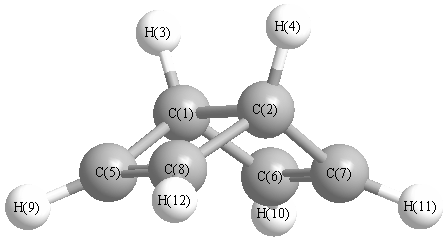
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-311+G(3df,2p)
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3357 |
3050 |
8.30 |
238.31 |
0.04 |
0.07 |
| 2 |
A1 |
3241 |
2945 |
42.21 |
143.01 |
0.11 |
0.20 |
| 3 |
A1 |
1757 |
1597 |
0.26 |
88.08 |
0.02 |
0.04 |
| 4 |
A1 |
1300 |
1181 |
4.29 |
32.22 |
0.11 |
0.19 |
| 5 |
A1 |
1144 |
1039 |
1.01 |
12.35 |
0.29 |
0.45 |
| 6 |
A1 |
1026 |
932 |
27.90 |
14.03 |
0.20 |
0.33 |
| 7 |
A1 |
943 |
857 |
0.00 |
4.39 |
0.49 |
0.66 |
| 8 |
A1 |
895 |
813 |
78.65 |
8.63 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
| 9 |
A1 |
423 |
384 |
5.89 |
2.73 |
0.46 |
0.63 |
| 10 |
A2 |
3322 |
3018 |
0.00 |
144.83 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A2 |
1428 |
1297 |
0.00 |
5.84 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
A2 |
1326 |
1205 |
0.00 |
7.83 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 13 |
A2 |
1069 |
971 |
0.00 |
1.54 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 14 |
A2 |
1023 |
930 |
0.00 |
1.39 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 15 |
A2 |
855 |
777 |
0.00 |
3.73 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 16 |
A2 |
365 |
331 |
0.00 |
1.05 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 17 |
B1 |
3355 |
3048 |
34.46 |
59.74 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 18 |
B1 |
1729 |
1571 |
17.92 |
0.19 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 19 |
B1 |
1345 |
1222 |
9.23 |
0.24 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 20 |
B1 |
1193 |
1084 |
0.32 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 21 |
B1 |
1073 |
975 |
2.17 |
7.60 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 22 |
B1 |
804 |
731 |
50.26 |
0.20 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 23 |
B2 |
3324 |
3020 |
30.22 |
39.89 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 24 |
B2 |
3232 |
2937 |
26.88 |
112.43 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 25 |
B2 |
1425 |
1295 |
43.44 |
0.00 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 26 |
B2 |
1288 |
1170 |
6.76 |
0.24 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 27 |
B2 |
1090 |
991 |
3.12 |
4.17 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 28 |
B2 |
1019 |
926 |
5.65 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 29 |
B2 |
913 |
829 |
10.65 |
0.44 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 30 |
B2 |
542 |
492 |
7.09 |
1.97 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22901.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9086) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20807.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-311+G(3df,2p)
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.364 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.364 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.094 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.094 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
-0.017 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-0.017 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.017 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
C |
-0.017 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.152 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.110 |
0.110 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.298 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-32.748 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-36.869 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.490 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
3.836 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.346 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -4.691 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.551 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.629 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
9.999 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.406 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
117.838 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.855 |