Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -246.991003 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -246.999519 |
| HF Energy | -246.991003 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 182.993923 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3362 |
3021 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3301 |
2966 |
36.26 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3215 |
2889 |
58.66 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3202 |
2877 |
113.26 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3197 |
2873 |
23.66 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1962 |
1763 |
577.27 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1687 |
1516 |
31.03 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1656 |
1488 |
9.09 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1627 |
1462 |
14.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1593 |
1431 |
44.18 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1587 |
1426 |
13.33 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1557 |
1399 |
131.54 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1405 |
1262 |
62.17 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1200 |
1078 |
139.85 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1186 |
1065 |
10.77 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
942 |
846 |
4.74 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
712 |
640 |
10.59 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
426 |
383 |
1.72 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
351 |
316 |
14.11 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
3250 |
2921 |
71.13 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3250 |
2920 |
31.78 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
1648 |
1481 |
13.57 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
1627 |
1462 |
2.30 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1288 |
1157 |
6.59 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1239 |
1114 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1165 |
1047 |
5.88 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
346 |
311 |
32.26 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
243 |
218 |
1.60 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
162 |
145 |
0.28 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
83 |
75 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24235.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21775.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.691 |
-0.821 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
0.218 |
-1.920 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.337 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-1.446 |
0.332 |
0.000 |
| C5 |
0.659 |
1.620 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.770 |
-0.664 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.793 |
-0.688 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
-1.828 |
0.840 |
0.881 |
| H9 |
-1.828 |
0.840 |
-0.881 |
| H10 |
1.733 |
1.488 |
0.000 |
| H11 |
0.387 |
2.196 |
-0.880 |
| H12 |
0.387 |
2.196 |
0.880 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
C4 |
C5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
| C1 | | 1.1964 | 1.3488 | 2.4286 | 2.4412 | 1.0906 | 2.4874 | 3.1432 | 3.1432 | 2.5330 | 3.1567 | 3.1567 |
O2 | 1.1964 | | 2.2679 | 2.8004 | 3.5675 | 1.9964 | 2.3583 | 3.5467 | 3.5467 | 3.7293 | 4.2117 | 4.2117 | N3 | 1.3488 | 2.2679 | | 1.4464 | 1.4423 | 2.0341 | 2.0654 | 2.0904 | 2.0904 | 2.0803 | 2.0919 | 2.0919 | C4 | 2.4286 | 2.8004 | 1.4464 | | 2.4685 | 3.3675 | 1.0774 | 1.0860 | 1.0860 | 3.3832 | 2.7581 | 2.7581 | C5 | 2.4412 | 3.5675 | 1.4423 | 2.4685 | | 2.5403 | 3.3677 | 2.7515 | 2.7515 | 1.0821 | 1.0860 | 1.0860 | H6 | 1.0906 | 1.9964 | 2.0341 | 3.3675 | 2.5403 | | 3.5632 | 3.9982 | 3.9982 | 2.1524 | 3.2963 | 3.2963 | H7 | 2.4874 | 2.3583 | 2.0654 | 1.0774 | 3.3677 | 3.5632 | | 1.7642 | 1.7642 | 4.1435 | 3.7202 | 3.7202 | H8 | 3.1432 | 3.5467 | 2.0904 | 1.0860 | 2.7515 | 3.9982 | 1.7642 | | 1.7616 | 3.7253 | 3.1373 | 2.5966 | H9 | 3.1432 | 3.5467 | 2.0904 | 1.0860 | 2.7515 | 3.9982 | 1.7642 | 1.7616 | | 3.7253 | 2.5966 | 3.1373 | H10 | 2.5330 | 3.7293 | 2.0803 | 3.3832 | 1.0821 | 2.1524 | 4.1435 | 3.7253 | 3.7253 | | 1.7572 | 1.7572 | H11 | 3.1567 | 4.2117 | 2.0919 | 2.7581 | 1.0860 | 3.2963 | 3.7202 | 3.1373 | 2.5966 | 1.7572 | | 1.7598 | H12 | 3.1567 | 4.2117 | 2.0919 | 2.7581 | 1.0860 | 3.2963 | 3.7202 | 2.5966 | 3.1373 | 1.7572 | 1.7598 | |
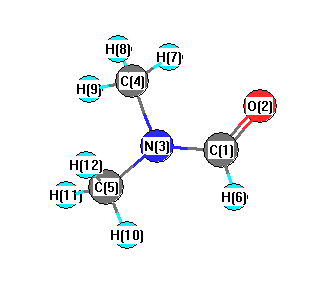 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
C4 |
120.609 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
C5 |
121.975 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
125.899 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.536 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H6 |
112.565 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H7 |
108.967 |
| N3 |
C4 |
H8 |
110.461 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H9 |
110.461 |
| N3 |
C5 |
