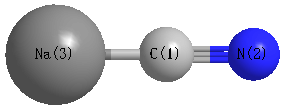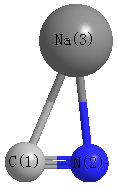Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.139945 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.139330 |
| HF Energy | -255.139945 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 46.672724 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.678 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.849 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.547 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1714 | 2.2246 |
N2 | 1.1714 | | 3.3959 | Na3 | 2.2246 | 3.3959 | |
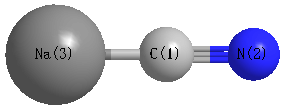 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.081 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.459 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.540 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.153 |
10.153 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.152 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.152 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-13.017 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.067 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-2.067 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.135 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 8.269 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.841 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.841 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.956 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
62.862 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.929 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.145628 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.145372 |
| HF Energy | -255.145628 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 51.828232 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.114 |
0.670 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.072 |
0.000 |
| Na3 |
-0.608 |
-1.047 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1840 | 2.4320 |
N2 | 1.1840 | | 2.2044 | Na3 | 2.4320 | 2.2044 | |
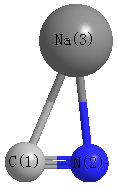 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
86.192 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
29.063 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
64.745 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.031 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.436 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.466 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-4.395 |
-7.048 |
0.000 |
8.306 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.374 |
3.611 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.611 |
-14.143 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-17.479 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.562 |
3.611 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.611 |
4.284 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.721 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.442 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.231 |
|---|
| xy | 3.611 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.023 |
-0.014 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.014 |
3.750 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.965 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
44.439 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.666 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.138698 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -255.138698 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 48.868551 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
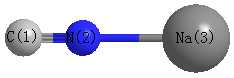
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.848 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.666 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.432 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1823 | 3.2802 |
N2 | 1.1823 | | 2.0979 | Na3 | 3.2802 | 2.0979 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.120 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.498 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.618 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.159 |
10.159 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.117 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.117 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-14.999 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.059 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-1.059 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.118 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.236 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.753 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.753 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.009 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.405 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.510 |