Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -268.254810 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -268.254810 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 193.298917 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3052 |
3008 |
31.57 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
2931 |
2889 |
2.48 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2922 |
2881 |
166.93 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1517 |
1496 |
3.89 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1483 |
1462 |
1.16 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1347 |
1328 |
6.70 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1222 |
1205 |
7.15 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1177 |
1160 |
38.46 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1127 |
1111 |
15.30 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1089 |
1073 |
165.43 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
927 |
914 |
2.28 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
923 |
909 |
8.52 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
711 |
701 |
1.70 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
269 |
265 |
0.56 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B |
3056 |
3012 |
45.94 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B |
2959 |
2917 |
108.90 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B |
2941 |
2899 |
98.62 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B |
1480 |
1459 |
2.08 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
1396 |
1376 |
8.52 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
1310 |
1291 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
1197 |
1180 |
2.93 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
1121 |
1105 |
12.76 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1012 |
997 |
22.27 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
911 |
898 |
69.37 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
877 |
864 |
31.37 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
631 |
622 |
3.37 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
75i |
74i |
16.98 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19755.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9857) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19473.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.210 |
| C2 |
-0.302 |
0.701 |
-0.949 |
| C3 |
0.302 |
-0.701 |
-0.949 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
1.157 |
0.376 |
| O5 |
0.000 |
-1.157 |
0.376 |
| H6 |
0.904 |
0.046 |
1.839 |
| H7 |
-0.904 |
-0.046 |
1.839 |
| H8 |
-1.391 |
0.665 |
-1.120 |
| H9 |
1.391 |
-0.665 |
-1.120 |
| H10 |
-0.163 |
-1.392 |
-1.660 |
| H11 |
0.163 |
1.392 |
-1.660 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2897 | 2.2897 | 1.4264 | 1.4264 | 1.1027 | 1.1027 | 2.7940 | 2.7940 | 3.1935 | 3.1935 |
C2 | 2.2897 | | 1.5254 | 1.4332 | 2.3013 | 3.1074 | 2.9487 | 1.1034 | 2.1815 | 2.2141 | 1.0947 | C3 | 2.2897 | 1.5254 | | 2.3013 | 1.4332 | 2.9487 | 3.1074 | 2.1815 | 1.1034 | 1.0947 | 2.2141 | O4 | 1.4264 | 1.4332 | 2.3013 | | 2.3139 | 2.0477 | 2.0994 | 2.1010 | 2.7371 | 3.2657 | 2.0552 | O5 | 1.4264 | 2.3013 | 1.4332 | 2.3139 | | 2.0994 | 2.0477 | 2.7371 | 2.1010 | 2.0552 | 3.2657 | H6 | 1.1027 | 3.1074 | 2.9487 | 2.0477 | 2.0994 | | 1.8112 | 3.7958 | 3.0821 | 3.9304 | 3.8212 | H7 | 1.1027 | 2.9487 | 3.1074 | 2.0994 | 2.0477 | 1.8112 | | 3.0821 | 3.7958 | 3.8212 | 3.9304 | H8 | 2.7940 | 1.1034 | 2.1815 | 2.1010 | 2.7371 | 3.7958 | 3.0821 | | 3.0837 | 2.4557 | 1.7981 | H9 | 2.7940 | 2.1815 | 1.1034 | 2.7371 | 2.1010 | 3.0821 | 3.7958 | 3.0837 | | 1.7981 | 2.4557 | H10 | 3.1935 | 2.2141 | 1.0947 | 3.2657 | 2.0552 | 3.9304 | 3.8212 | 2.4557 | 1.7981 | | 2.8025 | H11 | 3.1935 | 1.0947 | 2.2141 | 2.0552 | 3.2657 | 3.8212 | 3.9304 | 1.7981 | 2.4557 | 2.8025 | |
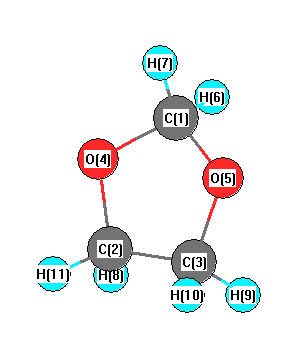 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
106.435 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
106.435 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
102.053 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.992 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.514 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
102.053 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.992 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
114.514 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
108.381 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.435 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.661 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.190 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
108.156 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.661 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.435 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.190 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.156 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.294 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.694 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.694 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.040 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.040 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.364 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.364 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.160 |
1.160 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.344 |
-0.246 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.246 |
-34.625 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-25.950 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.944 |
-0.246 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.246 |
-6.978 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.035 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 12.069 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.282 |
|---|
| xy | -0.246 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.467 |
-0.098 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.098 |
5.412 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.975 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
94.070 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.699 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -268.255258 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -268.263472 |
