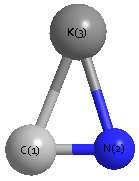Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.763136 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.762554 |
| HF Energy | -692.763136 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 60.229980 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.327 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.305 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.484 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.6322 | 3.8115 |
C2 | 2.6322 | | 1.1793 | N3 | 3.8115 | 1.1793 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
180.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.981 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.642 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.339 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.723 |
12.723 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.441 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.441 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.532 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
103.252 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.161 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.765535 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.764858 |
| HF Energy | -692.765535 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 63.556505 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.230 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.437 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.249 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 3.6667 | 2.4791 |
C2 | 3.6667 | | 1.1876 | N3 | 2.4791 | 1.1876 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.916 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.330 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.586 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.572 |
12.572 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.458 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
3.458 |
0.001 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.001 |
7.379 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
92.024 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.593 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -692.767371 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -692.767202 |
| HF Energy | -692.767371 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 67.749769 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| K1 |
0.000 |
1.058 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.633 |
-1.637 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.542 |
-1.469 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
| K1 | | 2.7685 | 2.5843 |
C2 | 2.7685 | | 1.1869 | N3 | 2.5843 | 1.1869 | |
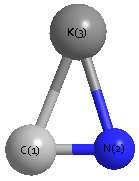 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| K1 |
C2 |
N3 |
68.631 |
|
K1 |
N3 |
C2 |
86.047 |
| C2 |
K1 |
N3 |
25.321 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/6-31+G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
K |
0.898 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.469 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.428 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.373 |
10.629 |
0.000 |
10.636 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.262 |
-0.288 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.288 |
5.075 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.729 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
73.197 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.556 |