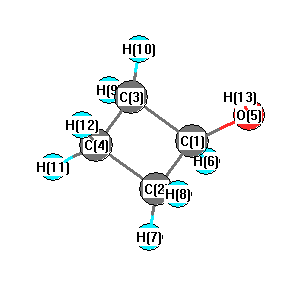
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
4176 |
3769 |
30.95 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3277 |
2958 |
108.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3262 |
2944 |
18.49 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3238 |
2923 |
12.22 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3218 |
2905 |
33.68 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3197 |
2885 |
32.25 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1652 |
1491 |
10.01 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1618 |
1460 |
3.58 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1570 |
1417 |
92.23 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1448 |
1307 |
1.02 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1400 |
1264 |
14.93 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1322 |
1193 |
0.21 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1261 |
1138 |
154.55 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1179 |
1064 |
34.27 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1050 |
948 |
8.39 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
980 |
884 |
1.73 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
817 |
738 |
4.90 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
662 |
597 |
3.22 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
493 |
445 |
5.58 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
192 |
173 |
1.93 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
3257 |
2940 |
46.26 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
3191 |
2880 |
50.50 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1610 |
1453 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
1436 |
1296 |
2.61 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
1384 |
1250 |
0.46 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
1369 |
1236 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
1306 |
1179 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
1140 |
1029 |
12.65 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
1022 |
923 |
6.46 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
989 |
893 |
0.30 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
851 |
768 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
422 |
381 |
36.51 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
321 |
290 |
102.80 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27153.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9026) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24508.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.239 |
0.012 |
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.251 |
-0.016 |
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.251 |
0.074 |
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.250 |
0.038 |
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.649 |
0.034 |
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.126 |
-0.180 |
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.123 |
-0.069 |
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.109 |
0.442 |
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.123 |
0.026 |
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.109 |
0.051 |
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.125 |
-0.127 |
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.121 |
0.409 |
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.328 |
-0.692 |
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.300 |
-1.710 |
0.000 |
1.737 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.616 |
1.292 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.292 |
-36.878 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-32.098 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.872 |
1.292 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.292 |
-7.021 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.149 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 0.298 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 9.263 |
|---|
| xy | 1.292 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.302 |
-0.248 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.248 |
6.228 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.172 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
108.475 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.415 |