Vibrational Frequencies calculated at TPSSh/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3528 |
3385 |
6.53 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3212 |
3081 |
23.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3187 |
3057 |
5.01 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3169 |
3040 |
22.17 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1700 |
1631 |
88.15 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1665 |
1597 |
48.27 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1550 |
1487 |
51.52 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1315 |
1261 |
53.62 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1212 |
1163 |
7.95 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1055 |
1012 |
2.12 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1007 |
966 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
973 |
934 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
873 |
838 |
11.12 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
831 |
797 |
2.76 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
758 |
727 |
89.42 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
700 |
671 |
9.01 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
638 |
612 |
321.38 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
528 |
506 |
2.07 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
503 |
482 |
45.00 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
222 |
213 |
5.22 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3629 |
3481 |
5.84 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3193 |
3063 |
55.99 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
3170 |
3041 |
7.12 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1643 |
1577 |
4.20 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1517 |
1456 |
1.67 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1383 |
1327 |
6.97 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1377 |
1321 |
1.01 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1190 |
1141 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1150 |
1104 |
2.57 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1077 |
1033 |
3.08 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
947 |
909 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
825 |
792 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
625 |
600 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
412 |
395 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
373 |
357 |
0.08 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
291 |
279 |
23.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25712.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9594) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24668.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
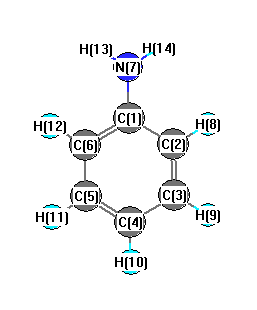
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.296 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.198 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.163 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.168 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.163 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.198 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.804 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.149 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.144 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.329 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.329 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.184 |
1.270 |
0.000 |
1.737 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.673 |
-0.106 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.106 |
13.720 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.376 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
192.269 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.866 |