Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3944 |
3590 |
115.53 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3917 |
3566 |
104.54 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3772 |
3434 |
10.22 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3720 |
3387 |
389.54 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3619 |
3294 |
389.44 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3228 |
2939 |
57.42 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
3154 |
2872 |
113.43 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1917 |
1745 |
773.25 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1851 |
1685 |
196.78 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1801 |
1639 |
26.01 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1780 |
1621 |
15.94 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1557 |
1417 |
57.19 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1546 |
1408 |
26.01 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1452 |
1322 |
72.22 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1420 |
1292 |
148.83 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1237 |
1126 |
117.03 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1189 |
1083 |
1.81 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1182 |
1076 |
7.08 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
668 |
608 |
16.63 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
616 |
561 |
10.10 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
176 |
160 |
58.85 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
142 |
130 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
136 |
124 |
3.90 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1193 |
1087 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1191 |
1084 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
856 |
780 |
130.86 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
854 |
778 |
6.35 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
736 |
670 |
66.91 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
475 |
432 |
120.17 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
312 |
284 |
82.98 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
153 |
139 |
9.45 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
87 |
79 |
138.57 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
40 |
36 |
4.12 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24959.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9104) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22723.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
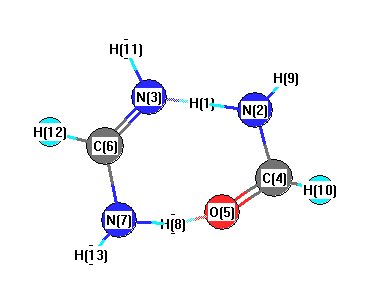
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
H |
0.439 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
N |
-0.357 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.557 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.193 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.708 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.201 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
N |
-0.340 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.385 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.090 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.669 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.083 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.621 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.069 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.532 |
-1.003 |
0.000 |
1.831 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.758 |
9.773 |
0.000 |
| y |
9.773 |
-26.149 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-39.883 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.257 |
9.773 |
0.000 |
| y |
9.773 |
8.672 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-11.929 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -23.858 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.610 |
|---|
| xy | 9.773 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.464 |
-0.134 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.134 |
9.895 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.733 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
229.649 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.154 |