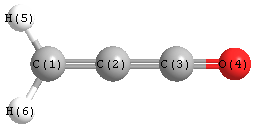Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.747583 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.747583 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 88.688776 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3067 |
2972 |
31.11 |
234.52 |
0.11 |
0.19 |
| 2 |
A1 |
2304 |
2232 |
991.49 |
46.18 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 3 |
A1 |
1787 |
1732 |
39.29 |
2.90 |
0.58 |
0.74 |
| 4 |
A1 |
1488 |
1441 |
3.51 |
11.76 |
0.53 |
0.70 |
| 5 |
A1 |
929 |
900 |
6.25 |
51.77 |
0.15 |
0.26 |
| 6 |
B1 |
1028 |
996 |
22.99 |
1.79 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 7 |
B1 |
651 |
631 |
18.91 |
0.18 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
B1 |
221 |
214 |
0.42 |
1.94 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
B2 |
3130 |
3033 |
7.16 |
146.80 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 10 |
B2 |
1072 |
1039 |
2.41 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
B2 |
460 |
446 |
8.04 |
2.93 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
B2 |
124i |
120i |
14.22 |
0.09 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 8006.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9689) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7757.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.867 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.554 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.717 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.889 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.921 |
-2.445 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-0.921 |
-2.445 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3127 | 2.5840 | 3.7559 | 1.0873 | 1.0873 |
C2 | 1.3127 | | 1.2714 | 2.4433 | 2.1031 | 2.1031 | C3 | 2.5840 | 1.2714 | | 1.1719 | 3.2936 | 3.2936 | O4 | 3.7559 | 2.4433 | 1.1719 | | 4.4309 | 4.4309 | H5 | 1.0873 | 2.1031 | 3.2936 | 4.4309 | | 1.8415 | H6 | 1.0873 | 2.1031 | 3.2936 | 4.4309 | 1.8415 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
180.000 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.128 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
122.128 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
180.000 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.745 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.445 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.138 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.520 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.626 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.345 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.821 |
2.821 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.861 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.652 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.305 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.382 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.069 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.451 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.902 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.209 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.826 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.308 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.296 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
82.160 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.064 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -190.748313 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -190.748313 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 88.895754 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3145 |
3048 |
6.79 |
127.36 |
0.70 |
0.82 |
| 2 |
A' |
3074 |
2979 |
30.01 |
194.25 |
0.11 |
0.20 |
| 3 |
A' |
2227 |
2158 |
1010.49 |
52.53 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 4 |
A' |
1765 |
1711 |
12.27 |
4.28 |
0.26 |
0.41 |
| 5 |
A' |
1490 |
1443 |
1.41 |
12.17 |
0.57 |
0.73 |
| 6 |
A' |
1078 |
1044 |
17.84 |
2.47 |
0.04 |
0.07 |
| 7 |
A' |
948 |
919 |
3.24 |
44.66 |
0.11 |
0.20 |
| 8 |
A' |
499 |
484 |
12.64 |
4.32 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 9 |
A' |
152 |
147 |
22.33 |
5.08 |
0.71 |
0.83 |
| 10 |
A" |
1034 |
1002 |
22.69 |
1.91 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A" |
696 |
674 |
13.88 |
0.27 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
A" |
266 |
257 |
0.98 |
2.49 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 8187.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9689) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7932.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.919 |
-1.577 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
-0.631 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.315 |
0.621 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
-0.782 |
1.689 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
1.985 |
-1.362 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.651 |
-2.629 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3194 | 2.5210 | 3.6831 | 1.0873 | 1.0855 |
C2 | 1.3194 | | 1.2905 | 2.4482 | 2.1153 | 2.1020 | C3 | 2.5210 | 1.2905 | | 1.1661 | 3.0368 | 3.3906 | O4 | 3.6831 | 2.4482 | 1.1661 | | 4.1193 | 4.5501 | H5 | 1.0873 | 2.1153 | 3.0368 | 4.1193 | | 1.8397 | H6 | 1.0855 | 2.1020 | 3.3906 | 4.5501 | 1.8397 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
149.999 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.728 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.560 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
170.526 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
115.713 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at B3LYP/aug-cc-pVQZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.647 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.293 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.693 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.568 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.425 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.390 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.739 |
-1.869 |
0.000 |
2.553 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.236 |
-0.750 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.750 |
-22.993 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.975 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.748 |
-0.750 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.750 |
-0.387 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.361 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.721 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.757 |
|---|
| xy | -0.750 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.839 |
-2.519 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.519 |
9.627 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.875 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
80.347 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.964 |