Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -157.356822 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -157.367687 |
| HF Energy | -157.356822 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 131.089685 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
3208 |
2902 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
3152 |
2851 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
3135 |
2836 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
1620 |
1466 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Ag |
1606 |
1452 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Ag |
1538 |
1391 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Ag |
1523 |
1378 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
Ag |
1262 |
1141 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
Ag |
1127 |
1019 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
Ag |
894 |
809 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
Ag |
451 |
408 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
Au |
3210 |
2903 |
179.65 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
Au |
3169 |
2867 |
13.46 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Au |
1614 |
1460 |
12.02 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
Au |
1395 |
1262 |
0.24 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
Au |
1031 |
933 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
Au |
785 |
710 |
2.21 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
Au |
239 |
216 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
Au |
126 |
114 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
Bg |
3202 |
2896 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
Bg |
3148 |
2847 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
Bg |
1613 |
1459 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
Bg |
1438 |
1301 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
Bg |
1313 |
1188 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
Bg |
869 |
786 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
Bg |
276 |
250 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
Bu |
3209 |
2903 |
123.15 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
Bu |
3149 |
2848 |
91.55 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
Bu |
3141 |
2842 |
59.76 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
Bu |
1628 |
1473 |
6.48 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
Bu |
1607 |
1454 |
1.95 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
Bu |
1536 |
1390 |
3.23 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
Bu |
1437 |
1300 |
4.12 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
Bu |
1085 |
982 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
Bu |
1044 |
945 |
2.99 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
Bu |
277 |
251 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30527.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27615.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.420 |
0.637 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.420 |
-0.637 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.420 |
1.910 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
0.420 |
-1.910 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
1.072 |
0.635 |
0.869 |
| H6 |
1.072 |
0.635 |
-0.869 |
| H7 |
-1.072 |
-0.635 |
0.869 |
| H8 |
-1.072 |
-0.635 |
-0.869 |
| H9 |
0.207 |
2.794 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
-0.207 |
-2.794 |
0.000 |
| H11 |
-1.058 |
1.957 |
-0.876 |
| H12 |
-1.058 |
1.957 |
0.876 |
| H13 |
1.058 |
-1.957 |
-0.876 |
| H14 |
1.058 |
-1.957 |
0.876 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
| C1 | | 1.5258 | 1.5247 | 2.5468 | 1.0867 | 1.0867 | 2.1447 | 2.1447 | 2.1676 | 3.4879 | 2.1668 | 2.1668 | 2.8116 | 2.8116 |
C2 | 1.5258 | | 2.5468 | 1.5247 | 2.1447 | 2.1447 | 1.0867 | 1.0867 | 3.4879 | 2.1676 | 2.8116 | 2.8116 | 2.1668 | 2.1668 | C3 | 1.5247 | 2.5468 | | 3.9106 | 2.1462 | 2.1462 | 2.7671 | 2.7671 | 1.0839 | 4.7087 | 1.0850 | 1.0850 | 4.2315 | 4.2315 | C4 | 2.5468 | 1.5247 | 3.9106 | | 2.7671 | 2.7671 | 2.1462 | 2.1462 | 4.7087 | 1.0839 | 4.2315 | 4.2315 | 1.0850 | 1.0850 | H5 | 1.0867 | 2.1447 | 2.1462 | 2.7671 | | 1.7382 | 2.4924 | 3.0386 | 2.4831 | 3.7617 | 3.0549 | 2.5076 | 3.1248 | 2.5923 | H6 | 1.0867 | 2.1447 | 2.1462 | 2.7671 | 1.7382 | | 3.0386 | 2.4924 | 2.4831 | 3.7617 | 2.5076 | 3.0549 | 2.5923 | 3.1248 | H7 | 2.1447 | 1.0867 | 2.7671 | 2.1462 | 2.4924 | 3.0386 | | 1.7382 | 3.7617 | 2.4831 | 3.1248 | 2.5923 | 3.0549 | 2.5076 | H8 | 2.1447 | 1.0867 | 2.7671 | 2.1462 | 3.0386 | 2.4924 | 1.7382 | | 3.7617 | 2.4831 | 2.5923 | 3.1248 | 2.5076 | 3.0549 | H9 | 2.1676 | 3.4879 | 1.0839 | 4.7087 | 2.4831 | 2.4831 | 3.7617 | 3.7617 | | 5.6036 | 1.7517 | 1.7517 | 4.9059 | 4.9059 | H10 | 3.4879 | 2.1676 | 4.7087 | 1.0839 | 3.7617 | 3.7617 | 2.4831 | 2.4831 | 5.6036 | | 4.9059 | 4.9059 | 1.7517 | 1.7517 | H11 | 2.1668 | 2.8116 | 1.0850 | 4.2315 | 3.0549 | 2.5076 | 3.1248 | 2.5923 | 1.7517 | 4.9059 | | 1.7516 | 4.4502 | 4.7825 | H12 | 2.1668 | 2.8116 | 1.0850 | 4.2315 | 2.5076 | 3.0549 | 2.5923 | 3.1248 | 1.7517 | 4.9059 | 1.7516 | | 4.7825 | 4.4502 | H13 | 2.8116 | 2.1668 | 4.2315 | 1.0850 | 3.1248 | 2.5923 | 3.0549 | 2.5076 | 4.9059 | 1.7517 | 4.4502 | 4.7825 | | 1.7516 | H14 | 2.8116 | 2.1668 | 4.2315 | 1.0850 | 2.5923 | 3.1248 | 2.5076 | 3.0549 | 4.9059 | 1.7517 | 4.7825 | 4.4502 | 1.7516 | |
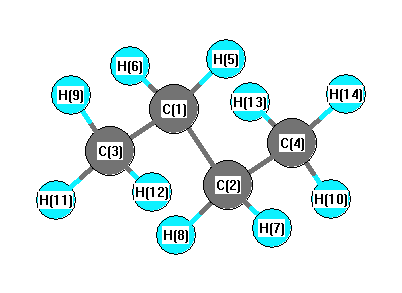 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C4 |