| HF Energy | -268.255258 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 193.267008 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3065 |
3021 |
36.31 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3049 |
3005 |
47.94 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3014 |
2971 |
49.51 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2971 |
2928 |
80.02 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2932 |
2890 |
65.82 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2857 |
2816 |
144.74 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1511 |
1490 |
2.18 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1496 |
1475 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1482 |
1461 |
1.45 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1394 |
1374 |
10.90 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1339 |
1320 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1314 |
1296 |
0.10 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1242 |
1224 |
5.15 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1199 |
1182 |
1.43 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1183 |
1166 |
1.98 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1156 |
1139 |
37.35 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1126 |
1110 |
8.44 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1064 |
1049 |
147.14 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1007 |
992 |
25.87 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
945 |
931 |
35.64 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
923 |
909 |
20.25 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
895 |
882 |
83.28 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
843 |
831 |
11.14 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
721 |
711 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
676 |
667 |
4.28 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
293 |
289 |
11.01 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
51 |
50 |
3.17 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19873.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9857) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19588.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.167 |
-0.095 |
0.167 |
| C2 |
-1.040 |
-0.666 |
-0.034 |
| C3 |
-0.845 |
0.860 |
0.138 |
| O4 |
0.298 |
-1.190 |
-0.098 |
| O5 |
0.508 |
1.072 |
-0.278 |
| H6 |
1.379 |
-0.030 |
1.255 |
| H7 |
2.094 |
-0.220 |
-0.404 |
| H8 |
-1.554 |
-0.920 |
-0.969 |
| H9 |
-0.975 |
1.161 |
1.192 |
| H10 |
-1.496 |
1.467 |
-0.497 |
| H11 |
-1.588 |
-1.107 |
0.812 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2892 | 2.2279 | 1.4228 | 1.4128 | 1.1100 | 1.0950 | 3.0626 | 2.6867 | 3.1588 | 3.0049 |
C2 | 2.2892 | | 1.5478 | 1.4391 | 2.3401 | 2.8137 | 3.1870 | 1.0974 | 2.2007 | 2.2297 | 1.0996 | C3 | 2.2279 | 1.5478 | | 2.3592 | 1.4312 | 2.6429 | 3.1774 | 2.2136 | 1.1035 | 1.0936 | 2.2079 | O4 | 1.4228 | 1.4391 | 2.3592 | | 2.2788 | 2.0841 | 2.0633 | 2.0646 | 2.9687 | 3.2311 | 2.0956 | O5 | 1.4128 | 2.3401 | 1.4312 | 2.2788 | | 2.0795 | 2.0495 | 2.9494 | 2.0899 | 2.0544 | 3.2135 | H6 | 1.1100 | 2.8137 | 2.6429 | 2.0841 | 2.0795 | | 1.8157 | 3.7871 | 2.6389 | 3.6847 | 3.1868 | H7 | 1.0950 | 3.1870 | 3.1774 | 2.0633 | 2.0495 | 1.8157 | | 3.7573 | 3.7242 | 3.9679 | 3.9768 | H8 | 3.0626 | 1.0974 | 2.2136 | 2.0646 | 2.9494 | 3.7871 | 3.7573 | | 3.0559 | 2.4347 | 1.7911 | H9 | 2.6867 | 2.2007 | 1.1035 | 2.9687 | 2.0899 | 2.6389 | 3.7242 | 3.0559 | | 1.7935 | 2.3799 | H10 | 3.1588 | 2.2297 | 1.0936 | 3.2311 | 2.0544 | 3.6847 | 3.9679 | 2.4347 | 1.7935 | | 2.8890 | H11 | 3.0049 | 1.0996 | 2.2079 | 2.0956 | 3.2135 | 3.1868 | 3.9768 | 1.7911 | 2.3799 | 2.8890 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
107.566 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
104.887 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
101.806 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.920 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.648 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
103.005 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.942 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
113.678 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.748 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.457 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.187 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.555 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.446 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.299 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.285 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.007 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.950 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.860 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.084 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.306 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.163 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.008 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.086 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.365 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.339 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.083 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.111 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.108 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.121 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.101 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.180 |
0.375 |
0.778 |
1.462 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.006 |
-0.836 |
0.567 |
| y |
-0.836 |
-34.273 |
0.386 |
| z |
0.567 |
0.386 |
-29.699 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
5.980 |
-0.836 |
0.567 |
| y |
-0.836 |
-6.420 |
0.386 |
| z |
0.567 |
0.386 |
0.441 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.881 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 8.267 |
|---|
| xy | -0.836 |
|---|
| xz | 0.567 |
|---|
| yz | 0.386 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.882 |
-0.101 |
0.065 |
| y |
-0.101 |
5.469 |
0.089 |
| z |
0.065 |
0.089 |
5.357 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
94.159 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.704 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -268.254782 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -268.254782 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 193.288610 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3056 |
