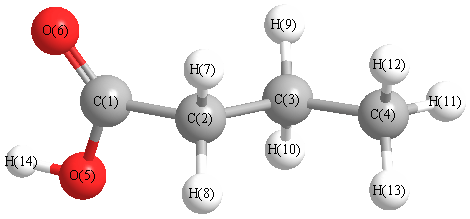Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3736 |
3614 |
61.90 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3108 |
3007 |
25.42 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3091 |
2990 |
32.07 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3086 |
2985 |
28.43 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3058 |
2959 |
2.21 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3053 |
2954 |
16.18 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3031 |
2933 |
14.02 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3025 |
2926 |
21.70 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1805 |
1746 |
344.90 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1511 |
1462 |
8.19 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1499 |
1451 |
7.81 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1496 |
1448 |
1.20 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1484 |
1436 |
4.69 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1417 |
1370 |
1.36 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1384 |
1339 |
19.72 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1363 |
1319 |
45.99 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1328 |
1285 |
4.09 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1302 |
1259 |
2.76 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1263 |
1222 |
12.08 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1199 |
1160 |
138.79 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1113 |
1077 |
7.15 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1074 |
1039 |
127.73 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1039 |
1005 |
2.02 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
914 |
884 |
1.19 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
896 |
867 |
2.95 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
876 |
847 |
10.76 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
756 |
732 |
5.01 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
742 |
718 |
31.13 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
620 |
599 |
68.49 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
582 |
563 |
51.96 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
431 |
417 |
3.30 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
330 |
319 |
0.99 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
239 |
232 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
186 |
180 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
91 |
89 |
0.42 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
36 |
35 |
0.91 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26080.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9675) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25233.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.533 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.112 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.212 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.743 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.389 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-0.732 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.168 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.211 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.155 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.168 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.190 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.178 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.268 |
1.428 |
0.210 |
1.921 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-35.995 |
4.915 |
-0.269 |
| y |
4.915 |
-40.781 |
-1.358 |
| z |
-0.269 |
-1.358 |
-36.475 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.633 |
4.915 |
-0.269 |
| y |
4.915 |
-4.546 |
-1.358 |
| z |
-0.269 |
-1.358 |
1.913 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.826 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 4.786 |
|---|
| xy | 4.915 |
|---|
| xz | -0.269 |
|---|
| yz | -1.358 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
10.465 |
-0.052 |
-0.325 |
| y |
-0.052 |
8.458 |
0.024 |
| z |
-0.325 |
0.024 |
7.464 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
209.207 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.464 |