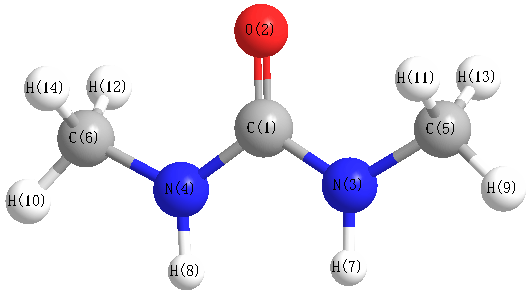
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at TPSSh/aug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3573 |
3456 |
10.85 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3153 |
3050 |
10.37 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3096 |
2995 |
8.97 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3012 |
2914 |
4.36 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1735 |
1678 |
255.98 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1519 |
1470 |
17.08 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1484 |
1435 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1467 |
1419 |
5.36 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1430 |
1383 |
11.13 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1187 |
1148 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1166 |
1128 |
2.37 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1130 |
1093 |
7.54 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
912 |
882 |
1.99 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
518 |
501 |
40.69 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
400 |
386 |
45.35 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
217 |
210 |
3.85 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
178 |
172 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
82 |
80 |
0.39 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
3570 |
3453 |
5.58 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3152 |
3049 |
3.98 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3097 |
2995 |
62.90 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3011 |
2913 |
145.34 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1557 |
1506 |
325.32 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
1498 |
1449 |
11.01 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1477 |
1428 |
76.44 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1434 |
1387 |
8.70 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1248 |
1207 |
228.32 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1144 |
1106 |
27.39 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1129 |
1092 |
8.71 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1038 |
1004 |
1.68 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
748 |
723 |
4.78 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
713 |
690 |
26.69 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
480 |
464 |
110.20 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
313 |
303 |
41.61 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
119 |
115 |
10.54 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
90 |
87 |
0.36 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26037.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9673) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25186.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at TPSSh/aug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.757 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.559 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.208 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.208 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.740 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
0.740 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
-0.142 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
-0.142 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
-0.236 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
-0.236 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
-0.138 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
-0.138 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
-0.115 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
-0.115 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.668 |
3.668 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.020 |
-0.530 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.530 |
11.744 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
8.929 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
193.865 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.924 |