Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/Def2TZVPP
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -157.359918 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -157.370793 |
| HF Energy | -157.359918 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 131.095781 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/Def2TZVPP
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
Ag |
3211 |
2911 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
Ag |
3154 |
2859 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
Ag |
3138 |
2844 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Ag |
1621 |
1469 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
Ag |
1606 |
1456 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
Ag |
1539 |
1395 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
Ag |
1523 |
1381 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
Ag |
1261 |
1143 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
Ag |
1127 |
1021 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
Ag |
894 |
810 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
Ag |
451 |
409 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
Au |
3213 |
2913 |
180.95 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
Au |
3173 |
2876 |
13.60 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
Au |
1615 |
1464 |
12.28 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
Au |
1395 |
1264 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
Au |
1031 |
935 |
0.44 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
Au |
785 |
712 |
2.23 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
Au |
240 |
217 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
Au |
126 |
114 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
Bg |
3205 |
2905 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
Bg |
3151 |
2856 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
Bg |
1613 |
1462 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
Bg |
1438 |
1303 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
Bg |
1313 |
1190 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
Bg |
870 |
788 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
Bg |
277 |
251 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
Bu |
3213 |
2912 |
123.58 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
Bu |
3152 |
2857 |
93.41 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
Bu |
3145 |
2850 |
58.48 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
Bu |
1629 |
1477 |
6.35 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
Bu |
1607 |
1457 |
2.04 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
Bu |
1537 |
1393 |
3.48 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
Bu |
1437 |
1302 |
3.87 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
Bu |
1085 |
983 |
0.42 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
Bu |
1045 |
947 |
3.10 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
Bu |
277 |
251 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30547.7 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9064) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27688.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/Def2TZVPP
Point Group is C2h
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.419 |
0.637 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
-0.419 |
-0.637 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-0.419 |
1.910 |
0.000 |
| C4 |
0.419 |
-1.910 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
1.072 |
0.636 |
0.868 |
| H6 |
1.072 |
0.636 |
-0.868 |
| H7 |
-1.072 |
-0.636 |
0.868 |
| H8 |
-1.072 |
-0.636 |
-0.868 |
| H9 |
0.205 |
2.795 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
-0.205 |
-2.795 |
0.000 |
| H11 |
-1.058 |
1.957 |
-0.875 |
| H12 |
-1.058 |
1.957 |
0.875 |
| H13 |
1.058 |
-1.957 |
-0.875 |
| H14 |
1.058 |
-1.957 |
0.875 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
| C1 | | 1.5260 | 1.5240 | 2.5475 | 1.0863 | 1.0863 | 2.1446 | 2.1446 | 2.1685 | 3.4891 | 2.1655 | 2.1655 | 2.8116 | 2.8116 |
