Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -304.110967 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -304.116362 |
| HF Energy | -304.110967 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3593 |
3523 |
36.60 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3569 |
3500 |
62.04 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2969 |
2911 |
35.48 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2948 |
2890 |
39.26 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1783 |
1748 |
239.28 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1497 |
1467 |
8.50 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1463 |
1434 |
35.76 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1348 |
1322 |
114.62 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1290 |
1265 |
17.66 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1228 |
1204 |
1.27 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1156 |
1134 |
131.71 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1094 |
1072 |
227.03 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1024 |
1004 |
0.73 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
838 |
821 |
36.86 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
660 |
647 |
131.37 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
632 |
620 |
14.14 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
492 |
482 |
3.07 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
462 |
453 |
25.54 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
296 |
291 |
70.67 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
281 |
276 |
9.84 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
29 |
29 |
16.59 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14326.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14045.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.748 |
-0.751 |
0.006 |
| C2 |
0.516 |
0.096 |
0.000 |
| O3 |
1.647 |
-0.650 |
-0.004 |
| O4 |
0.503 |
1.317 |
0.002 |
| O5 |
-1.899 |
0.057 |
-0.007 |
| H6 |
-0.719 |
-1.421 |
-0.873 |
| H7 |
-0.721 |
-1.402 |
0.900 |
| H8 |
-1.569 |
0.979 |
0.008 |
| H9 |
2.393 |
-0.014 |
-0.005 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.5216 | 2.3975 | 2.4174 | 1.4071 | 1.1056 | 1.1062 | 1.9152 | 3.2262 |
C2 | 1.5216 | | 1.3556 | 1.2209 | 2.4156 | 2.1427 | 2.1407 | 2.2637 | 1.8802 | O3 | 2.3975 | 1.3556 | | 2.2757 | 3.6167 | 2.6368 | 2.6437 | 3.6052 | 0.9803 | O4 | 2.4174 | 1.2209 | 2.2757 | | 2.7130 | 3.1239 | 3.1141 | 2.0994 | 2.3109 | O5 | 1.4071 | 2.4156 | 3.6167 | 2.7130 | | 2.0805 | 2.0836 | 0.9795 | 4.2928 | H6 | 1.1056 | 2.1427 | 2.6368 | 3.1239 | 2.0805 | | 1.7735 | 2.6941 | 3.5244 | H7 | 1.1062 | 2.1407 | 2.6437 | 3.1141 | 2.0836 | 1.7735 | | 2.6805 | 3.5270 | H8 | 1.9152 | 2.2637 | 3.6052 | 2.0994 | 0.9795 | 2.6941 | 2.6805 | | 4.0839 | H9 | 3.2262 | 1.8802 | 0.9803 | 2.3109 | 4.2928 | 3.5244 | 3.5270 | 4.0839 | |
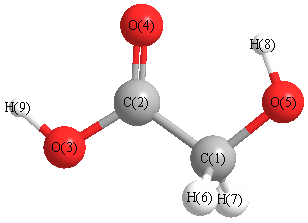 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
112.081 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.200 |
| C1 |
O5 |
H8 |
106.259 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
111.496 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.181 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.859 |
| C2 |
O3 |
H9 |
107.384 |
|
O3 |
C2 |
O4 |
124.719 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.519 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.940 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
106.637 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.084 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.508 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.533 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.449 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.605 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.405 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.411 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.239 |
-0.714 |
0.030 |
2.350 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.138 |
-0.101 |
-0.067 |
| y |
-0.101 |
-29.994 |
0.012 |
| z |
-0.067 |
0.012 |
-27.900 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.809 |
-0.101 |
-0.067 |
| y |
-0.101 |
-1.975 |
0.012 |
| z |
-0.067 |
0.012 |
1.166 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.332 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.856 |
|---|
| xy | -0.101 |
|---|
| xz | -0.067 |
|---|
| yz | 0.012 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.487 |
-0.107 |
-0.003 |
| y |
-0.107 |
5.281 |
-0.000 |
| z |
-0.003 |
-0.000 |
3.033 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
111.932 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.580 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -304.110968 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -304.116346 |
| HF Energy | -304.110968 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3594 |
3524 |
36.48 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3571 |
3501 |
62.17 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2968 |
2910 |
35.77 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2948 |
2891 |
39.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1783 |
1748 |
239.51 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1497 |
1467 |
8.43 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1462 |
1434 |
35.56 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1348 |
1321 |
114.80 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1290 |
1264 |
17.80 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1228 |
1204 |
1.18 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1156 |
1134 |
131.54 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1094 |
1072 |
227.04 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1024 |
1004 |
0.68 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
838 |
821 |
37.08 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
660 |
647 |
131.30 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
632 |
620 |
14.04 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
491 |
482 |
3.21 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
462 |
453 |
25.60 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
292 |
286 |
71.13 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
281 |
276 |
8.56 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
24 |
24 |
17.32 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14321.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9804) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14040.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-31G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.748 |
-0.751 |
-0.000 |
| C2 |
0.516 |
0.096 |
-0.000 |
| O3 |
1.647 |
-0.650 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
0.503 |
1.317 |
-0.000 |
| O5 |
-1.900 |
0.057 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
-0.720 |
-1.411 |
-0.887 |
| H7 |
-0.720 |
-1.412 |
0.886 |
| H8 |
-1.569 |
0.979 |
-0.000 |
| H9 |
2.393 |
-0.014 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.5217 | 2.3970 | 2.4176 | 1.4071 | 1.1060 | 1.1059 | 1.9152 | 3.2261 |
C2 | 1.5217 | | 1.3555 | 1.2208 | 2.4156 | 2.1418 | 2.1419 | 2.2637 | 1.8804 | O3 | 2.3970 | 1.3555 | | 2.2757 | 3.6164 | 2.6399 | 2.6395 | 3.6050 | 0.9802 | O4 | 2.4176 | 1.2208 | 2.2757 | | 2.7133 | 3.1189 | 3.1194 | 2.0996 | 2.3115 | O5 | 1.4071 | 2.4156 | 3.6164 | 2.7133 | | 2.0823 | 2.0821 | 0.9793 | 4.2930 | H6 | 1.1060 | 2.1418 | 2.6399 | 3.1189 | 2.0823 | | 1.7735 | 2.6871 | 3.5254 | H7 | 1.1059 | 2.1419 | 2.6395 | 3.1194 | 2.0821 | 1.7735 | | 2.6878 | 3.5253 | H8 | 1.9152 | 2.2637 | 3.6050 | 2.0996 | 0.9793 | 2.6871 | 2.6878 | | 4.0843 | H9 | 3.2261 | 1.8804 | 0.9802 | 2.3115 | 4.2930 | 3.5254 | 3.5253 | 4.0843 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
113.767 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O4 |
122.376 |
| C1 |
O5 |
H8 |
105.412 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
111.771 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.835 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.431 |
| C2 |
O3 |
H9 |
106.800 |
|
O3 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.214 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.427 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.883 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
106.330 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.084 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.508 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.533 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.449 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.605 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.405 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.411 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.241 |
-0.715 |
-0.002 |
2.352 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.134 |
-0.105 |
0.003 |
| y |
-0.105 |
-29.995 |
-0.001 |
| z |
0.003 |
-0.001 |
-27.900 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.813 |
-0.105 |
0.003 |
| y |
-0.105 |
-1.978 |
-0.001 |
| z |
0.003 |
-0.001 |
1.165 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.330 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.861 |
|---|
| xy | -0.105 |
|---|
| xz | 0.003 |
|---|
| yz | -0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.486 |
-0.108 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.108 |
5.281 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.032 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
111.930 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.580 |
