Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -304.246120 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -304.251684 |
| HF Energy | -304.246120 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 179.132864 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3662 |
3610 |
46.99 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3636 |
3585 |
65.60 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2966 |
2925 |
22.08 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2945 |
2904 |
38.07 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1758 |
1733 |
261.95 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1462 |
1442 |
8.86 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1431 |
1411 |
19.58 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1324 |
1306 |
102.33 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1271 |
1253 |
23.38 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1228 |
1211 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1134 |
1118 |
111.65 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1075 |
1060 |
252.89 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1011 |
997 |
1.21 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
833 |
821 |
36.79 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
643 |
634 |
104.63 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
632 |
623 |
12.87 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
496 |
489 |
7.08 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
460 |
454 |
23.16 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
338 |
333 |
70.00 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
269 |
265 |
10.43 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
91 |
89 |
7.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14331.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.986) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14130.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.743 |
-0.746 |
0.004 |
| C2 |
0.515 |
0.099 |
0.000 |
| O3 |
1.643 |
-0.649 |
-0.003 |
| O4 |
0.507 |
1.312 |
0.002 |
| O5 |
-1.901 |
0.054 |
-0.005 |
| H6 |
-0.714 |
-1.409 |
-0.874 |
| H7 |
-0.714 |
-1.394 |
0.894 |
| H8 |
-1.587 |
0.974 |
0.006 |
| H9 |
2.390 |
-0.026 |
-0.003 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.5157 | 2.3880 | 2.4084 | 1.4070 | 1.1006 | 1.1011 | 1.9153 | 3.2145 |
C2 | 1.5157 | | 1.3537 | 1.2131 | 2.4160 | 2.1324 | 2.1304 | 2.2763 | 1.8790 | O3 | 2.3880 | 1.3537 | | 2.2665 | 3.6126 | 2.6245 | 2.6291 | 3.6144 | 0.9725 | O4 | 2.4084 | 1.2131 | 2.2665 | | 2.7170 | 3.1083 | 3.1004 | 2.1213 | 2.3099 | O5 | 1.4070 | 2.4160 | 3.6126 | 2.7170 | | 2.0745 | 2.0770 | 0.9718 | 4.2911 | H6 | 1.1006 | 2.1324 | 2.6245 | 3.1083 | 2.0745 | | 1.7677 | 2.6856 | 3.5071 | H7 | 1.1011 | 2.1304 | 2.6291 | 3.1004 | 2.0770 | 1.7677 | | 2.6753 | 3.5080 | H8 | 1.9153 | 2.2763 | 3.6144 | 2.1213 | 0.9718 | 2.6856 | 2.6753 | | 4.1003 | H9 | 3.2145 | 1.8790 | 0.9725 | 2.3099 | 4.2911 | 3.5071 | 3.5080 | 4.1003 | |
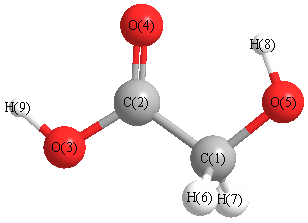 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
112.160 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.276 |
| C1 |
O5 |
H8 |
106.670 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
111.899 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.017 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.645 |
| C2 |
O3 |
H9 |
107.811 |
|
O3 |
C2 |
O4 |
124.563 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.437 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.843 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
106.772 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.069 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.240 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.232 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.299 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.332 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.065 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.064 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.216 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.025 |
-0.893 |
0.022 |
2.213 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.423 |
-0.140 |
-0.045 |
| y |
-0.140 |
-30.465 |
0.009 |
| z |
-0.045 |
0.009 |
-28.221 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.920 |
-0.140 |
-0.045 |
| y |
-0.140 |
-2.143 |
0.009 |
| z |
-0.045 |
0.009 |
1.223 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.446 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.042 |
|---|
| xy | -0.140 |
|---|
| xz | -0.045 |
|---|
| yz | 0.009 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.292 |
-0.053 |
-0.001 |
| y |
-0.053 |
5.876 |
-0.001 |
| z |
-0.001 |
-0.001 |
3.782 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
111.848 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.576 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -304.246121 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -304.251679 |