C2 | 1.5260 | | 2.5475 | 1.5240 | 2.1446 | 2.1446 | 1.0863 | 1.0863 | 3.4891 | 2.1685 | 2.8116 | 2.8116 | 2.1655 | 2.1655 | C3 | 1.5240 | 2.5475 | | 3.9110 | 2.1453 | 2.1453 | 2.7678 | 2.7678 | 1.0833 | 4.7102 | 1.0844 | 1.0844 | 4.2311 | 4.2311 | C4 | 2.5475 | 1.5240 | 3.9110 | | 2.7678 | 2.7678 | 2.1453 | 2.1453 | 4.7102 | 1.0833 | 4.2311 | 4.2311 | 1.0844 | 1.0844 | H5 | 1.0863 | 2.1446 | 2.1453 | 2.7678 | | 1.7365 | 2.4930 | 3.0381 | 2.4839 | 3.7626 | 3.0533 | 2.5066 | 3.1244 | 2.5928 | H6 | 1.0863 | 2.1446 | 2.1453 | 2.7678 | 1.7365 | | 3.0381 | 2.4930 | 2.4839 | 3.7626 | 2.5066 | 3.0533 | 2.5928 | 3.1244 | H7 | 2.1446 | 1.0863 | 2.7678 | 2.1453 | 2.4930 | 3.0381 | | 1.7365 | 3.7626 | 2.4839 | 3.1244 | 2.5928 | 3.0533 | 2.5066 | H8 | 2.1446 | 1.0863 | 2.7678 | 2.1453 | 3.0381 | 2.4930 | 1.7365 | | 3.7626 | 2.4839 | 2.5928 | 3.1244 | 2.5066 | 3.0533 | H9 | 2.1685 | 3.4891 | 1.0833 | 4.7102 | 2.4839 | 2.4839 | 3.7626 | 3.7626 | | 5.6056 | 1.7503 | 1.7503 | 4.9070 | 4.9070 | H10 | 3.4891 | 2.1685 | 4.7102 | 1.0833 | 3.7626 | 3.7626 | 2.4839 | 2.4839 | 5.6056 | | 4.9070 | 4.9070 | 1.7503 | 1.7503 | H11 | 2.1655 | 2.8116 | 1.0844 | 4.2311 | 3.0533 | 2.5066 | 3.1244 | 2.5928 | 1.7503 | 4.9070 | | 1.7503 | 4.4494 | 4.7813 | H12 | 2.1655 | 2.8116 | 1.0844 | 4.2311 | 2.5066 | 3.0533 | 2.5928 | 3.1244 | 1.7503 | 4.9070 | 1.7503 | | 4.7813 | 4.4494 | H13 | 2.8116 | 2.1655 | 4.2311 | 1.0844 | 3.1244 | 2.5928 | 3.0533 | 2.5066 | 4.9070 | 1.7503 | 4.4494 | 4.7813 | | 1.7503 | H14 | 2.8116 | 2.1655 | 4.2311 | 1.0844 | 2.5928 | 3.1244 | 2.5066 | 3.0533 | 4.9070 | 1.7503 | 4.7813 | 4.4494 | 1.7503 | |
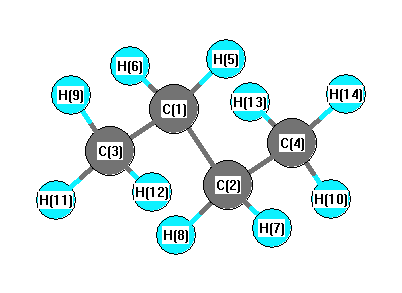 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C4 |
113.280 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.205 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.205 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
111.424 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.117 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H12 |
111.117 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C3 |
113.280 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.205 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.205 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
111.424 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.117 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H14 |
111.117 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H5 |
109.392 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.392 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.392 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.392 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
106.115 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.115 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.695 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.695 |
| H10 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.695 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.695 |
| H11 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.615 |
|
H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.615 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/Def2TZVPP
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.023 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.023 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.178 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.178 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.025 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.025 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.025 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.025 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.059 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.059 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.046 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.000 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.877 |
0.465 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.465 |
-29.413 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.044 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-0.149 |
0.465 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.465 |
-0.952 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.101 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 2.201 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.535 |
|---|
| xy | 0.465 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.887 |
-0.248 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.248 |
8.138 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.584 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
118.634 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.892 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/Def2TZVPP
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -157.358283 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -157.369209 |
