Jump to
S1C2
S1C3
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -266.899205 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -266.899205 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 196.678892 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3246 |
2936 |
36.61 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3172 |
2869 |
92.38 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3157 |
2855 |
65.15 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
1694 |
1533 |
3.82 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
1654 |
1496 |
0.76 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1520 |
1375 |
5.57 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1365 |
1234 |
11.76 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1339 |
1211 |
78.67 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1286 |
1164 |
209.99 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1255 |
1136 |
29.68 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1062 |
961 |
3.22 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1023 |
925 |
7.61 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
802 |
725 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
254 |
230 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
B |
3253 |
2943 |
49.91 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
B |
3207 |
2901 |
68.13 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
B |
3164 |
2862 |
84.58 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
B |
1645 |
1488 |
3.09 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
B |
1575 |
1425 |
11.40 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
1479 |
1338 |
1.33 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
1343 |
1215 |
10.32 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
1263 |
1142 |
24.45 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
1210 |
1094 |
55.96 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
1059 |
958 |
72.82 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
977 |
884 |
15.66 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
707 |
639 |
5.63 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
57i |
51i |
19.11 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21826.3 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19744.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.198 |
| C2 |
-0.263 |
0.711 |
-0.940 |
| C3 |
0.263 |
-0.711 |
-0.940 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
1.123 |
0.374 |
| O5 |
0.000 |
-1.123 |
0.374 |
| H6 |
0.887 |
0.028 |
1.820 |
| H7 |
-0.887 |
-0.028 |
1.820 |
| H8 |
-1.329 |
0.739 |
-1.143 |
| H9 |
1.329 |
-0.739 |
-1.143 |
| H10 |
-0.248 |
-1.370 |
-1.625 |
| H11 |
0.248 |
1.370 |
-1.625 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2681 | 2.2681 | 1.3930 | 1.3930 | 1.0836 | 1.0836 | 2.7919 | 2.7919 | 3.1475 | 3.1475 |
C2 | 2.2681 | | 1.5168 | 1.4019 | 2.2717 | 3.0667 | 2.9238 | 1.0856 | 2.1636 | 2.1915 | 1.0796 | C3 | 2.2681 | 1.5168 | | 2.2717 | 1.4019 | 2.9238 | 3.0667 | 2.1636 | 1.0856 | 1.0796 | 2.1915 | O4 | 1.3930 | 1.4019 | 2.2717 | | 2.2467 | 2.0191 | 2.0497 | 2.0538 | 2.7455 | 3.2056 | 2.0292 | O5 | 1.3930 | 2.2717 | 1.4019 | 2.2467 | | 2.0497 | 2.0191 | 2.7455 | 2.0538 | 2.0292 | 3.2056 | H6 | 1.0836 | 3.0667 | 2.9238 | 2.0191 | 2.0497 | | 1.7750 | 3.7680 | 3.0923 | 3.8867 | 3.7516 | H7 | 1.0836 | 2.9238 | 3.0667 | 2.0497 | 2.0191 | 1.7750 | | 3.0923 | 3.7680 | 3.7516 | 3.8867 | H8 | 2.7919 | 1.0856 | 2.1636 | 2.0538 | 2.7455 | 3.7680 | 3.0923 | | 3.0418 | 2.4186 | 1.7662 | H9 | 2.7919 | 2.1636 | 1.0856 | 2.7455 | 2.0538 | 3.0923 | 3.7680 | 3.0418 | | 1.7662 | 2.4186 | H10 | 3.1475 | 2.1915 | 1.0796 | 3.2056 | 2.0292 | 3.8867 | 3.7516 | 2.4186 | 1.7662 | | 2.7854 | H11 | 3.1475 | 1.0796 | 2.1915 | 2.0292 | 3.2056 | 3.7516 | 3.8867 | 1.7662 | 2.4186 | 2.7854 | |
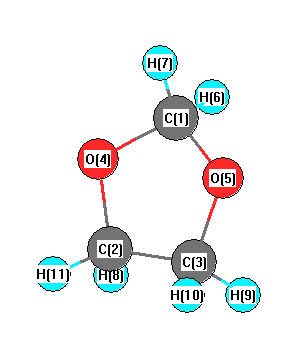 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
108.486 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
108.486 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
102.149 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.404 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.082 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
102.149 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.404 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
114.082 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.492 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.584 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.094 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.663 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.028 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.094 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.584 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.663 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.028 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.974 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.309 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.309 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.289 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.702 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.702 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.844 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.844 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.584 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.584 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.514 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.514 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.592 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.592 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.246 |
1.246 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-29.149 |
-0.356 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.356 |
-34.979 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-26.007 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.343 |
-0.356 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.356 |
-7.401 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.057 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 12.115 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 5.829 |
|---|
| xy | -0.356 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.438 |
-0.107 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.107 |
5.674 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.706 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