H10 |
110.177 |
|
N3 |
C5 |
H11 |
110.879 |
| N3 |
C5 |
H12 |
110.879 |
|
C4 |
N3 |
C5 |
117.416 |
| H7 |
C4 |
H8 |
109.264 |
|
H7 |
C4 |
H9 |
109.264 |
| H8 |
C4 |
H9 |
108.401 |
|
H10 |
C5 |
H11 |
108.288 |
| H10 |
C5 |
H12 |
108.288 |
|
H11 |
C5 |
H12 |
108.239 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.522 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.579 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.607 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.294 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.281 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.142 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.232 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.181 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.175 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.175 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.415 |
4.068 |
0.000 |
4.089 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.076 |
0.559 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.559 |
-37.394 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-31.040 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
7.140 |
0.559 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.559 |
-8.336 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.195 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.391 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 10.317 |
|---|
| xy | 0.559 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.901 |
-0.150 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.150 |
7.014 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.238 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
122.645 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.075 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -246.991003 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -246.999520 |
| HF Energy | -246.991003 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 182.993948 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3363 |
3021 |
2.47 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3301 |
2966 |
36.28 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3250 |
2921 |
55.71 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3249 |
2920 |
47.24 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3216 |
2889 |
60.34 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3202 |
2877 |
111.50 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3197 |
2873 |
23.71 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1962 |
1762 |
577.19 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1687 |
1516 |
30.98 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1656 |
1488 |
9.13 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1648 |
1481 |
13.56 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1627 |
1462 |
2.31 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1627 |
1462 |
13.97 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1593 |
1431 |
43.41 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1587 |
1426 |
14.25 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1557 |
1399 |
131.61 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1405 |
1262 |
62.08 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1288 |
1157 |
6.60 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1239 |
1114 |
0.06 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1200 |
1078 |
139.98 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1186 |
1065 |
10.68 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1165 |
1047 |
5.89 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
942 |
846 |
4.77 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
712 |
640 |
10.58 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
426 |
383 |
1.71 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
351 |
316 |
14.12 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
346 |
311 |
32.25 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
243 |
218 |
1.60 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
162 |
145 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
84 |
76 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24236.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21776.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.864 |
-0.637 |
-0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.930 |
-0.094 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.337 |
-0.022 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
0.425 |
1.422 |
-0.000 |
| C5 |
1.574 |
-0.763 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
-0.777 |
-1.724 |
-0.001 |
| H7 |
0.957 |
1.770 |
-0.881 |
| H8 |
-0.571 |
1.833 |
-0.001 |
| H9 |
0.956 |
1.770 |
0.881 |
| H10 |
2.166 |
-0.528 |
-0.880 |
| H11 |
2.166 |
-0.528 |
0.880 |
| H12 |
1.373 |
-1.826 |
0.001 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
C4 |
C5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
| C1 | | 1.1964 | 1.3488 | 2.4285 | 2.4414 | 1.0905 | 3.1435 | 2.4871 | 3.1430 | 3.1566 | 3.1571 | 2.5332 |