113.201 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.198 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.198 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.268 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.143 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.143 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C3 |
113.201 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.198 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.198 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
111.268 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.143 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H14 |
111.143 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.398 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.398 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.398 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.398 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
106.211 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.211 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.734 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.734 |
| H10 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.734 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.734 |
| H11 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.645 |
|
H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.645 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.554 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.554 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-1.187 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-1.187 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.309 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.309 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.309 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.309 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.369 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.369 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.377 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.377 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.377 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.377 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.851 |
0.465 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.465 |
-29.394 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.000 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.155 |
0.465 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.465 |
-0.969 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.123 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.246 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.543 |
|---|
| xy | 0.465 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.076 |
-0.283 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.283 |
8.357 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.684 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
118.625 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.892 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -157.355175 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -157.366091 |
| HF Energy | -157.355175 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 132.732787 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3223 |
2916 |
65.66 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3204 |
2899 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3170 |
2867 |
33.13 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3153 |
2853 |
34.26 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3139 |
2839 |
20.61 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1627 |
1472 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1623 |
1468 |
4.94 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1605 |
1452 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1536 |
1390 |
2.37 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1505 |
1361 |
0.23 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1419 |
1284 |
0.34 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1298 |
1174 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1150 |
1041 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1069 |
967 |
0.34 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
887 |
802 |
0.15 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
842 |
762 |
0.86 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
344 |
311 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
276 |
250 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
117 |
106 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3213 |
2906 |
88.69 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3207 |
2901 |
132.02 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3169 |
2866 |
38.66 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
3151 |
2850 |
28.06 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
3138 |
2838 |
29.91 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1622 |
1467 |
9.86 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1613 |
1460 |
5.28 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1603 |
1450 |
0.62 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1541 |
1394 |
5.34 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1490 |
1348 |
3.26 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1393 |
1260 |
0.34 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
1250 |
1130 |
1.77 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
1043 |
943 |
0.80 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
1019 |
922 |
1.48 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
804 |
728 |
2.29 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
462 |
417 |
