Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -375.785899 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -375.785899 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 193.049441 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3345 |
3005 |
67.56 |
27.44 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
| 2 |
A |
3327 |
2990 |
9.91 |
100.44 |
0.54 |
0.70 |
| 3 |
A |
3274 |
2942 |
22.42 |
92.66 |
0.10 |
0.18 |
| 4 |
A |
1664 |
1495 |
5.01 |
8.43 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
A |
1632 |
1466 |
16.86 |
2.26 |
0.45 |
0.63 |
| 6 |
A |
1570 |
1411 |
39.48 |
4.26 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 7 |
A |
1492 |
1341 |
40.44 |
2.67 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
A |
1386 |
1246 |
18.65 |
8.89 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 9 |
A |
1292 |
1161 |
125.79 |
4.62 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 10 |
A |
1259 |
1131 |
119.46 |
4.81 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A |
1244 |
1118 |
101.29 |
1.51 |
0.17 |
0.29 |
| 12 |
A |
1211 |
1088 |
77.43 |
5.20 |
0.46 |
0.63 |
| 13 |
A |
1003 |
902 |
39.14 |
5.56 |
0.31 |
0.48 |
| 14 |
A |
626 |
563 |
6.14 |
1.45 |
0.37 |
0.54 |
| 15 |
A |
521 |
468 |
24.48 |
0.57 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 16 |
A |
462 |
415 |
6.94 |
1.37 |
0.47 |
0.64 |
| 17 |
A |
263 |
236 |
10.09 |
0.04 |
0.49 |
0.65 |
| 18 |
A |
128 |
115 |
9.48 |
0.00 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12850.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11546.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.770 |
-0.593 |
-0.276 |
| C2 |
0.466 |
0.021 |
0.326 |
| F3 |
-1.854 |
0.114 |
0.148 |
| F4 |
1.518 |
-0.745 |
-0.009 |
| F5 |
0.666 |
1.242 |
-0.183 |
| H6 |
-0.710 |
-0.547 |
-1.354 |
| H7 |
-0.868 |
-1.620 |
0.046 |
| H8 |
0.417 |
0.101 |
1.400 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.5059 | 1.3622 | 2.3084 | 2.3322 | 1.0807 | 1.0807 | 2.1683 |
C2 | 1.5059 | | 2.3286 | 1.3434 | 1.3384 | 2.1284 | 2.1331 | 1.0780 | F3 | 1.3622 | 2.3286 | | 3.4830 | 2.7807 | 2.0006 | 1.9974 | 2.5930 | F4 | 2.3084 | 1.3434 | 3.4830 | | 2.1688 | 2.6105 | 2.5421 | 1.9782 | F5 | 2.3322 | 1.3384 | 2.7807 | 2.1688 | | 2.5429 | 3.2554 | 1.9672 | H6 | 1.0807 | 2.1284 | 2.0006 | 2.6105 | 2.5429 | | 1.7716 | 3.0460 | H7 | 1.0807 | 2.1331 | 1.9974 | 2.5421 | 3.2554 | 1.7716 | | 2.5391 | H8 | 2.1683 | 1.0780 | 2.5930 | 1.9782 | 1.9672 | 3.0460 | 2.5391 | |
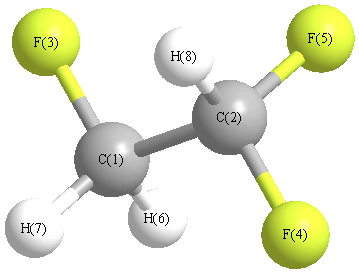 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
F4 |
108.095 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
F5 |
110.026 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
113.056 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F3 |
108.465 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.652 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.024 |
| F3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.423 |
|
F3 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.153 |
| F4 |
C2 |
F5 |
107.942 |
|
F4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.075 |
| F5 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.521 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.096 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.039 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.590 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
F |
-0.396 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.385 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
F |
-0.375 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.186 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.175 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.290 |
-1.636 |
0.441 |
1.719 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-32.863 |
1.798 |
1.600 |
| y |
1.798 |
-27.843 |
0.585 |
| z |
1.600 |
0.585 |
-24.358 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.763 |
1.798 |
1.600 |
| y |
1.798 |
0.768 |
0.585 |
| z |
1.600 |
0.585 |
5.995 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 11.989 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.020 |
|---|
| xy | 1.798 |
|---|
| xz | 1.600 |
|---|
| yz | 0.585 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.139 |
-0.002 |
0.010 |
| y |
-0.002 |
3.211 |
0.016 |
| z |
0.010 |
0.016 |
3.202 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
108.876 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.434 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -375.782869 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -375.782869 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 196.031214 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3309 |