91.900 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.586 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C3
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -266.899295 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -266.907767 |
| HF Energy | -266.899295 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 196.707722 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3260 |
2949 |
41.63 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3237 |
2929 |
51.15 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3230 |
2922 |
60.39 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3179 |
2876 |
57.93 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3152 |
2851 |
68.24 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3141 |
2841 |
110.59 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1691 |
1529 |
3.71 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1658 |
1500 |
1.10 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1645 |
1488 |
2.84 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1573 |
1423 |
12.29 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1518 |
1374 |
3.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1481 |
1340 |
1.98 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1379 |
1247 |
8.65 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1351 |
1222 |
20.41 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1323 |
1197 |
66.28 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1302 |
1178 |
127.79 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1263 |
1142 |
34.21 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1245 |
1126 |
97.18 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1205 |
1090 |
54.28 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1075 |
972 |
30.61 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1054 |
954 |
51.21 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1021 |
923 |
11.68 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
962 |
870 |
13.52 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
805 |
728 |
0.42 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
720 |
651 |
5.90 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
256 |
232 |
6.99 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
65 |
59 |
11.71 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21894.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19806.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.185 |
-0.052 |
0.086 |
| C2 |
-0.999 |
-0.688 |
-0.104 |
| C3 |
-0.874 |
0.804 |
0.168 |
| O4 |
0.323 |
-1.147 |
0.028 |
| O5 |
0.439 |
1.071 |
-0.236 |
| H6 |
1.595 |
0.031 |
1.090 |
| H7 |
1.984 |
-0.163 |
-0.633 |
| H8 |
-1.355 |
-0.884 |
-1.108 |
| H9 |
-1.001 |
1.029 |
1.223 |
| H10 |
-1.552 |
1.414 |
-0.409 |
| H11 |
-1.635 |
-1.201 |
0.604 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2828 | 2.2318 | 1.3953 | 1.3857 | 1.0872 | 1.0803 | 2.9276 | 2.6913 | 3.1440 | 3.0894 |
C2 | 2.2828 | | 1.5223 | 1.4054 | 2.2759 | 2.9441 | 3.0747 | 1.0836 | 2.1704 | 2.1950 | 1.0811 | C3 | 2.2318 | 1.5223 | | 2.2938 | 1.3999 | 2.7465 | 3.1220 | 2.1701 | 1.0865 | 1.0788 | 2.1889 | O4 | 1.3953 | 1.4054 | 2.2938 | | 2.2367 | 2.0327 | 2.0410 | 2.0437 | 2.8139 | 3.2040 | 2.0417 | O5 | 1.3857 | 2.2759 | 1.3999 | 2.2367 | | 2.0432 | 2.0162 | 2.7928 | 2.0513 | 2.0279 | 3.1892 | H6 | 1.0872 | 2.9441 | 2.7465 | 2.0327 | 2.0432 | | 1.7764 | 3.7905 | 2.7845 | 3.7497 | 3.4910 | H7 | 1.0803 | 3.0747 | 3.1220 | 2.0410 | 2.0162 | 1.7764 | | 3.4491 | 3.7120 | 3.8781 | 3.9632 | H8 | 2.9276 | 1.0836 | 2.1701 | 2.0437 | 2.7928 | 3.7905 | 3.4491 | | 3.0365 | 2.4095 | 1.7637 | H9 | 2.6913 | 2.1704 | 1.0865 | 2.8139 | 2.0513 | 2.7845 | 3.7120 | 3.0365 | | 1.7655 | 2.3999 | H10 | 3.1440 | 2.1950 | 1.0788 | 3.2040 | 2.0279 | 3.7497 | 3.8781 | 2.4095 | 1.7655 | | 2.8056 | H11 | 3.0894 | 1.0811 | 2.1889 | 2.0417 | 3.1892 | 3.4910 | 3.9632 | 1.7637 | 2.3999 | 2.8056 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
109.190 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
106.486 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
102.227 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.501 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.014 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
103.090 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.665 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
113.361 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.081 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.305 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.419 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.719 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.710 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
110.847 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.066 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.546 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.113 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
110.080 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.126 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.238 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.525 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.683 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.588 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-1.032 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.989 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.843 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.721 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.513 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.447 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.675 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.619 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.246 |
0.271 |
0.535 |
1.383 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.012 |
-0.484 |
0.286 |
| y |
-0.484 |
-34.715 |
0.905 |
| z |
0.286 |
0.905 |
-29.426 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.058 |
-0.484 |
0.286 |
| y |
-0.484 |
-6.996 |
0.905 |
| z |
0.286 |
0.905 |
0.938 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.876 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 8.703 |
|---|
| xy | -0.484 |
|---|
| xz | 0.286 |
|---|
| yz | 0.905 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.687 |
-0.033 |
0.040 |
| y |
-0.033 |
5.713 |
0.075 |
| z |
0.040 |
0.075 |
5.399 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
91.874 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.585 |
