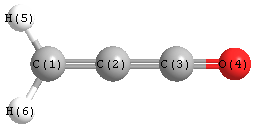Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -189.563735 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -189.563735 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 89.196677 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A1 |
3259 |
2972 |
29.93 |
167.86 |
0.10 |
0.19 |
| 2 |
A1 |
2458 |
2242 |
1777.37 |
96.74 |
0.49 |
0.66 |
| 3 |
A1 |
1930 |
1760 |
63.73 |
16.16 |
0.04 |
0.08 |
| 4 |
A1 |
1583 |
1443 |
2.88 |
9.15 |
0.59 |
0.74 |
| 5 |
A1 |
990 |
903 |
5.40 |
69.64 |
0.15 |
0.26 |
| 6 |
B1 |
1157 |
1055 |
24.11 |
6.42 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 7 |
B1 |
713 |
650 |
35.78 |
0.99 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 8 |
B1 |
220 |
201 |
1.26 |
3.44 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
B2 |
3343 |
3049 |
4.62 |
114.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 10 |
B2 |
1139 |
1039 |
4.92 |
0.01 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
B2 |
534 |
487 |
17.43 |
5.19 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
B2 |
106i |
96i |
19.33 |
0.07 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 8609.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.912) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7852.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is C2v
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-1.862 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.551 |
| C3 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.723 |
| O4 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.875 |
| H5 |
0.000 |
0.921 |
-2.433 |
| H6 |
0.000 |
-0.921 |
-2.433 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3104 | 2.5846 | 3.7370 | 1.0839 | 1.0839 |
C2 | 1.3104 | | 1.2741 | 2.4265 | 2.0950 | 2.0950 | C3 | 2.5846 | 1.2741 | | 1.1524 | 3.2874 | 3.2874 | O4 | 3.7370 | 2.4265 | 1.1524 | | 4.4055 | 4.4055 | H5 | 1.0839 | 2.0950 | 3.2874 | 4.4055 | | 1.8424 | H6 | 1.0839 | 2.0950 | 3.2874 | 4.4055 | 1.8424 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
180.000 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
121.799 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.799 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
180.000 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
116.403 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.714 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.346 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
1.098 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.699 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.384 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.384 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-3.130 |
3.130 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-23.227 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-22.840 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-22.208 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.702 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
-0.123 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.825 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.650 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -0.387 |
|---|
| xy | 0.000 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
3.810 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.000 |
4.149 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
11.147 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
81.636 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.035 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -189.564363 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -189.564363 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 89.488605 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3346 |
3052 |
6.11 |
100.75 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 2 |
A' |
3260 |
2973 |
33.09 |
133.86 |
0.11 |
0.19 |
| 3 |
A' |
2352 |
2145 |
1885.49 |
87.95 |
0.51 |
0.67 |
| 4 |
A' |
1899 |
1732 |
9.21 |
35.69 |
0.17 |
0.28 |
| 5 |
A' |
1589 |
1449 |
2.32 |
12.83 |
0.61 |
0.76 |
| 6 |
A' |
1144 |
1043 |
47.02 |
2.92 |
0.09 |
0.16 |
| 7 |
A' |
1006 |
917 |
5.34 |
56.59 |
0.09 |
0.16 |
| 8 |
A' |
579 |
528 |
32.12 |
7.09 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 9 |
A' |
121 |
110 |
45.79 |
6.63 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 10 |
A" |
1162 |
1060 |
23.76 |
6.23 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A" |
769 |
702 |
27.09 |
1.21 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 12 |
A" |
294 |
268 |
2.23 |
4.43 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 8759.9 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.912) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 7989.0 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
1.016 |
-1.493 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
-0.653 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.360 |
0.597 |
0.000 |
| O4 |
-0.855 |
1.628 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
2.048 |
-1.162 |
0.000 |
| H6 |
0.858 |
-2.565 |
0.000 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
H5 |
H6 |
| C1 | | 1.3185 | 2.5028 | 3.6388 | 1.0844 | 1.0828 |
C2 | 1.3185 | | 1.3008 | 2.4356 | 2.1109 | 2.0957 | C3 | 2.5028 | 1.3008 | | 1.1432 | 2.9830 | 3.3885 | O4 | 3.6388 | 2.4356 | 1.1432 | | 4.0267 | 4.5290 | H5 | 1.0844 | 2.1109 | 2.9830 | 4.0267 | | 1.8392 | H6 | 1.0828 | 2.0957 | 3.3885 | 4.5290 | 1.8392 | |
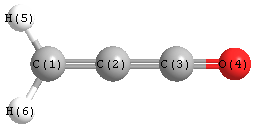 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
145.694 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
122.623 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
121.246 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
O4 |
170.467 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
116.131 |
|
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/daug-cc-pVDZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
1.189 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.645 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
0.965 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
O |
-0.602 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
-0.446 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
-0.461 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.116 |
-1.629 |
0.000 |
2.671 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-22.177 |
-1.035 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.035 |
-23.346 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-23.429 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
1.210 |
-1.035 |
0.000 |
| y |
-1.035 |
-0.543 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.667 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -1.334 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 1.168 |
|---|
| xy | -1.035 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.098 |
-2.646 |
0.000 |
| y |
-2.646 |
9.098 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
3.879 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
79.308 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
8.906 |