O2 | 1.1964 | | 2.2680 | 2.8005 | 3.5677 | 1.9964 | 3.5474 | 2.3582 | 3.5464 | 4.2119 | 4.2119 | 3.7295 | N3 | 1.3488 | 2.2680 | | 1.4462 | 1.4424 | 2.0340 | 2.0906 | 2.0651 | 2.0902 | 2.0920 | 2.0919 | 2.0803 | C4 | 2.4285 | 2.8005 | 1.4462 | | 2.4683 | 3.3672 | 1.0861 | 1.0774 | 1.0860 | 2.7581 | 2.7577 | 3.3830 | C5 | 2.4414 | 3.5677 | 1.4424 | 2.4683 | | 2.5404 | 2.7514 | 3.3675 | 2.7515 | 1.0860 | 1.0859 | 1.0821 | H6 | 1.0905 | 1.9964 | 2.0340 | 3.3672 | 2.5404 | | 3.9981 | 3.5629 | 3.9982 | 3.2958 | 3.2970 | 2.1526 | H7 | 3.1435 | 3.5474 | 2.0906 | 1.0861 | 2.7514 | 3.9981 | | 1.7641 | 1.7616 | 2.5966 | 3.1366 | 3.7253 | H8 | 2.4871 | 2.3582 | 2.0651 | 1.0774 | 3.3675 | 3.5629 | 1.7641 | | 1.7642 | 3.7200 | 3.7200 | 4.1432 | H9 | 3.1430 | 3.5464 | 2.0902 | 1.0860 | 2.7515 | 3.9982 | 1.7616 | 1.7642 | | 3.1378 | 2.5964 | 3.7251 | H10 | 3.1566 | 4.2119 | 2.0920 | 2.7581 | 1.0860 | 3.2958 | 2.5966 | 3.7200 | 3.1378 | | 1.7598 | 1.7572 | H11 | 3.1571 | 4.2119 | 2.0919 | 2.7577 | 1.0859 | 3.2970 | 3.1366 | 3.7200 | 2.5964 | 1.7598 | | 1.7571 | H12 | 2.5332 | 3.7295 | 2.0803 | 3.3830 | 1.0821 | 2.1526 | 3.7253 | 4.1432 | 3.7251 | 1.7572 | 1.7571 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
C4 |
120.611 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
C5 |
121.982 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
125.905 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.536 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H6 |
112.559 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H7 |
110.486 |
| N3 |
C4 |
H8 |
108.960 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H9 |
110.457 |
| N3 |
C5 |
H10 |
110.884 |
|
N3 |
C5 |
H11 |
110.878 |
| N3 |
C5 |
H12 |
110.175 |
|
C4 |
N3 |
C5 |
117.407 |
| H7 |
C4 |
H8 |
109.259 |
|
H7 |
C4 |
H9 |
108.392 |
| H8 |
C4 |
H9 |
109.265 |
|
H10 |
C5 |
H11 |
108.237 |
| H10 |
C5 |
H12 |
108.291 |
|
H11 |
C5 |
H12 |
108.286 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.522 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.579 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.607 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.294 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.281 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.142 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.232 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.175 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.175 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.181 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
4.033 |
-0.678 |
-0.002 |
4.089 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-37.422 |
0.113 |
0.003 |
| y |
0.113 |
-27.049 |
-0.001 |
| z |
0.003 |
-0.001 |
-31.040 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-8.377 |
0.113 |
0.003 |
| y |
0.113 |
7.181 |
-0.001 |
| z |
0.003 |
-0.001 |
1.196 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.391 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.372 |
|---|
| xy | 0.113 |
|---|
| xz | 0.003 |
|---|
| yz | -0.001 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.029 |
0.077 |
-0.000 |
| y |
0.077 |
5.885 |
0.001 |
| z |
-0.000 |
0.001 |
4.238 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
122.647 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.075 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/6-31G*
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -246.987944 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -246.987944 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 182.768613 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3362 |
3021 |
2.65 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3313 |
2977 |
23.69 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3214 |
2888 |
60.23 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3203 |
2878 |
78.83 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3193 |
2869 |
59.24 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1966 |
1767 |
538.39 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1671 |
1501 |
42.39 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1660 |
1491 |
10.52 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1627 |
1462 |
22.39 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1590 |
1428 |
6.43 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1584 |
1423 |
3.06 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1545 |
1388 |
187.28 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1410 |
1266 |
49.16 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1212 |
1089 |
97.64 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1178 |
1058 |
44.92 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
936 |
841 |
5.24 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
712 |
640 |
9.28 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
423 |
380 |
1.36 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
339 |
304 |
13.85 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
3262 |
2931 |
