Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -437.464041 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -437.464041 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 42.221210 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3046 |
2925 |
161.05 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
1457 |
1399 |
44.23 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
853 |
819 |
6.11 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
B1 |
173i |
166i |
75.46 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B2 |
3111 |
2988 |
124.53 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
944 |
907 |
4.90 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4618.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9603) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4435.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.626 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.106 |
| H3 |
0.000 |
0.926 |
-1.687 |
| H4 |
0.000 |
-0.926 |
-1.687 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
C2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| S1 | | 1.7318 | 2.4918 | 2.4918 |
C2 | 1.7318 | | 1.0937 | 1.0937 | H3 | 2.4918 | 1.0937 | | 1.8528 | H4 | 2.4918 | 1.0937 | 1.8528 | |
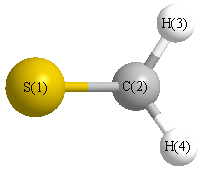 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
C2 |
H3 |
122.112 |
|
S1 |
C2 |
H4 |
122.112 |
| H3 |
C2 |
H4 |
115.776 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
-0.624 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.473 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.048 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.048 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.344 |
1.344 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.871 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-24.093 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-26.232 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.292 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.458 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.750 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.500 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.778 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.200 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.268 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.645 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
36.672 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.056 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -437.464065 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -437.464893 |
| HF Energy | -437.464065 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 42.205315 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3035 |
2915 |
167.14 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1457 |
1399 |
44.62 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
851 |
817 |
6.44 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
240 |
231 |
71.08 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A" |
3100 |
2977 |
129.40 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
950 |
912 |
4.80 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4816.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9603) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 4625.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
-0.010 |
-0.625 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.010 |
1.108 |
0.000 |
| H3 |
0.114 |
1.681 |
0.924 |
| H4 |
0.114 |
1.681 |
-0.924 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
C2 |
H3 |
H4 |
| S1 | | 1.7332 | 2.4876 | 2.4876 |
C2 | 1.7332 | | 1.0946 | 1.0946 | H3 | 2.4876 | 1.0946 | | 1.8486 | H4 | 2.4876 | 1.0946 | 1.8486 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
C2 |
H3 |
121.568 |
|
S1 |
C2 |
H4 |
121.568 |
| H3 |
C2 |
H4 |
115.224 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
-0.624 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.472 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.048 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.048 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.240 |
1.320 |
0.000 |
1.342 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.845 |
0.276 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.276 |
-26.299 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.118 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.363 |
0.276 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.276 |
-1.817 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.454 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.909 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.454 |
|---|
| xy | 0.276 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.217 |
0.047 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.047 |
6.662 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.274 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
36.678 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.056 |
