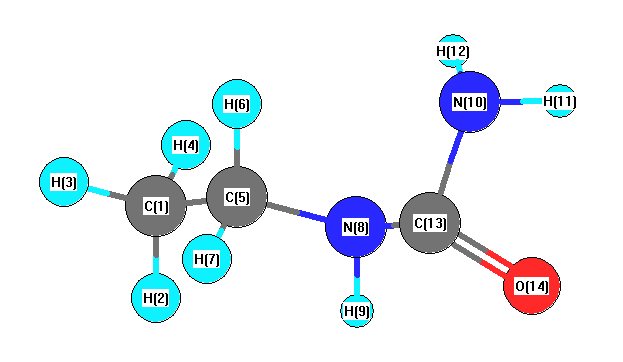
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/6-31G**
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3966 |
3579 |
46.97 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3879 |
3501 |
41.31 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3840 |
3466 |
40.31 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3269 |
2951 |
38.80 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3259 |
2941 |
51.89 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3202 |
2890 |
37.93 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3189 |
2878 |
20.47 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3172 |
2863 |
51.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1970 |
1778 |
654.65 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1784 |
1611 |
192.54 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1668 |
1505 |
4.13 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1635 |
1476 |
4.07 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1622 |
1464 |
8.07 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1615 |
1458 |
33.82 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1564 |
1412 |
261.55 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1553 |
1402 |
52.60 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1494 |
1348 |
31.08 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1418 |
1280 |
3.85 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1304 |
1177 |
20.67 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1270 |
1146 |
3.27 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1225 |
1106 |
37.03 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1157 |
1044 |
12.52 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1062 |
959 |
2.97 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
970 |
876 |
2.79 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
890 |
803 |
10.69 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
870 |
785 |
95.44 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
644 |
581 |
60.58 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
609 |
550 |
15.52 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
574 |
518 |
129.73 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
526 |
475 |
37.14 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
409 |
369 |
169.24 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
388 |
350 |
5.44 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
291 |
262 |
2.22 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
215 |
194 |
3.54 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
113 |
102 |
7.19 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
64 |
58 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 28339.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9026) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25579.2 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/6-31G**
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.365 |
-0.352 |
|
|
| 2 |
H |
0.126 |
0.102 |
|
|
| 3 |
H |
0.129 |
0.070 |
|
|
| 4 |
H |
0.133 |
0.098 |
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.003 |
0.541 |
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.111 |
-0.056 |
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.131 |
-0.051 |
|
|
| 8 |
N |
-0.733 |
-0.903 |
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.315 |
0.375 |
|
|
| 10 |
N |
-0.766 |
-1.027 |
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.318 |
0.411 |
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.300 |
0.401 |
|
|
| 13 |
C |
0.934 |
1.109 |
|
|
| 14 |
O |
-0.636 |
-0.718 |
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-3.272 |
2.944 |
-0.580 |
4.439 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-38.664 |
7.358 |
-1.690 |
| y |
7.358 |
-35.106 |
-1.755 |
| z |
-1.690 |
-1.755 |
-37.929 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.146 |
7.358 |
-1.690 |
| y |
7.358 |
3.190 |
-1.755 |
| z |
-1.690 |
-1.755 |
-1.045 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -2.089 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.557 |
|---|
| xy | 7.358 |
|---|
| xz | -1.690 |
|---|
| yz | -1.755 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.984 |
-0.238 |
0.118 |
| y |
-0.238 |
6.825 |
-0.096 |
| z |
0.118 |
-0.096 |
4.747 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
200.617 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.164 |