42.41 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
3254 |
2924 |
58.18 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
1651 |
1484 |
2.84 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
1641 |
1474 |
9.05 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
1275 |
1146 |
4.73 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
1241 |
1115 |
0.64 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1169 |
1050 |
6.91 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
341 |
306 |
34.53 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
213 |
192 |
2.31 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
107 |
96 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
196i |
176i |
0.02 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24047.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21606.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/6-31G*
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.654 |
-0.837 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
0.152 |
-1.923 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.341 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
-1.448 |
0.381 |
0.000 |
| C5 |
0.745 |
1.585 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
1.738 |
-0.710 |
0.000 |
| H7 |
-1.820 |
-0.630 |
0.000 |
| H8 |
-1.817 |
0.896 |
0.881 |
| H9 |
-1.817 |
0.896 |
-0.881 |
| H10 |
0.047 |
2.410 |
0.000 |
| H11 |
1.371 |
1.679 |
0.882 |
| H12 |
1.371 |
1.679 |
-0.882 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
O2 |
N3 |
C4 |
C5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
| C1 | | 1.1968 | 1.3475 | 2.4289 | 2.4238 | 1.0920 | 2.4827 | 3.1442 | 3.1442 | 3.3031 | 2.7609 | 2.7609 |
O2 | 1.1968 | | 2.2699 | 2.8054 | 3.5585 | 1.9972 | 2.3587 | 3.5502 | 3.5502 | 4.3348 | 3.9041 | 3.9041 | N3 | 1.3475 | 2.2699 | | 1.4483 | 1.4501 | 2.0316 | 2.0632 | 2.0946 | 2.0946 | 2.0692 | 2.1088 | 2.1088 | C4 | 2.4289 | 2.8054 | 1.4483 | | 2.5020 | 3.3677 | 1.0775 | 1.0855 | 1.0855 | 2.5201 | 3.2262 | 3.2262 | C5 | 2.4238 | 3.5585 | 1.4501 | 2.5020 | | 2.5007 | 3.3897 | 2.7966 | 2.7966 | 1.0808 | 1.0852 | 1.0852 | H6 | 1.0920 | 1.9972 | 2.0316 | 3.3677 | 2.5007 | | 3.5595 | 3.9999 | 3.9999 | 3.5489 | 2.5730 | 2.5730 | H7 | 2.4827 | 2.3587 | 2.0632 | 1.0775 | 3.3897 | 3.5595 | | 1.7620 | 1.7620 | 3.5677 | 4.0366 | 4.0366 | H8 | 3.1442 | 3.5502 | 2.0946 | 1.0855 | 2.7966 | 3.9999 | 1.7620 | | 1.7628 | 2.5586 | 3.2834 | 3.7268 | H9 | 3.1442 | 3.5502 | 2.0946 | 1.0855 | 2.7966 | 3.9999 | 1.7620 | 1.7628 | | 2.5586 | 3.7268 | 3.2834 | H10 | 3.3031 | 4.3348 | 2.0692 | 2.5201 | 1.0808 | 3.5489 | 3.5677 | 2.5586 | 2.5586 | | 1.7506 | 1.7506 | H11 | 2.7609 | 3.9041 | 2.1088 | 3.2262 | 1.0852 | 2.5730 | 4.0366 | 3.2834 | 3.7268 | 1.7506 | | 1.7634 | H12 | 2.7609 | 3.9041 | 2.1088 | 3.2262 | 1.0852 | 2.5730 | 4.0366 | 3.7268 | 3.2834 | 1.7506 | 1.7634 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
N3 |
C4 |
120.597 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
C5 |
120.037 |
| O2 |
C1 |
N3 |
126.191 |
|
O2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.456 |
| N3 |
C1 |
H6 |
112.353 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H7 |
108.658 |
| N3 |
C4 |
H8 |
110.699 |
|
N3 |
C4 |
H9 |
110.699 |
| N3 |
C5 |
H10 |
108.806 |
|
N3 |
C5 |
H11 |
111.756 |
| N3 |
C5 |
H12 |
111.756 |
|
C4 |
N3 |
C5 |
119.367 |
| H7 |
C4 |
H8 |
109.092 |
|
H7 |
C4 |
H9 |
109.092 |
| H8 |
C4 |
H9 |
108.570 |
|
H10 |
C5 |
H11 |
107.848 |
| H10 |
C5 |
H12 |
107.848 |
|
H11 |
C5 |
H12 |
108.678 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.524 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.581 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.615 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.292 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.293 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.143 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.230 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.167 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.189 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.180 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.180 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.476 |
4.153 |
0.000 |
4.181 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.255 |
0.100 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.100 |
-37.002 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.975 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.733 |
0.100 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.100 |
-7.887 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.154 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.307 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 9.747 |
|---|
| xy | 0.100 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.944 |
-0.028 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.028 |
6.825 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.248 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
122.816 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.082 |
