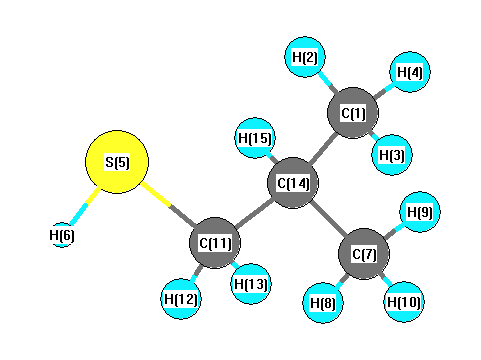
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/aug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3244 |
2953 |
27.53 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3232 |
2942 |
37.43 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3217 |
2929 |
79.99 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3211 |
2923 |
46.49 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3203 |
2916 |
9.09 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3193 |
2907 |
29.49 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3156 |
2873 |
31.04 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3151 |
2868 |
3.99 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
3148 |
2866 |
25.84 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
2853 |
2598 |
4.25 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1627 |
1481 |
11.18 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1622 |
1476 |
3.64 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1616 |
1471 |
3.86 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1606 |
1462 |
1.72 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1601 |
1457 |
2.80 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1548 |
1409 |
6.43 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1531 |
1394 |
4.30 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1497 |
1363 |
2.27 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1481 |
1348 |
1.96 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1398 |
1272 |
26.00 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1343 |
1223 |
3.25 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1289 |
1174 |
6.49 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1232 |
1122 |
2.75 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1174 |
1069 |
2.24 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1045 |
951 |
0.45 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1037 |
944 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1006 |
916 |
1.08 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
977 |
889 |
2.74 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
945 |
860 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
852 |
775 |
3.57 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
772 |
703 |
2.71 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
455 |
415 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
419 |
381 |
1.22 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
361 |
328 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
268 |
244 |
0.09 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
236 |
214 |
0.37 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A |
221 |
201 |
1.55 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A |
175 |
160 |
11.95 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A |
82 |
75 |
8.49 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30510.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9104) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27776.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/aug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-1.027 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.290 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.268 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.278 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
S |
-0.361 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.031 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-1.052 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.267 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.264 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.274 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
C |
-0.436 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.309 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.271 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
C |
0.230 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.396 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
1.188 |
-1.095 |
0.630 |
1.734 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-42.027 |
2.439 |
-1.845 |
| y |
2.439 |
-40.948 |
-1.144 |
| z |
-1.845 |
-1.144 |
-41.879 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.613 |
2.439 |
-1.845 |
| y |
2.439 |
1.005 |
-1.144 |
| z |
-1.845 |
-1.144 |
-0.392 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.784 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.079 |
|---|
| xy | 2.439 |
|---|
| xz | -1.845 |
|---|
| yz | -1.144 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
12.061 |
-0.181 |
0.072 |
| y |
-0.181 |
9.782 |
-0.024 |
| z |
0.072 |
-0.024 |
8.932 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
202.132 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.217 |