2973 |
68.92 |
84.88 |
0.15 |
0.26 |
| 2 |
A' |
3263 |
2932 |
17.35 |
80.41 |
0.19 |
0.32 |
| 3 |
A' |
1661 |
1493 |
5.94 |
6.46 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
A' |
1605 |
1442 |
36.04 |
3.30 |
0.46 |
0.63 |
| 5 |
A' |
1576 |
1416 |
37.61 |
3.12 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 6 |
A' |
1311 |
1178 |
144.74 |
5.51 |
0.50 |
0.66 |
| 7 |
A' |
1221 |
1097 |
21.97 |
3.53 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
A' |
963 |
866 |
47.79 |
7.97 |
0.18 |
0.30 |
| 9 |
A' |
826 |
742 |
64.28 |
2.48 |
0.50 |
0.67 |
| 10 |
A' |
556 |
500 |
16.32 |
1.16 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A' |
253 |
227 |
2.48 |
0.09 |
0.35 |
0.52 |
| 12 |
A" |
3318 |
2982 |
36.83 |
52.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 13 |
A" |
1568 |
1409 |
50.90 |
1.65 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 14 |
A" |
1406 |
1263 |
24.19 |
14.71 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 15 |
A" |
1286 |
1155 |
107.10 |
1.21 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 16 |
A" |
1075 |
966 |
67.11 |
3.59 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 17 |
A" |
401 |
360 |
0.11 |
0.10 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 18 |
A" |
122 |
109 |
2.70 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12859.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11554.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.738 |
-0.826 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.352 |
0.628 |
0.000 |
| F3 |
-0.385 |
-1.591 |
0.000 |
| F4 |
-0.385 |
0.907 |
1.082 |
| F5 |
-0.385 |
0.907 |
-1.082 |
| H6 |
1.318 |
-1.050 |
-0.885 |
| H7 |
1.318 |
-1.050 |
0.885 |
| H8 |
1.219 |
1.273 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
F3 |
F4 |
F5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.5046 | 1.3582 | 2.3320 | 2.3320 | 1.0817 | 1.0817 | 2.1536 |
C2 | 1.5046 | | 2.3381 | 1.3393 | 1.3393 | 2.1289 | 2.1289 | 1.0803 | F3 | 1.3582 | 2.3381 | | 2.7225 | 2.7225 | 1.9937 | 1.9937 | 3.2822 | F4 | 2.3320 | 1.3393 | 2.7225 | | 2.1649 | 3.2563 | 2.6021 | 1.9696 | F5 | 2.3320 | 1.3393 | 2.7225 | 2.1649 | | 2.6021 | 3.2563 | 1.9696 | H6 | 1.0817 | 2.1289 | 1.9937 | 3.2563 | 2.6021 | | 1.7703 | 2.4879 | H7 | 1.0817 | 2.1289 | 1.9937 | 2.6021 | 3.2563 | 1.7703 | | 2.4879 | H8 | 2.1536 | 1.0803 | 3.2822 | 1.9696 | 1.9696 | 2.4879 | 2.4879 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
F4 |
110.037 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
F5 |
110.037 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.793 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F3 |
109.408 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.720 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.720 |
| F3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.071 |
|
F3 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.071 |
| F4 |
C2 |
F5 |
107.847 |
|
F4 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.511 |
| F5 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.511 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.833 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.048 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.601 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
F |
-0.387 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.377 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
F |
-0.377 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.172 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.150 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
3.356 |
0.158 |
0.000 |
3.360 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-24.664 |
-0.328 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.328 |
-28.530 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.263 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
3.733 |
-0.328 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.328 |
-2.067 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.666 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.332 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.867 |
|---|
| xy | -0.328 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.199 |
0.016 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.016 |
3.167 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.231 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
100.474 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.024 |
