |
| z |
0.116 |
-1.427 |
1.174 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.347 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.413 |
|---|
| xy | 5.196 |
|---|
| xz | 0.116 |
|---|
| yz | -1.427 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.503 |
0.019 |
-0.362 |
| y |
0.019 |
7.642 |
0.019 |
| z |
-0.362 |
0.019 |
6.411 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
210.387 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.505 |