0.14 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
228 |
206 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30564.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27649.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.251 |
0.722 |
0.615 |
| C2 |
-0.251 |
-0.722 |
0.615 |
| C3 |
-0.251 |
1.569 |
-0.551 |
| C4 |
0.251 |
-1.569 |
-0.551 |
| H5 |
-0.054 |
1.193 |
1.545 |
| H6 |
1.338 |
0.722 |
0.618 |
| H7 |
0.054 |
-1.193 |
1.545 |
| H8 |
-1.338 |
-0.722 |
0.618 |
| H9 |
0.089 |
2.594 |
-0.457 |
| H10 |
-0.089 |
-2.594 |
-0.457 |
| H11 |
0.102 |
1.196 |
-1.505 |
| H12 |
-1.336 |
1.584 |
-0.583 |
| H13 |
-0.102 |
-1.196 |
-1.505 |
| H14 |
1.336 |
-1.584 |
-0.583 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
| C1 | | 1.5296 | 1.5266 | 2.5716 | 1.0857 | 1.0869 | 2.1382 | 2.1477 | 2.1633 | 3.5022 | 2.1773 | 2.1671 | 2.8807 | 2.8162 |
C2 | 1.5296 | | 2.5716 | 1.5266 | 2.1382 | 2.1477 | 1.0857 | 1.0869 | 3.5022 | 2.1633 | 2.8807 | 2.8162 | 2.1773 | 2.1671 | C3 | 1.5266 | 2.5716 | | 3.1786 | 2.1386 | 2.1474 | 3.4811 | 2.7931 | 1.0840 | 4.1676 | 1.0832 | 1.0853 | 2.9286 | 3.5302 | C4 | 2.5716 | 1.5266 | 3.1786 | | 3.4811 | 2.7931 | 2.1386 | 2.1474 | 4.1676 | 1.0840 | 2.9286 | 3.5302 | 1.0832 | 1.0853 | H5 | 1.0857 | 2.1382 | 2.1386 | 3.4811 | | 1.7373 | 2.3889 | 2.4849 | 2.4477 | 4.2841 | 3.0535 | 2.5142 | 3.8741 | 3.7645 | H6 | 1.0869 | 2.1477 | 2.1474 | 2.7931 | 1.7373 | | 2.4849 | 3.0411 | 2.4940 | 3.7675 | 2.5019 | 3.0554 | 3.2034 | 2.6004 | H7 | 2.1382 | 1.0857 | 3.4811 | 2.1386 | 2.3889 | 2.4849 | | 1.7373 | 4.2841 | 2.4477 | 3.8741 | 3.7645 | 3.0535 | 2.5142 | H8 | 2.1477 | 1.0869 | 2.7931 | 2.1474 | 2.4849 | 3.0411 | 1.7373 | | 3.7675 | 2.4940 | 3.2034 | 2.6004 | 2.5019 | 3.0554 | H9 | 2.1633 | 3.5022 | 1.0840 | 4.1676 | 2.4477 | 2.4940 | 4.2841 | 3.7675 | | 5.1912 | 1.7472 | 1.7515 | 3.9365 | 4.3618 | H10 | 3.5022 | 2.1633 | 4.1676 | 1.0840 | 4.2841 | 3.7675 | 2.4477 | 2.4940 | 5.1912 | | 3.9365 | 4.3618 | 1.7472 | 1.7515 | H11 | 2.1773 | 2.8807 | 1.0832 | 2.9286 | 3.0535 | 2.5019 | 3.8741 | 3.2034 | 1.7472 | 3.9365 | | 1.7518 | 2.4001 | 3.1777 | H12 | 2.1671 | 2.8162 | 1.0853 | 3.5302 | 2.5142 | 3.0554 | 3.7645 | 2.6004 | 1.7515 | 4.3618 | 1.7518 | | 3.1777 | 4.1441 | H13 | 2.8807 | 2.1773 | 2.9286 | 1.0832 | 3.8741 | 3.2034 | 3.0535 | 2.5019 | 3.9365 | 1.7472 | 2.4001 | 3.1777 | | 1.7518 | H14 | 2.8162 | 2.1671 | 3.5302 | 1.0853 | 3.7645 | 2.6004 | 2.5142 | 3.0554 | 4.3618 | 1.7515 | 3.1777 | 4.1441 | 1.7518 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C4 |
114.581 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.496 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.164 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.783 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.959 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.004 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C3 |
114.581 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.496 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.164 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.783 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.959 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H14 |
111.004 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.726 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.347 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.726 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.347 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
106.191 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.191 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.449 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.688 |
| H10 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.449 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.688 |
| H11 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.770 |
|
H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.770 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.325 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.325 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-1.459 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-1.459 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.343 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.389 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.343 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.389 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.230 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.230 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.431 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.392 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.431 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.392 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.097 |
0.097 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.331 |
0.090 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.090 |
-28.940 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.789 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.533 |
0.090 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.090 |
-0.379 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.154 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.307 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.608 |
|---|
| xy | 0.090 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.804 |
-0.084 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.084 |
7.962 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.160 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
107.020 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.345 |
