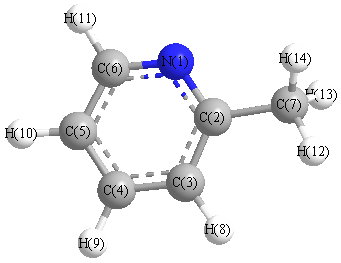
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3355 |
3035 |
11.38 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3344 |
3025 |
22.07 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3323 |
3006 |
9.72 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3310 |
2994 |
17.72 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
3244 |
2935 |
22.94 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
3174 |
2871 |
23.81 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1782 |
1612 |
91.97 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1759 |
1591 |
40.21 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1642 |
1486 |
27.50 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1610 |
1457 |
30.35 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1580 |
1430 |
15.44 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1537 |
1391 |
0.41 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1434 |
1297 |
12.19 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
1350 |
1222 |
4.89 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
1302 |
1178 |
0.20 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
1208 |
1093 |
1.23 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A' |
1168 |
1057 |
19.15 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A' |
1142 |
1033 |
7.05 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A' |
1092 |
988 |
3.24 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A' |
1067 |
965 |
1.85 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A' |
870 |
787 |
0.14 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A' |
685 |
620 |
2.31 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A' |
589 |
533 |
1.99 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A' |
381 |
345 |
3.38 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
3230 |
2922 |
17.11 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
1595 |
1443 |
5.69 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
1165 |
1054 |
4.28 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
A" |
1132 |
1024 |
0.56 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
A" |
1102 |
997 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
A" |
987 |
893 |
0.07 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
A" |
845 |
765 |
52.80 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
A" |
814 |
737 |
12.87 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
A" |
532 |
481 |
5.38 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
A" |
461 |
417 |
3.84 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
A" |
224 |
203 |
3.59 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
A" |
74 |
67 |
0.53 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27055.0 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 24474.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
N |
-1.300 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
0.645 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.594 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.156 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
C |
0.068 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
C |
-1.013 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
C |
-0.987 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.553 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.503 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.477 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.867 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.292 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.323 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.323 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.764 |
-0.709 |
0.000 |
1.902 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-41.248 |
-1.827 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.827 |
-36.600 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-44.739 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.578 |
-1.827 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.827 |
6.393 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-5.816 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -11.631 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -4.647 |
|---|
| xy | -1.827 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
11.622 |
-0.154 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.154 |
13.625 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
7.295 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
189.274 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
13.758 |