Jump to
S1C1
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -266.899216 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -266.899216 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 196.676612 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3253 |
2942 |
49.93 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3246 |
2936 |
36.63 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3207 |
2901 |
68.15 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3172 |
2869 |
92.59 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3164 |
2862 |
84.57 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3157 |
2855 |
64.94 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1694 |
1533 |
3.81 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1654 |
1496 |
0.77 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1645 |
1488 |
3.09 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1575 |
1425 |
11.39 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1520 |
1375 |
5.56 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1479 |
1338 |
1.34 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1365 |
1234 |
11.78 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1343 |
1215 |
10.31 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1339 |
1211 |
78.54 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1286 |
1164 |
210.17 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1263 |
1142 |
24.41 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1255 |
1136 |
29.64 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1210 |
1094 |
56.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
1062 |
961 |
3.21 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
1059 |
958 |
72.82 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
1023 |
925 |
7.63 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
977 |
884 |
15.65 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
802 |
725 |
0.51 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
707 |
639 |
5.63 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
254 |
230 |
0.32 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
57i |
51i |
19.10 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 21825.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 19743.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.198 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.940 |
0.740 |
0.165 |
| C3 |
-0.940 |
-0.740 |
-0.165 |
| O4 |
0.374 |
1.113 |
-0.152 |
| O5 |
0.374 |
-1.113 |
0.152 |
| H6 |
1.820 |
-0.093 |
-0.882 |
| H7 |
1.820 |
0.092 |
0.883 |
| H8 |
-1.143 |
0.912 |
1.217 |
| H9 |
-1.144 |
-0.912 |
-1.217 |
| H10 |
-1.625 |
-1.324 |
0.431 |
| H11 |
-1.625 |
1.324 |
-0.431 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
O5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 2.2681 | 2.2682 | 1.3930 | 1.3931 | 1.0836 | 1.0836 | 2.7920 | 2.7922 | 3.1475 | 3.1475 |
C2 | 2.2681 | | 1.5168 | 1.4019 | 2.2718 | 3.0668 | 2.9237 | 1.0856 | 2.1635 | 2.1915 | 1.0796 | C3 | 2.2682 | 1.5168 | | 2.2718 | 1.4019 | 2.9240 | 3.0666 | 2.1635 | 1.0856 | 1.0796 | 2.1915 | O4 | 1.3930 | 1.4019 | 2.2718 | | 2.2467 | 2.0191 | 2.0497 | 2.0538 | 2.7457 | 3.2056 | 2.0293 | O5 | 1.3931 | 2.2718 | 1.4019 | 2.2467 | | 2.0497 | 2.0192 | 2.7457 | 2.0538 | 2.0293 | 3.2056 | H6 | 1.0836 | 3.0668 | 2.9240 | 2.0191 | 2.0497 | | 1.7750 | 3.7681 | 3.0929 | 3.8869 | 3.7517 | H7 | 1.0836 | 2.9237 | 3.0666 | 2.0497 | 2.0192 | 1.7750 | | 3.0924 | 3.7682 | 3.7514 | 3.8867 | H8 | 2.7920 | 1.0856 | 2.1635 | 2.0538 | 2.7457 | 3.7681 | 3.0924 | | 3.0417 | 2.4185 | 1.7661 | H9 | 2.7922 | 2.1635 | 1.0856 | 2.7457 | 2.0538 | 3.0929 | 3.7682 | 3.0417 | | 1.7661 | 2.4185 | H10 | 3.1475 | 2.1915 | 1.0796 | 3.2056 | 2.0293 | 3.8869 | 3.7514 | 2.4185 | 1.7661 | | 2.7855 | H11 | 3.1475 | 1.0796 | 2.1915 | 2.0293 | 3.2056 | 3.7517 | 3.8867 | 1.7661 | 2.4185 | 2.7855 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
O4 |
C2 |
108.488 |
|
C1 |
O5 |
C3 |
108.491 |
| C2 |
C3 |
O5 |
102.152 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.401 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
114.080 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
O4 |
102.151 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
111.401 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H11 |
114.080 |
| O4 |
C1 |
O5 |
107.492 |
|
O4 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.585 |
| O4 |
C1 |
H7 |
111.095 |
|
O4 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.667 |
| O4 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.030 |
|
O5 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.094 |
| O5 |
C1 |
H7 |
108.585 |
|
O5 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.667 |
| O5 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.030 |
|
H6 |
C1 |
H7 |
109.973 |
| H8 |
C2 |
H11 |
109.306 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
109.306 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.366 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.749 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.749 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.960 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
O |
-0.960 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.684 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.684 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.563 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.563 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.646 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.646 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.246 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.246 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-26.007 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
-34.777 |
1.123 |
| z |
0.000 |
1.123 |
-29.351 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
6.058 |
-0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.000 |
-7.098 |
1.123 |
| z |
0.000 |
1.123 |
1.041 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.081 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 8.771 |
|---|
| xy | -0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 1.123 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.706 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
5.699 |
0.072 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.072 |
5.413 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
91.902 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.587 |
