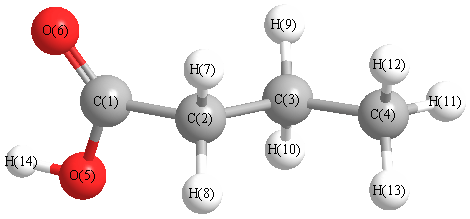Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
4098 |
3707 |
117.42 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3254 |
2944 |
35.12 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3220 |
2913 |
49.17 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3217 |
2910 |
54.07 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3194 |
2889 |
5.94 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3191 |
2886 |
12.23 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3166 |
2864 |
13.03 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
3155 |
2854 |
34.30 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1986 |
1797 |
464.98 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1629 |
1474 |
7.52 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1615 |
1461 |
7.74 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1612 |
1458 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1606 |
1453 |
8.35 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1541 |
1394 |
6.12 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1522 |
1377 |
28.49 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1488 |
1346 |
69.40 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1435 |
1298 |
2.18 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1411 |
1276 |
4.19 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1369 |
1238 |
35.72 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1323 |
1197 |
152.56 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1207 |
1092 |
9.62 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1180 |
1067 |
87.90 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
1105 |
999 |
1.11 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
979 |
886 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
967 |
875 |
2.56 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
947 |
857 |
6.53 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
812 |
734 |
23.13 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A |
797 |
721 |
22.10 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A |
663 |
600 |
70.19 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A |
614 |
555 |
82.61 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A |
464 |
420 |
3.86 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A |
352 |
318 |
1.47 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A |
262 |
237 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A |
201 |
181 |
0.17 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A |
96 |
87 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A |
40 |
36 |
0.96 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27857.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 25199.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
1.267 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.125 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.486 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-1.277 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.813 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
O |
-1.318 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.322 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.448 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.354 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.459 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.282 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.431 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.426 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.030 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.406 |
1.545 |
0.359 |
2.119 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.393 |
5.598 |
0.206 |
| y |
5.598 |
-40.068 |
-1.599 |
| z |
0.206 |
-1.599 |
-36.252 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.767 |
5.598 |
0.206 |
| y |
5.598 |
-3.745 |
-1.599 |
| z |
0.206 |
-1.599 |
1.978 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.957 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 3.675 |
|---|
| xy | 5.598 |
|---|
| xz | 0.206 |
|---|
| yz | -1.599 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
9.190 |
-0.157 |
-0.247 |
| y |
-0.157 |
7.602 |
0.047 |
| z |
-0.247 |
0.047 |
6.837 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
206.689 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
14.377 |