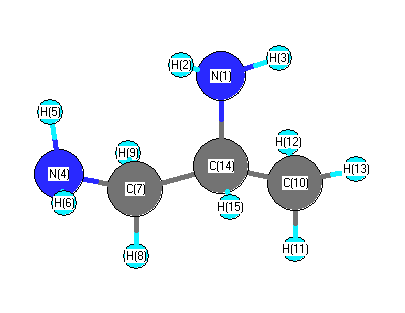
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G*
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3822 |
3434 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3810 |
3423 |
0.14 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3732 |
3353 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3727 |
3349 |
0.65 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3278 |
2946 |
65.91 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3262 |
2931 |
20.91 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3259 |
2928 |
52.25 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3216 |
2890 |
52.25 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3200 |
2876 |
25.29 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
3100 |
2785 |
94.86 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1843 |
1656 |
21.95 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1831 |
1645 |
52.19 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1647 |
1480 |
1.55 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1639 |
1473 |
3.54 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1630 |
1465 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1577 |
1417 |
1.25 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1560 |
1402 |
10.63 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1537 |
1381 |
13.21 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1511 |
1357 |
4.96 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1478 |
1328 |
15.70 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1378 |
1238 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1321 |
1187 |
8.12 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1271 |
1142 |
9.74 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1194 |
1073 |
17.91 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1142 |
1026 |
16.91 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1102 |
991 |
2.50 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1035 |
930 |
12.52 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
997 |
896 |
118.70 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
966 |
868 |
134.44 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
932 |
837 |
80.95 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
861 |
773 |
61.39 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
527 |
473 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
505 |
454 |
21.35 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
398 |
357 |
0.97 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
374 |
336 |
60.74 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
280 |
252 |
14.23 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
269 |
242 |
32.25 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
243 |
219 |
24.84 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
130 |
117 |
5.21 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 32790.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8985) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29462.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G*
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-0.847 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.327 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.337 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.851 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.340 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.328 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.104 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.158 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.173 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
C |
-0.490 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.162 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.177 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.156 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.006 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.127 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.111 |
1.159 |
1.840 |
2.441 |
| CHELPG |
1.084 |
1.176 |
1.810 |
2.416 |
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
1.097 |
1.166 |
1.807 |
2.414 |
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.290 |
-2.902 |
-0.934 |
| y |
-2.902 |
-31.173 |
1.811 |
| z |
-0.934 |
1.811 |
-33.447 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.980 |
-2.902 |
-0.934 |
| y |
-2.902 |
3.696 |
1.811 |
| z |
-0.934 |
1.811 |
0.284 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.568 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -5.117 |
|---|
| xy | -2.902 |
|---|
| xz | -0.934 |
|---|
| yz | 1.811 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.987 |
-0.243 |
-0.136 |
| y |
-0.243 |
6.578 |
-0.109 |
| z |
-0.136 |
-0.109 |
5.850 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
143.330 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.972 |