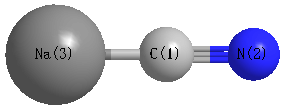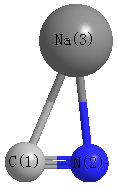Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.174791 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.174219 |
| HF Energy | -255.174791 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 46.691252 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.686 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.850 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.551 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1635 | 2.2376 |
N2 | 1.1635 | | 3.4011 | Na3 | 2.2376 | 3.4011 | |
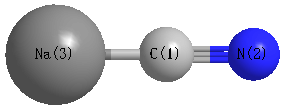 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.341 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.309 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.650 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.387 |
10.387 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.204 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.204 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-13.441 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.881 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-1.881 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.762 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 7.525 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.709 |
0.000 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.709 |
0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
5.839 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
63.211 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.951 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.179480 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.179229 |
| HF Energy | -255.179480 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 51.845673 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-311G**
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.093 |
0.655 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
1.087 |
0.000 |
| Na3 |
-0.596 |
-1.049 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1750 | 2.3997 |
N2 | 1.1750 | | 2.2174 | Na3 | 2.3997 | 2.2174 | |
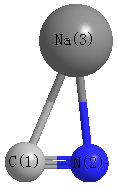 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
84.068 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
29.144 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
66.788 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.173 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.390 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.563 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-4.537 |
-7.246 |
0.000 |
8.549 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-19.713 |
3.381 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.381 |
-14.176 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-17.368 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.941 |
3.381 |
0.000 |
| y |
3.381 |
4.364 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.423 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.847 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.537 |
|---|
| xy | 3.381 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.095 |
0.076 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.076 |
3.721 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.896 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
44.698 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.686 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -255.176015 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -255.175188 |
| HF Energy | -255.176015 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 48.897189 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-311G**
Point Group is C∞v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.847 |
| N2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.673 |
| Na3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.435 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
| C1 | | 1.1742 | 3.2823 |
N2 | 1.1742 | | 2.1080 | Na3 | 3.2823 | 2.1080 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N2 |
Na3 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
Na3 |
N2 |
0.000 |
| N2 |
C1 |
Na3 |
0.000 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.210 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.480 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Na |
0.691 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
10.545 |
10.545 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-17.149 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-17.149 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-15.952 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.599 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.599 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.197 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.395 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.639 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.639 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.878 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
56.759 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
7.534 |