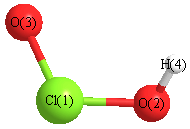Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/CEP-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -46.344192 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -46.344192 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 36.644490 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/CEP-31G
Geometric Data calculated at HF/CEP-31G
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Cl1 |
0.074 |
-0.650 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
1.280 |
0.640 |
-0.001 |
| O3 |
-1.532 |
0.559 |
-0.000 |
| H4 |
0.764 |
1.460 |
0.004 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Cl1 |
O2 |
O3 |
H4 |
| Cl1 | | 1.7662 | 2.0100 | 2.2205 |
O2 | 1.7662 | | 2.8129 | 0.9695 | O3 | 2.0100 | 2.8129 | | 2.4661 | H4 | 2.2205 | 0.9695 | 2.4661 | |
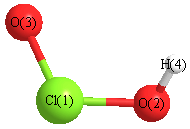 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Cl1 |
O2 |
H4 |
104.744 |
|
O2 |
Cl1 |
O3 |
96.089 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/CEP-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
0.419 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.543 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.308 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.431 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.553 |
0.609 |
0.013 |
0.823 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.500 |
1.180 |
0.010 |
| y |
1.180 |
-18.476 |
0.018 |
| z |
0.010 |
0.018 |
-24.081 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-7.221 |
1.180 |
0.010 |
| y |
1.180 |
7.815 |
0.018 |
| z |
0.010 |
0.018 |
-0.593 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.186 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -10.024 |
|---|
| xy | 1.180 |
|---|
| xz | 0.010 |
|---|
| yz | 0.018 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
48.748 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.982 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/CEP-31G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -46.344195 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -46.345324 |
| HF Energy | -46.344195 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 36.599117 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/CEP-31G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3940 |
3552 |
141.62 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1381 |
1245 |
25.35 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
769 |
693 |
2.16 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
307 |
277 |
63.74 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
173 |
156 |
10.92 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
231 |
208 |
291.55 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3400.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9014) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 3065.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/CEP-31G
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Cl1 |
0.000 |
0.653 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-1.347 |
-0.488 |
0.000 |
| O3 |
1.464 |
-0.730 |
0.000 |
| H4 |
-0.932 |
-1.364 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Cl1 |
O2 |
O3 |
H4 |
| Cl1 | | 1.7658 | 2.0137 | 2.2217 |
O2 | 1.7658 | | 2.8216 | 0.9694 | O3 | 2.0137 | 2.8216 | | 2.4780 | H4 | 2.2217 | 0.9694 | 2.4780 | |
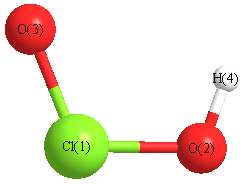 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Cl1 |
O2 |
H4 |
104.863 |
|
O2 |
Cl1 |
O3 |
96.365 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/CEP-31G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Cl |
0.417 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.543 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.305 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.431 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.616 |
-0.560 |
0.000 |
0.832 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.087 |
2.292 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.292 |
-18.875 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.083 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-6.608 |
2.292 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.292 |
7.210 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.602 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.205 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -9.212 |
|---|
| xy | 2.292 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.824 |
0.075 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.075 |
3.751 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.427 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
48.879 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
6.991 |