| HF Energy | -304.246121 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 179.121780 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3662 |
3611 |
46.88 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3638 |
3587 |
65.53 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2966 |
2924 |
21.89 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
2946 |
2904 |
38.22 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1758 |
1733 |
262.06 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1462 |
1442 |
8.85 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1430 |
1410 |
19.26 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1323 |
1305 |
101.43 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1271 |
1253 |
24.05 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1228 |
1211 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1134 |
1118 |
110.51 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1075 |
1060 |
254.54 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1011 |
997 |
1.19 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
833 |
821 |
36.88 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
642 |
633 |
104.50 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
631 |
623 |
12.65 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
496 |
489 |
7.39 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
460 |
454 |
23.17 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
334 |
330 |
69.85 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
268 |
264 |
10.39 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
90 |
89 |
7.28 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14328.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.986) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14127.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.743 |
-0.746 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.515 |
0.100 |
0.000 |
| O3 |
1.643 |
-0.650 |
-0.000 |
| O4 |
0.508 |
1.313 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
-1.901 |
0.054 |
-0.000 |
| H6 |
-0.714 |
-1.402 |
-0.883 |
| H7 |
-0.714 |
-1.401 |
0.884 |
| H8 |
-1.588 |
0.973 |
0.000 |
| H9 |
2.390 |
-0.027 |
-0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.5156 | 2.3877 | 2.4086 | 1.4070 | 1.1009 | 1.1009 | 1.9155 | 3.2143 |
C2 | 1.5156 | | 1.3539 | 1.2130 | 2.4163 | 2.1315 | 2.1315 | 2.2769 | 1.8792 | O3 | 2.3877 | 1.3539 | | 2.2668 | 3.6127 | 2.6263 | 2.6266 | 3.6151 | 0.9724 | O4 | 2.4086 | 1.2130 | 2.2668 | | 2.7178 | 3.1048 | 3.1045 | 2.1226 | 2.3102 | O5 | 1.4070 | 2.4163 | 3.6127 | 2.7178 | | 2.0756 | 2.0758 | 0.9717 | 4.2915 | H6 | 1.1009 | 2.1315 | 2.6263 | 3.1048 | 2.0756 | | 1.7676 | 2.6808 | 3.5071 | H7 | 1.1009 | 2.1315 | 2.6266 | 3.1045 | 2.0758 | 1.7676 | | 2.6803 | 3.5074 | H8 | 1.9155 | 2.2769 | 3.6151 | 2.1226 | 0.9717 | 2.6808 | 2.6803 | | 4.1014 | H9 | 3.2143 | 1.8792 | 0.9724 | 2.3102 | 4.2915 | 3.5071 | 3.5074 | 4.1014 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
113.853 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O4 |
122.409 |
| C1 |
O5 |
H8 |
105.938 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
112.169 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.800 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.067 |
| C2 |
O3 |
H9 |
107.172 |
|
O3 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.033 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.604 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.590 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
106.423 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B97D3/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.069 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.240 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.232 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.299 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.332 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.065 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.065 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.208 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.216 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.023 |
-0.892 |
0.001 |
2.211 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.422 |
-0.144 |
-0.004 |
| y |
-0.144 |
-30.465 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.004 |
0.001 |
-28.221 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.921 |
-0.144 |
-0.004 |
| y |
-0.144 |
-2.144 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.004 |
0.001 |
1.223 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.446 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.043 |
|---|
| xy | -0.144 |
|---|
| xz | -0.004 |
|---|
| yz | 0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.292 |
-0.054 |
-0.000 |
| y |
-0.054 |
5.877 |
0.000 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
3.782 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
111.864 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.577 |
