Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.942500 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.946511 |
| HF Energy | -169.942500 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.877250 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3825 |
3701 |
78.73 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3526 |
3412 |
13.57 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3031 |
2933 |
52.59 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1747 |
1690 |
223.09 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1413 |
1367 |
13.71 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1321 |
1278 |
172.21 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1185 |
1147 |
39.37 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1047 |
1013 |
220.97 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
618 |
598 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1035 |
1001 |
2.08 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
825 |
798 |
66.01 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
417 |
403 |
64.13 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9995.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9675) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9670.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.375 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.001 |
-0.537 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.196 |
-0.008 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.342 |
1.414 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-1.853 |
-0.090 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.831 |
0.783 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3546 | 1.2562 | 1.0941 | 1.9107 | 1.8757 |
O2 | 1.3546 | | 2.2601 | 2.0602 | 0.9622 | 3.1247 | N3 | 1.2562 | 2.2601 | | 2.0952 | 3.0504 | 1.0145 | H4 | 1.0941 | 2.0602 | 2.0952 | | 2.1326 | 2.2625 | H5 | 1.9107 | 0.9622 | 3.0504 | 2.1326 | | 3.7860 | H6 | 1.8757 | 3.1247 | 1.0145 | 2.2625 | 3.7860 | |
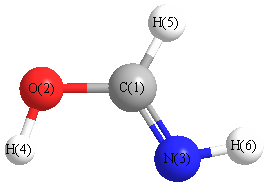 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
109.959 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
110.944 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
119.874 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
114.143 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
125.984 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.004 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.276 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.433 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.423 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.163 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.119 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-2.058 |
3.089 |
0.000 |
3.712 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-14.455 |
1.222 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.222 |
-18.323 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.194 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
4.303 |
1.222 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.222 |
-1.499 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.804 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.609 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.868 |
|---|
| xy | 1.222 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.731 |
-0.005 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.005 |
3.963 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.034 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.535 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.445 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.950626 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.954777 |
| HF Energy | -169.950626 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 71.208463 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3721 |
3600 |
51.13 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3525 |
3410 |
11.08 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3105 |
3004 |
26.56 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1716 |
1661 |
292.16 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1394 |
1348 |
21.57 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1365 |
1320 |
3.37 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1186 |
1147 |
97.63 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1062 |
1028 |
189.97 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
590 |
570 |
46.12 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1050 |
1016 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
827 |
800 |
33.19 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
622 |
602 |
164.11 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10080.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9675) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9753.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.416 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.111 |
-0.343 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.157 |
-0.084 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.263 |
1.473 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.826 |
-1.270 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.877 |
0.630 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3452 | 1.2604 | 1.0891 | 1.8775 | 1.8888 |
O2 | 1.3452 | | 2.2820 | 2.0042 | 0.9695 | 3.1418 | N3 | 1.2604 | 2.2820 | | 2.1073 | 2.3102 | 1.0145 | H4 | 1.0891 | 2.0042 | 2.1073 | | 2.8001 | 2.2994 | H5 | 1.8775 | 0.9695 | 2.3102 | 2.8001 | | 3.3039 | H6 | 1.8888 | 3.1418 | 1.0145 | 2.2994 | 3.3039 | |
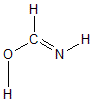 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
107.294 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
111.808 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
122.249 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
110.391 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
127.360 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.039 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.295 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.447 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.483 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.190 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.107 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.029 |
1.007 |
0.000 |
1.008 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.953 |
3.237 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.237 |
-14.552 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.186 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.084 |
3.237 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.237 |
5.018 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.934 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.868 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.401 |
|---|
| xy | 3.237 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.301 |
0.065 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.065 |
4.225 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.019 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
40.894 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.395 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -169.944997 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -169.949080 |
| HF Energy | -169.944997 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 70.803819 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3758 |
3636 |
38.05 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3442 |
3330 |
8.90 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3155 |
3053 |
9.54 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1717 |
1661 |
287.06 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1407 |
1361 |
1.28 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1337 |
1294 |
34.99 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1118 |
1082 |
263.67 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1069 |
1034 |
53.13 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
587 |
568 |
29.42 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A" |
1067 |
1032 |
61.46 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A" |
850 |
822 |
51.76 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A" |
515 |
499 |
69.18 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 10010.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9675) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 9685.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.440 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.098 |
-0.358 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.220 |
0.130 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.307 |
1.482 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.832 |
-1.287 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.385 |
-0.877 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
H4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3579 | 1.2591 | 1.0858 | 1.9174 | 1.9118 |
O2 | 1.3579 | | 2.3694 | 2.0027 | 0.9665 | 2.5373 | N3 | 1.2591 | 2.3694 | | 2.0398 | 2.4939 | 1.0205 | H4 | 1.0858 | 2.0027 | 2.0398 | | 2.8181 | 2.9033 | H5 | 1.9174 | 0.9665 | 2.4939 | 2.8181 | | 2.2548 | H6 | 1.9118 | 2.5373 | 1.0205 | 2.9033 | 2.2548 | |
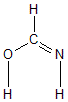 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O2 |
H5 |
110.015 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
113.582 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
129.709 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H4 |
109.577 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H4 |
120.714 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.053 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.291 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.420 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.499 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.148 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.117 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.980 |
-1.739 |
0.000 |
1.996 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.266 |
-2.037 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.037 |
-13.463 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-19.135 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.967 |
-2.037 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.037 |
7.737 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.770 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.540 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -9.803 |
|---|
| xy | -2.037 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.204 |
0.009 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.009 |
4.284 |
0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
3.004 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
41.339 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.430 |


