Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at HF/SDD
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1589.827313 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -1589.827313 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 319.905488 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/SDD
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
474 |
427 |
0.00 |
100.18 |
0.08 |
0.15 |
| 2 |
A1 |
131 |
118 |
0.00 |
8.67 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 3 |
B1 |
445 |
401 |
0.00 |
48.95 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 4 |
B2 |
300 |
270 |
0.50 |
16.49 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
E |
417 |
375 |
1.64 |
12.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
E |
417 |
375 |
1.64 |
12.25 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 1091.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9004) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 982.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/SDD
Point Group is D2d
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
1.581 |
0.298 |
| S2 |
0.000 |
-1.581 |
0.298 |
| S3 |
-1.581 |
0.000 |
-0.298 |
| S4 |
1.581 |
0.000 |
-0.298 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
| S1 | | 3.1617 | 2.3136 | 2.3136 |
S2 | 3.1617 | | 2.3136 | 2.3136 | S3 | 2.3136 | 2.3136 | | 3.1617 | S4 | 2.3136 | 2.3136 | 3.1617 | |
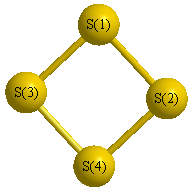 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
S2 |
S4 |
46.900 |
|
S1 |
S3 |
S4 |
46.900 |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
46.900 |
|
S2 |
S4 |
S3 |
46.900 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/SDD
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-52.900 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-52.900 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-57.369 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.235 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
2.235 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-4.469 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -8.939 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
13.550 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
13.550 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.502 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
199.587 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.128 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at HF/SDD
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1589.773349 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -1589.773349 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 310.402010 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/SDD
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
512 |
461 |
1.66 |
114.95 |
0.70 |
0.82 |
| 2 |
A1 |
442 |
398 |
4.62 |
1690.03 |
0.30 |
0.46 |
| 3 |
A1 |
126 |
113 |
0.70 |
77.01 |
0.41 |
0.58 |
| 4 |
A2 |
159 |
143 |
0.00 |
2.73 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 5 |
B2 |
409 |
368 |
528.45 |
10.83 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 6 |
B2 |
285 |
256 |
1.63 |
13.58 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 965.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9004) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 869.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/SDD
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
1.080 |
0.998 |
| S2 |
0.000 |
-1.080 |
0.998 |
| S3 |
0.000 |
1.717 |
-0.998 |
| S4 |
0.000 |
-1.717 |
-0.998 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
| S1 | | 2.1594 | 2.0945 | 3.4355 |
S2 | 2.1594 | | 3.4355 | 2.0945 | S3 | 2.0945 | 3.4355 | | 3.4343 | S4 | 3.4355 | 2.0945 | 3.4343 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
S2 |
S4 |
107.719 |
|
S1 |
S3 |
S4 |
72.281 |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
107.719 |
|
S2 |
S4 |
S3 |
72.281 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/SDD
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
0.061 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
S |
0.061 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
-0.061 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
S |
-0.061 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.464 |
1.464 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-53.486 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-57.393 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-53.856 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.139 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-3.722 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.584 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.167 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.907 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.552 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
29.302 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
12.237 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
229.646 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
15.154 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/SDD
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -1589.752505 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -1589.752505 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 317.639251 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/SDD
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
644 |
579 |
0.00 |
44.85 |
0.63 |
0.77 |
| 2 |
Ag |
338 |
305 |
0.00 |
3923.05 |
0.33 |
0.49 |
| 3 |
Au |
226 |
204 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 4 |
B1u |
607 |
546 |
52.56 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 5 |
B2u |
307i |
276i |
24.52 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
0.00 |
| 6 |
B3g |
299 |
269 |
0.00 |
39.41 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 903.6 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9004) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 813.6 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/SDD
Point Group is D2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| S1 |
0.000 |
1.009 |
1.326 |
| S2 |
0.000 |
1.009 |
-1.326 |
| S3 |
0.000 |
-1.009 |
1.326 |
| S4 |
0.000 |
-1.009 |
-1.326 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
S1 |
S2 |
S3 |
S4 |
| S1 | | 2.6527 | 2.0186 | 3.3334 |
S2 | 2.6527 | | 3.3334 | 2.0186 | S3 | 2.0186 | 3.3334 | | 2.6527 | S4 | 3.3334 | 2.0186 | 2.6527 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| S1 |
S2 |
S4 |
90.000 |
|
S1 |
S3 |
S4 |
90.000 |
| S2 |
S1 |
S3 |
90.000 |
|
S2 |
S4 |
S3 |
90.000 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/SDD
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
S |
0.000 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-53.606 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-53.910 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-56.432 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.564 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.109 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-2.674 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -5.347 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.303 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
2.514 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
12.784 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.494 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
211.915 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.557 |
