Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -184.496408 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -184.500670 |
| HF Energy | -184.496408 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 100.887050 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
4103 |
3350 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3920 |
3201 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
2894 |
2363 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1974 |
1612 |
8.29 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1447 |
1181 |
1.20 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
965 |
788 |
50.53 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
795 |
649 |
32.63 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
527 |
430 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
276 |
225 |
0.27 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
262 |
214 |
53.76 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
B |
4103 |
3350 |
0.96 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
B |
3922 |
3202 |
2.62 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
B |
1971 |
1609 |
7.33 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
B |
1456 |
1189 |
6.96 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B |
1446 |
1181 |
1.58 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B |
929 |
758 |
284.81 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B |
529 |
432 |
20.50 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B |
276 |
225 |
10.05 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 15896.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8165) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 12979.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/STO-3G
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.006 |
0.584 |
0.018 |
| C2 |
-0.006 |
-0.584 |
0.018 |
| N3 |
-0.006 |
1.970 |
-0.067 |
| N4 |
0.006 |
-1.970 |
-0.067 |
| H5 |
-0.327 |
2.455 |
0.785 |
| H6 |
0.865 |
2.392 |
-0.422 |
| H7 |
0.327 |
-2.455 |
0.785 |
| H8 |
-0.865 |
-2.392 |
-0.422 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
N4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.1682 | 1.3889 | 2.5558 | 2.0498 | 2.0495 | 3.1511 | 3.1324 |
C2 | 1.1682 | | 2.5558 | 1.3889 | 3.1511 | 3.1324 | 2.0498 | 2.0495 | N3 | 1.3889 | 2.5558 | | 3.9407 | 1.0315 | 1.0315 | 4.5193 | 4.4605 | N4 | 2.5558 | 1.3889 | 3.9407 | | 4.5193 | 4.4605 | 1.0315 | 1.0315 | H5 | 2.0498 | 3.1511 | 1.0315 | 4.5193 | | 1.6977 | 4.9540 | 5.0246 | H6 | 2.0495 | 3.1324 | 1.0315 | 4.4605 | 1.6977 | | 5.0246 | 5.0879 | H7 | 3.1511 | 2.0498 | 4.5193 | 1.0315 | 4.9540 | 5.0246 | | 1.6977 | H8 | 3.1324 | 2.0495 | 4.4605 | 1.0315 | 5.0246 | 5.0879 | 1.6977 | |
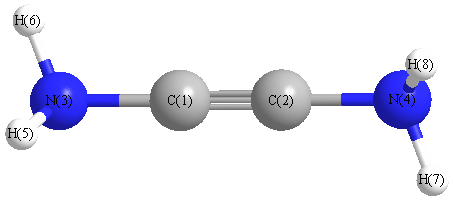 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
N4 |
176.310 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
114.947 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
114.922 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
176.310 |
| C2 |
N4 |
H7 |
114.947 |
|
C2 |
N4 |
H8 |
114.922 |
| H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
110.758 |
|
H7 |
N4 |
H8 |
110.758 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.009 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.009 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.376 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.376 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.185 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.183 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.185 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.107 |
2.107 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-21.157 |
5.380 |
0.000 |
| y |
5.380 |
-17.748 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-21.246 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-1.661 |
5.380 |
0.000 |
| y |
5.380 |
3.454 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.793 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -3.586 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.410 |
|---|
| xy | 5.380 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.197 |
0.463 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.463 |
5.177 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.232 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
97.961 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.898 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/STO-3G
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -184.485051 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -184.485051 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 102.036330 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
4052 |
3308 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A1 |
2818 |
2301 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A1 |
1897 |
1549 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A1 |
916 |
748 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
B1 |
516 |
421 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
B2 |
4060 |
3315 |
40.25 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
B2 |
1909 |
1559 |
11.03 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
B2 |
1551 |
1267 |
79.08 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
E |
4255 |
3474 |
12.46 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
E |
4255 |
3474 |
12.46 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
E |
1300 |
1061 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
E |
1300 |
1061 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
E |
543 |
443 |
7.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
E |
543 |
443 |
7.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
E |
267 |
218 |
9.14 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
E |
267 |
218 |
9.14 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
E |
616i |
503i |
336.28 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
E |
616i |
503i |
336.28 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14608.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8165) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 11928.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/STO-3G
Point Group is D2d
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.589 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.589 |
| N3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.949 |
| N4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.949 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.866 |
2.478 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-0.866 |
2.478 |
| H7 |
0.866 |
0.000 |
-2.478 |
| H8 |
-0.866 |
0.000 |
-2.478 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
N3 |
N4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
| C1 | | 1.1775 | 1.3603 | 2.5377 | 2.0781 | 2.0781 | 3.1865 | 3.1865 |
C2 | 1.1775 | | 2.5377 | 1.3603 | 3.1865 | 3.1865 | 2.0781 | 2.0781 | N3 | 1.3603 | 2.5377 | | 3.8980 | 1.0146 | 1.0146 | 4.5108 | 4.5108 | N4 | 2.5377 | 1.3603 | 3.8980 | | 4.5108 | 4.5108 | 1.0146 | 1.0146 | H5 | 2.0781 | 3.1865 | 1.0146 | 4.5108 | | 1.7317 | 5.1048 | 5.1048 | H6 | 2.0781 | 3.1865 | 1.0146 | 4.5108 | 1.7317 | | 5.1048 | 5.1048 | H7 | 3.1865 | 2.0781 | 4.5108 | 1.0146 | 5.1048 | 5.1048 | | 1.7317 | H8 | 3.1865 | 2.0781 | 4.5108 | 1.0146 | 5.1048 | 5.1048 | 1.7317 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
N4 |
180.000 |
|
C1 |
N3 |
H5 |
121.417 |
| C1 |
N3 |
H6 |
121.417 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
N3 |
180.000 |
| C2 |
N4 |
H7 |
121.417 |
|
C2 |
N4 |
H8 |
121.417 |
| H5 |
N3 |
H6 |
117.167 |
|
H7 |
N4 |
H8 |
117.167 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.021 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.021 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
-0.420 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
N |
-0.420 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.199 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-21.300 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-21.300 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-12.280 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-4.510 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-4.510 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
9.020 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 18.039 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.000 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
1.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
1.000 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.457 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
96.325 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.815 |
