Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2776.548234 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2776.552592 |
| HF Energy | -2776.548234 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 237.050183 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
2021 |
1828 |
300.78 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1009 |
913 |
181.89 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
891 |
806 |
516.76 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
519 |
469 |
1.86 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
294 |
266 |
0.38 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
162 |
146 |
0.12 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2447.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2214.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Br1 |
-0.682 |
-0.796 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
0.000 |
0.851 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
1.379 |
0.838 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
1.777 |
1.899 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Br1 |
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
| Br1 | | 1.7831 | 2.6304 | 3.6484 |
O2 | 1.7831 | | 1.3792 | 2.0627 | N3 | 2.6304 | 1.3792 | | 1.1333 | O4 | 3.6484 | 2.0627 | 1.1333 | |
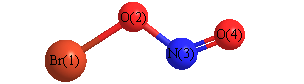 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br1 |
O2 |
N3 |
111.934 |
|
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
109.987 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Br |
0.350 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.444 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
0.396 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.301 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-0.458 |
-1.315 |
0.000 |
1.393 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-34.861 |
0.615 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.615 |
-34.693 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.480 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.775 |
0.615 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.615 |
-0.522 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.297 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.594 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.168 |
|---|
| xy | 0.615 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.303 |
1.991 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.991 |
6.799 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.187 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
138.059 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.750 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -2776.551198 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -2776.555819 |
| HF Energy | -2776.551198 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 247.021101 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
1972 |
1784 |
290.62 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
1009 |
913 |
148.50 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
862 |
780 |
196.27 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
650 |
588 |
2.88 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
254 |
230 |
0.43 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A" |
341 |
308 |
1.60 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2544.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9046) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 2301.8 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| Br1 |
0.000 |
0.907 |
0.000 |
| O2 |
-0.862 |
-0.674 |
0.000 |
| N3 |
-0.144 |
-1.813 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
0.988 |
-1.705 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
Br1 |
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
| Br1 | | 1.8007 | 2.7235 | 2.7926 |
O2 | 1.8007 | | 1.3460 | 2.1176 | N3 | 2.7235 | 1.3460 | | 1.1369 | O4 | 2.7926 | 2.1176 | 1.1369 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| Br1 |
O2 |
N3 |
119.177 |
|
O2 |
N3 |
O4 |
116.795 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
Br |
0.263 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
O |
-0.197 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
N |
0.188 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.254 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.198 |
0.877 |
0.000 |
0.899 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.036 |
1.130 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.130 |
-33.053 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-33.468 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.775 |
1.130 |
0.000 |
| y |
1.130 |
1.699 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.076 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.152 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.983 |
|---|
| xy | 1.130 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.173 |
-0.185 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.185 |
7.631 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.161 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
113.931 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.674 |
