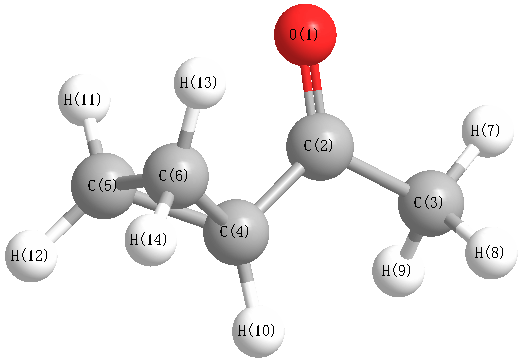
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at PBE1PBE/3-21G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3298 |
3166 |
1.17 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3250 |
3119 |
3.06 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3190 |
3062 |
3.04 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3190 |
3061 |
10.40 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3066 |
2943 |
0.88 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1762 |
1691 |
65.78 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1516 |
1455 |
9.70 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1504 |
1443 |
13.20 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1428 |
1370 |
50.51 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1414 |
1357 |
100.99 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1221 |
1172 |
65.67 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1210 |
1161 |
34.38 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1136 |
1090 |
17.19 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1093 |
1049 |
18.12 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
993 |
953 |
38.05 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
917 |
880 |
24.35 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
826 |
793 |
3.56 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
778 |
747 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
596 |
572 |
5.90 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
389 |
373 |
6.07 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
259 |
249 |
5.24 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
3282 |
3150 |
0.49 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
3188 |
3060 |
7.08 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
3131 |
3005 |
3.84 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1538 |
1476 |
15.79 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1483 |
1423 |
11.31 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1234 |
1184 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1152 |
1106 |
1.72 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1146 |
1100 |
6.25 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1095 |
1051 |
11.48 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
908 |
872 |
2.18 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
835 |
802 |
4.85 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
648 |
622 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
273 |
262 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
147 |
142 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
77 |
74 |
2.59 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 26585.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9598) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25516.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at PBE1PBE/3-21G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
O |
-0.477 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.492 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.708 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.461 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.400 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.400 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.251 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.243 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.243 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.226 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.259 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.237 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.259 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.237 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.648 |
0.521 |
0.000 |
2.699 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.506 |
-1.800 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.800 |
-34.510 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-35.961 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.271 |
-1.800 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.800 |
2.724 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.547 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.094 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.997 |
|---|
| xy | -1.800 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.077 |
-0.170 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.170 |
8.398 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.948 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
166.078 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.887 |