3012 |
45.81 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3052 |
3008 |
31.48 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2960 |
2918 |
108.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2940 |
2898 |
99.40 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
2932 |
2890 |
5.92 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
2923 |
2881 |
163.23 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1517 |
1495 |
3.94 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1483 |
1461 |
1.11 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1480 |
1458 |
2.06 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1396 |
1376 |
8.49 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1348 |
1328 |
6.65 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1310 |
1291 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1222 |
1205 |
7.49 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1197 |
1180 |
2.90 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1176 |
1160 |
38.37 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1127 |
1111 |
14.02 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1121 |
1105 |
12.78 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1089 |
1073 |
166.29 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1011 |
997 |
22.67 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
925 |
912 |
4.23 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
922 |
909 |
6.54 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
910 |
897 |
68.12 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
876 |
864 |
32.15 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
711 |
701 |
1.63 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
631 |
622 |
3.41 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
271 |
267 |
0.57 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
77i |
76i |
17.01 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19753.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9857) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19471.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/6-311G**
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.210 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.949 |
0.737 |
0.196 |
| C3 |
-0.949 |
-0.737 |
-0.196 |
| O4 |
0.376 |
1.144 |
-0.170 |
| O5 |
0.375 |
-1.145 |
0.170 |
| H6 |
1.839 |
-0.087 |
-0.901 |
| H7 |
1.839 |
0.087 |
0.902 |
| H8 |
-1.119 |
0.861 |
1.279 |
| H9 |
-1.119 |
-0.860 |
-1.279 |
| H10 |
-1.660 |
-1.353 |
0.363 |
| H11 |
-1.660 |
1.354 |
-0.363 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2898 | 2.2899 | 1.4265 | 1.4265 | 1.1027 | 1.1027 | 2.7931 | 2.7933 | 3.1939 | 3.1939 |
C2 | 2.2898 | | 1.5256 | 1.4333 | 2.3012 | 3.1077 | 2.9483 | 1.1034 | 2.1815 | 2.2145 | 1.0947 | C3 | 2.2899 | 1.5256 | | 2.3012 | 1.4333 | 2.9487 | 3.1075 | 2.1815 | 1.1034 | 1.0947 | 2.2145 | O4 | 1.4265 | 1.4333 | 2.3012 | | 2.3140 | 2.0477 | 2.0996 | 2.1011 | 2.7359 | 3.2660 | 2.0553 | O5 | 1.4265 | 2.3012 | 1.4333 | 2.3140 | | 2.0996 | 2.0477 | 2.7359 | 2.1011 | 2.0553 | 3.2661 | H6 | 1.1027 | 3.1077 | 2.9487 | 2.0477 | 2.0996 | | 1.8113 | 3.7952 | 3.0812 | 3.9304 | 3.8221 | H7 | 1.1027 | 2.9483 | 3.1075 | 2.0996 | 2.0477 | 1.8113 | | 3.0805 | 3.7953 | 3.8217 | 3.9302 | H8 | 2.7931 | 1.1034 | 2.1815 | 2.1011 | 2.7359 | 3.7952 | 3.0805 | | 3.0838 | 2.4564 | 1.7984 | H9 | 2.7933 | 2.1815 | 1.1034 | 2.7359 | 2.1011 | 3.0812 | 3.7953 | 3.0838 | | 1.7984 | 2.4564 | H10 | 3.1939 | 2.2145 | 1.0947 | 3.2660 | 2.0553 | 3.9304 | 3.8217 | 2.4564 | 1.7984 | | 2.8027 | H11 | 3.1939 | 1.0947 | 2.2145 | 2.0553 | 3.2661 | 3.8221 | 3.9302 | 1.7984 | 2.4564 | 2.8027 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
106.277 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
106.279 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
101.924 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.910 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.768 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
101.923 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.910 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
114.769 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
108.359 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.369 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.687 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.122 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
108.077 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.687 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.369 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.122 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.077 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.394 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.776 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.776 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/6-311G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.184 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.040 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.040 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.364 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.364 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.095 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.159 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.159 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-25.948 |
-0.001 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.001 |
-34.441 |
1.003 |
| z |
0.000 |
1.003 |
-29.528 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.037 |
-0.001 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.001 |
-6.703 |
1.003 |
| z |
0.000 |
1.003 |
0.666 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.332 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 8.493 |
|---|
| xy | -0.001 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 1.003 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.975 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
5.443 |
0.102 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.102 |
5.437 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
94.073 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.699 |
