Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/TZVP
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -302.777441 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -302.777441 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 181.959836 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/TZVP
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
4110 |
3734 |
101.54 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
4095 |
3721 |
130.66 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3193 |
2902 |
29.34 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
1996 |
1814 |
431.68 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1625 |
1477 |
7.04 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1610 |
1463 |
2.33 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1459 |
1326 |
126.39 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1386 |
1259 |
71.12 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1302 |
1183 |
160.11 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1228 |
1115 |
246.60 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
927 |
842 |
41.18 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
714 |
648 |
28.93 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
510 |
464 |
24.17 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
298 |
271 |
8.64 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A" |
3225 |
2930 |
21.74 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A" |
1369 |
1244 |
0.04 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
1142 |
1037 |
3.02 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
687 |
625 |
166.97 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A" |
544 |
494 |
20.22 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
257 |
233 |
90.15 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
52i |
47i |
40.94 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 15812.2 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9086) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14366.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/TZVP
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.576 |
-0.868 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.526 |
0.000 |
| O3 |
-0.935 |
1.458 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
1.160 |
0.760 |
0.000 |
| O5 |
0.418 |
-1.833 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
-1.209 |
-0.967 |
0.876 |
| H7 |
-1.209 |
-0.967 |
-0.876 |
| H8 |
1.264 |
-1.412 |
0.000 |
| H9 |
-0.528 |
2.314 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.5086 | 2.3544 | 2.3798 | 1.3848 | 1.0849 | 1.0849 | 1.9183 | 3.1826 |
C2 | 1.5086 | | 1.3206 | 1.1830 | 2.3960 | 2.1108 | 2.1108 | 2.3141 | 1.8640 | O3 | 2.3544 | 1.3206 | | 2.2081 | 3.5588 | 2.5927 | 2.5927 | 3.6163 | 0.9476 | O4 | 2.3798 | 1.1830 | 2.2081 | | 2.6976 | 3.0590 | 3.0590 | 2.1753 | 2.2935 | O5 | 1.3848 | 2.3960 | 3.5588 | 2.6976 | | 2.0403 | 2.0403 | 0.9450 | 4.2535 | H6 | 1.0849 | 2.1108 | 2.5927 | 3.0590 | 2.0403 | | 1.7511 | 2.6606 | 3.4629 | H7 | 1.0849 | 2.1108 | 2.5927 | 3.0590 | 2.0403 | 1.7511 | | 2.6606 | 3.4629 | H8 | 1.9183 | 2.3141 | 3.6163 | 2.1753 | 0.9450 | 2.6606 | 2.6606 | | 4.1346 | H9 | 3.1826 | 1.8640 | 0.9476 | 2.2935 | 4.2535 | 3.4629 | 3.4629 | 4.1346 | |
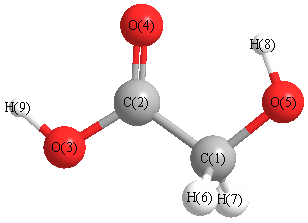 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
112.476 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.853 |
| C1 |
O5 |
H8 |
109.394 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
111.733 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.840 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.840 |
| C2 |
O3 |
H9 |
109.430 |
|
O3 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.672 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.822 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.822 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.619 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/TZVP
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.031 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.358 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.343 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.444 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.435 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.103 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.307 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.319 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.465 |
1.892 |
0.000 |
2.393 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-31.110 |
-0.767 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.767 |
-29.428 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.169 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.311 |
-0.767 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.767 |
0.212 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.100 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.199 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.682 |
|---|
| xy | -0.767 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.146 |
-0.023 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.023 |
4.707 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.352 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
109.866 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.482 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/TZVP
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -302.777455 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -302.783164 |
| HF Energy | -302.777455 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 181.884499 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/TZVP
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
4115 |
3739 |
96.13 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
4095 |
3721 |
129.51 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3242 |
2945 |
18.73 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3179 |
2889 |
32.39 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1998 |
1815 |
432.34 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1624 |
1476 |
6.76 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1608 |
1461 |
2.71 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1459 |
1326 |
129.56 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1408 |
1279 |
26.75 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1353 |
1229 |
45.31 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1299 |
1181 |
155.69 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1228 |
1116 |
234.02 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1137 |
1033 |
11.03 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
927 |
842 |
38.52 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
716 |
651 |
36.27 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
687 |
624 |
156.33 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
545 |
495 |
25.45 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
508 |
462 |
20.78 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
316 |
287 |
36.59 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
251 |
228 |
84.28 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
66 |
60 |
30.35 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 15879.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9086) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 14428.3 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/TZVP
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
-0.744 |
-0.726 |
0.052 |
| C2 |
0.517 |
0.101 |
0.003 |
| O3 |
1.608 |
-0.644 |
-0.031 |
| O4 |
0.531 |
1.283 |
0.017 |
| O5 |
-1.878 |
0.060 |
-0.065 |
| H6 |
-0.714 |
-1.451 |
-0.751 |
| H7 |
-0.732 |
-1.273 |
0.991 |
| H8 |
-1.652 |
0.964 |
0.093 |
| H9 |
2.372 |
-0.084 |
-0.036 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
| C1 | | 1.5089 | 2.3547 | 2.3803 | 1.3846 | 1.0826 | 1.0870 | 1.9183 | 3.1826 |
C2 | 1.5089 | | 1.3211 | 1.1827 | 2.3966 | 2.1197 | 2.1032 | 2.3361 | 1.8641 | O3 | 2.3547 | 1.3211 | | 2.2082 | 3.5562 | 2.5607 | 2.6292 | 3.6367 | 0.9476 | O4 | 2.3803 | 1.1827 | 2.2082 | | 2.7036 | 3.1014 | 3.0134 | 2.2080 | 2.2932 | O5 | 1.3846 | 2.3966 | 3.5562 | 2.7036 | | 2.0273 | 2.0513 | 0.9448 | 4.2523 | H6 | 1.0826 | 2.1197 | 2.5607 | 3.1014 | 2.0273 | | 1.7512 | 2.7247 | 3.4497 | H7 | 1.0870 | 2.1032 | 2.6292 | 3.0134 | 2.0513 | 1.7512 | | 2.5801 | 3.4786 | H8 | 1.9183 | 2.3361 | 3.6367 | 2.2080 | 0.9448 | 2.7247 | 2.5801 | | 4.1598 | H9 | 3.1826 | 1.8641 | 0.9476 | 2.2932 | 4.2523 | 3.4497 | 3.4786 | 4.1598 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
O3 |
112.442 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.886 |
| C1 |
O5 |
H8 |
109.428 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
O5 |
111.769 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.636 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.108 |
| C2 |
O3 |
H9 |
109.395 |
|
O3 |
C2 |
O4 |
123.661 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.907 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.627 |
| H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
107.639 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/TZVP
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.030 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.358 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
O |
-0.344 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.443 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.432 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.107 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.101 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.304 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.319 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.052 |
-1.090 |
0.395 |
2.357 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.012 |
-0.471 |
-0.833 |
| y |
-0.471 |
-31.389 |
0.186 |
| z |
-0.833 |
0.186 |
-28.165 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.765 |
-0.471 |
-0.833 |
| y |
-0.471 |
-2.800 |
0.186 |
| z |
-0.833 |
0.186 |
2.035 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 4.070 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 2.377 |
|---|
| xy | -0.471 |
|---|
| xz | -0.833 |
|---|
| yz | 0.186 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
4.735 |
-0.104 |
-0.007 |
| y |
-0.104 |
5.118 |
0.008 |
| z |
-0.007 |
0.008 |
3.366 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
109.945 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.485 |
