Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -207.909195 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -207.639241 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 102.340921 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3839 |
3682 |
53.91 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3041 |
2917 |
24.91 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
2307 |
2212 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1516 |
1454 |
2.92 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1459 |
1399 |
17.15 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1252 |
1201 |
60.39 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1078 |
1033 |
101.19 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
902 |
865 |
13.32 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
573 |
549 |
6.50 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
227 |
218 |
2.25 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
3073 |
2947 |
8.80 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
1274 |
1222 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A" |
1038 |
996 |
1.64 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A" |
357 |
343 |
4.32 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
193 |
185 |
111.18 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11064.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9591) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10611.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.797 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.655 |
-0.509 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-1.207 |
-1.524 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
1.403 |
0.599 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.333 |
1.343 |
0.885 |
| H6 |
-0.333 |
1.343 |
-0.885 |
| H7 |
1.828 |
1.461 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
| C1 | | 1.4616 | 2.6164 | 1.4164 | 1.0919 | 1.0919 | 1.9450 |
C2 | 1.4616 | | 1.1551 | 2.3374 | 2.0777 | 2.0777 | 3.1701 | N3 | 2.6164 | 1.1551 | | 3.3644 | 3.1249 | 3.1249 | 4.2571 | O4 | 1.4164 | 2.3374 | 3.3644 | | 2.0855 | 2.0855 | 0.9610 | H5 | 1.0919 | 2.0777 | 3.1249 | 2.0855 | | 1.7705 | 2.3389 | H6 | 1.0919 | 2.0777 | 3.1249 | 2.0855 | 1.7705 | | 2.3389 | H7 | 1.9450 | 3.1701 | 4.2571 | 0.9610 | 2.3389 | 2.3389 | |
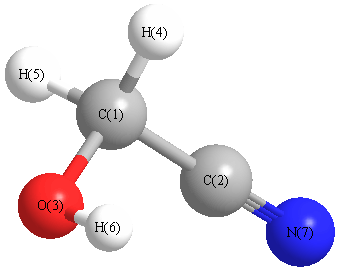 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
N7 |
24.941 |
|
C1 |
O3 |
H6 |
19.456 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O3 |
0.840 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
108.604 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.033 |
|
O3 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.444 |
| O3 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.593 |
|
H4 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.846 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.059 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.029 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.324 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.410 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.283 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.283 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.139 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.063 |
4.714 |
0.000 |
4.832 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.584 |
-0.797 |
0.005 |
| y |
-0.797 |
-23.609 |
-0.002 |
| z |
0.005 |
-0.002 |
-23.237 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.161 |
-0.797 |
0.005 |
| y |
-0.797 |
0.801 |
-0.002 |
| z |
0.005 |
-0.002 |
1.359 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.718 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.975 |
|---|
| xy | -0.797 |
|---|
| xz | 0.005 |
|---|
| yz | -0.002 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.279 |
1.080 |
-0.000 |
| y |
1.080 |
5.960 |
0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
4.082 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
78.966 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.886 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -207.911671 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -207.641630 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 102.280869 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3828 |
3672 |
51.30 |
65.05 |
0.16 |
0.27 |
| 2 |
A |
3132 |
3004 |
2.08 |
73.62 |
0.36 |
0.53 |
| 3 |
A |
3058 |
2933 |
19.16 |
119.71 |
0.10 |
0.19 |
| 4 |
A |
2291 |
2197 |
0.55 |
72.60 |
0.14 |
0.24 |
| 5 |
A |
1504 |
1442 |
3.72 |
7.31 |
0.62 |
0.76 |
| 6 |
A |
1420 |
1362 |
37.51 |
2.64 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 7 |
A |
1375 |
1318 |
3.32 |
2.68 |
0.55 |
0.71 |
| 8 |
A |
1232 |
1182 |
18.31 |
2.60 |
0.27 |
0.43 |
| 9 |
A |
1075 |
1031 |
97.60 |
7.45 |
0.25 |
0.39 |
| 10 |
A |
995 |
954 |
24.45 |
0.51 |
0.22 |
0.36 |
| 11 |
A |
904 |
867 |
14.84 |
3.62 |
0.06 |
0.11 |
| 12 |
A |
581 |
557 |
1.07 |
1.76 |
0.12 |
0.22 |
| 13 |
A |
372 |
357 |
26.34 |
0.70 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 14 |
A |
289 |
277 |
106.62 |
1.35 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 15 |
A |
212 |
204 |
13.90 |
2.39 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11133.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9591) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10678.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.566 |
0.592 |
0.038 |
| C2 |
0.822 |
0.114 |
-0.006 |
| O3 |
-1.508 |
-0.451 |
-0.109 |
| H4 |
-0.710 |
1.148 |
0.966 |
| H5 |
-0.729 |
1.275 |
-0.791 |
| H6 |
-1.395 |
-1.083 |
0.606 |
| N7 |
1.909 |
-0.281 |
-0.015 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
N7 |
| C1 | | 1.4688 | 1.4127 | 1.0913 | 1.0865 | 1.9528 | 2.6246 |
C2 | 1.4688 | | 2.4001 | 2.0881 | 2.0904 | 2.5927 | 1.1561 | O3 | 1.4127 | 2.4001 | | 2.0854 | 2.0120 | 0.9615 | 3.4222 | H4 | 1.0913 | 2.0881 | 2.0854 | | 1.7618 | 2.3611 | 3.1403 | H5 | 1.0865 | 2.0904 | 2.0120 | 1.7618 | | 2.8201 | 3.1590 | H6 | 1.9528 | 2.5927 | 0.9615 | 2.3611 | 2.8201 | | 3.4554 | N7 | 2.6246 | 1.1561 | 3.4222 | 3.1403 | 3.1590 | 3.4554 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
N7 |
178.397 |
|
C1 |
O3 |
H6 |
109.194 |
| C2 |
C1 |
O3 |
112.789 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H4 |
108.401 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.866 |
|
O3 |
C1 |
H4 |
112.144 |
| O3 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.497 |
|
H4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.985 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B2PLYP=FULLultrafine/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.032 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.000 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.462 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.273 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.343 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.164 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.350 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.417 |
1.235 |
1.265 |
2.995 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.506 |
1.151 |
-1.846 |
| y |
1.151 |
-21.013 |
-1.758 |
| z |
-1.846 |
-1.758 |
-22.207 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-10.896 |
1.151 |
-1.846 |
| y |
1.151 |
6.344 |
-1.758 |
| z |
-1.846 |
-1.758 |
4.552 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 9.104 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -11.493 |
|---|
| xy | 1.151 |
|---|
| xz | -1.846 |
|---|
| yz | -1.758 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.467 |
-0.348 |
-0.045 |
| y |
-0.348 |
4.653 |
-0.039 |
| z |
-0.045 |
-0.039 |
4.139 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
78.925 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.884 |
