Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3715 |
3568 |
26.36 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3588 |
3446 |
28.37 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3118 |
2994 |
50.39 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3114 |
2990 |
43.56 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3092 |
2969 |
8.53 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3064 |
2943 |
21.88 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3052 |
2931 |
29.06 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3040 |
2919 |
27.22 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3025 |
2905 |
11.98 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1805 |
1733 |
267.73 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1645 |
1579 |
106.03 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1539 |
1478 |
4.78 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1530 |
1470 |
6.22 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1522 |
1462 |
2.14 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1498 |
1439 |
5.15 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1443 |
1386 |
1.18 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1428 |
1371 |
59.92 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1377 |
1322 |
34.04 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1334 |
1281 |
29.85 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1285 |
1234 |
56.02 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1266 |
1216 |
9.63 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1146 |
1101 |
0.93 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1129 |
1084 |
3.44 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1083 |
1040 |
1.54 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1058 |
1016 |
2.41 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
932 |
895 |
2.09 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
896 |
860 |
1.12 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
852 |
818 |
3.52 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
757 |
727 |
6.24 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
674 |
647 |
8.39 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
617 |
593 |
18.16 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
519 |
498 |
6.03 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
425 |
408 |
1.80 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
342 |
328 |
2.62 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
250 |
240 |
0.70 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
201 |
193 |
229.74 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
187 |
180 |
9.55 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
92 |
88 |
1.35 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
40 |
39 |
4.74 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28840.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9603) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27695.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
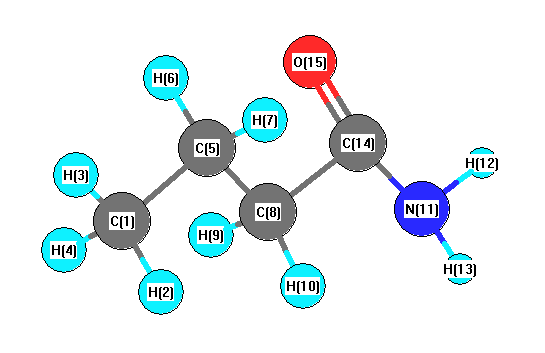
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.447 |
-0.210 |
|
-0.312 |
| 2 |
H |
0.141 |
0.049 |
|
0.077 |
| 3 |
H |
0.148 |
0.047 |
|
0.072 |
| 4 |
H |
0.138 |
0.038 |
|
0.065 |
| 5 |
C |
-0.244 |
0.222 |
|
0.250 |
| 6 |
H |
0.141 |
-0.034 |
|
-0.026 |
| 7 |
H |
0.169 |
-0.025 |
|
-0.021 |
| 8 |
C |
-0.356 |
-0.224 |
|
-0.285 |
| 9 |
H |
0.134 |
0.053 |
|
0.072 |
| 10 |
H |
0.164 |
0.052 |
|
0.075 |
| 11 |
N |
-0.748 |
-0.938 |
|
-0.937 |
| 12 |
H |
0.338 |
0.407 |
|
0.410 |
| 13 |
H |
0.332 |
0.385 |
|
0.388 |
| 14 |
C |
0.595 |
0.727 |
|
0.710 |
| 15 |
O |
-0.505 |
-0.551 |
|
-0.539 |
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.310 |
-3.493 |
0.105 |
3.508 |
| CHELPG |
0.311 |
-3.527 |
0.128 |
3.543 |
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
0.295 |
-3.513 |
0.126 |
3.528 |
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.498 |
-6.210 |
-0.034 |
| y |
-6.210 |
-38.482 |
-0.417 |
| z |
-0.034 |
-0.417 |
-37.616 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.550 |
-6.210 |
-0.034 |
| y |
-6.210 |
-3.425 |
-0.417 |
| z |
-0.034 |
-0.417 |
-2.125 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.251 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.983 |
|---|
| xy | -6.210 |
|---|
| xz | -0.034 |
|---|
| yz | -0.417 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.110 |
-0.363 |
-0.203 |
| y |
-0.363 |
7.881 |
0.102 |
| z |
-0.203 |
0.102 |
5.751 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
218.180 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.771 |