Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/STO-3G
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
4228 |
3452 |
27.82 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3752 |
3063 |
1.96 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3614 |
2951 |
3.56 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3605 |
2943 |
3.19 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3569 |
2914 |
2.44 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3538 |
2889 |
9.11 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1852 |
1512 |
0.68 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1847 |
1508 |
1.55 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1833 |
1497 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1823 |
1489 |
1.08 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1790 |
1461 |
9.53 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1746 |
1425 |
0.60 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1703 |
1390 |
4.15 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1602 |
1308 |
4.16 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1493 |
1219 |
39.24 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1341 |
1095 |
1.26 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1309 |
1069 |
4.18 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1255 |
1025 |
0.47 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1185 |
967 |
2.22 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
1074 |
877 |
4.89 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
469 |
383 |
5.88 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
443 |
361 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
208 |
170 |
2.04 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
3753 |
3065 |
3.42 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
3733 |
3048 |
4.30 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
3717 |
3035 |
0.95 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
3650 |
2980 |
13.63 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1837 |
1500 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1561 |
1275 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
1543 |
1260 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
1473 |
1203 |
0.43 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
1364 |
1114 |
7.33 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
1124 |
918 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
950 |
775 |
1.85 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
854 |
697 |
1.80 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
349 |
285 |
78.22 |
|
|
|
| 37 |
A" |
253 |
207 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 38 |
A" |
118 |
96 |
3.18 |
|
|
|
| 39 |
A" |
109 |
89 |
1.07 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 35831.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.8165) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 29256.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
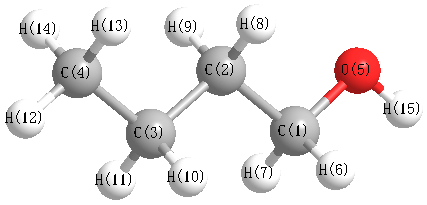
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/STO-3G
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.007 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.103 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.095 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.177 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.288 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.044 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.044 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.060 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.060 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.052 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.052 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.058 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.058 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.058 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
H |
0.170 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.076 |
-1.418 |
0.000 |
1.420 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.159 |
-3.464 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.464 |
-32.198 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-30.913 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
2.397 |
-3.464 |
0.000 |
| y |
-3.464 |
-2.162 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.235 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.470 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.039 |
|---|
| xy | -3.464 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.517 |
0.012 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.012 |
3.270 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.070 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
188.547 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.731 |