| HF Energy | -157.358283 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 132.740677 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/Def2TZVPP
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3227 |
2925 |
66.03 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3208 |
2908 |
0.29 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3173 |
2876 |
33.59 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3156 |
2861 |
33.61 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3142 |
2848 |
21.48 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
1628 |
1475 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
1623 |
1471 |
4.98 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1606 |
1455 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1537 |
1393 |
2.51 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1505 |
1364 |
0.22 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1419 |
1286 |
0.33 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1298 |
1176 |
0.19 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1150 |
1043 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1069 |
969 |
0.31 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
887 |
804 |
0.16 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
842 |
764 |
0.89 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
344 |
312 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
277 |
251 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
118 |
107 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
B |
3217 |
2916 |
89.15 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
B |
3210 |
2910 |
132.20 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
B |
3172 |
2875 |
38.47 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
B |
3154 |
2858 |
28.61 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
B |
3141 |
2847 |
29.93 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
B |
1623 |
1471 |
10.02 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
B |
1614 |
1463 |
5.36 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
B |
1604 |
1454 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
| 28 |
B |
1541 |
1397 |
5.31 |
|
|
|
| 29 |
B |
1490 |
1350 |
3.14 |
|
|
|
| 30 |
B |
1393 |
1262 |
0.35 |
|
|
|
| 31 |
B |
1249 |
1132 |
1.76 |
|
|
|
| 32 |
B |
1043 |
945 |
0.82 |
|
|
|
| 33 |
B |
1019 |
923 |
1.52 |
|
|
|
| 34 |
B |
805 |
729 |
2.34 |
|
|
|
| 35 |
B |
462 |
418 |
0.13 |
|
|
|
| 36 |
B |
229 |
207 |
0.02 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 30584.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9064) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 27722.1 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/Def2TZVPP
Point Group is C2
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.251 |
0.722 |
0.615 |
| C2 |
-0.251 |
-0.722 |
0.615 |
| C3 |
-0.251 |
1.568 |
-0.551 |
| C4 |
0.251 |
-1.568 |
-0.551 |
| H5 |
-0.054 |
1.193 |
1.544 |
| H6 |
1.338 |
0.722 |
0.618 |
| H7 |
0.054 |
-1.193 |
1.544 |
| H8 |
-1.338 |
-0.722 |
0.618 |
| H9 |
0.088 |
2.594 |
-0.457 |
| H10 |
-0.088 |
-2.594 |
-0.457 |
| H11 |
0.104 |
1.195 |
-1.504 |
| H12 |
-1.336 |
1.581 |
-0.583 |
| H13 |
-0.104 |
-1.195 |
-1.504 |
| H14 |
1.336 |
-1.581 |
-0.583 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
C4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
H12 |
H13 |
H14 |
| C1 | | 1.5292 | 1.5261 | 2.5704 | 1.0855 | 1.0867 | 2.1379 | 2.1472 | 2.1629 | 3.5011 | 2.1764 | 2.1663 | 2.8798 | 2.8138 |
C2 | 1.5292 | | 2.5704 | 1.5261 | 2.1379 | 2.1472 | 1.0855 | 1.0867 | 3.5011 | 2.1629 | 2.8798 | 2.8138 | 2.1764 | 2.1663 | C3 | 1.5261 | 2.5704 | | 3.1767 | 2.1378 | 2.1469 | 3.4801 | 2.7916 | 1.0839 | 4.1661 | 1.0831 | 1.0851 | 2.9268 | 3.5268 | C4 | 2.5704 | 1.5261 | 3.1767 | | 3.4801 | 2.7916 | 2.1378 | 2.1469 | 4.1661 | 1.0839 | 2.9268 | 3.5268 | 1.0831 | 1.0851 | H5 | 1.0855 | 2.1379 | 2.1378 | 3.4801 | | 1.7374 | 2.3891 | 2.4845 | 2.4465 | 4.2832 | 3.0523 | 2.5137 | 3.8728 | 3.7624 | H6 | 1.0867 | 2.1472 | 2.1469 | 2.7916 | 1.7374 | | 2.4845 | 3.0404 | 2.4944 | 3.7655 | 2.5002 | 3.0546 | 3.2025 | 2.5973 | H7 | 2.1379 | 1.0855 | 3.4801 | 2.1378 | 2.3891 | 2.4845 | | 1.7374 | 4.2832 | 2.4465 | 3.8728 | 3.7624 | 3.0523 | 2.5137 | H8 | 2.1472 | 1.0867 | 2.7916 | 2.1469 | 2.4845 | 3.0404 | 1.7374 | | 3.7655 | 2.4944 | 3.2025 | 2.5973 | 2.5002 | 3.0546 | H9 | 2.1629 | 3.5011 | 1.0839 | 4.1661 | 2.4465 | 2.4944 | 4.2832 | 3.7655 | | 5.1900 | 1.7471 | 1.7515 | 3.9353 | 4.3590 | H10 | 3.5011 | 2.1629 | 4.1661 | 1.0839 | 4.2832 | 3.7655 | 2.4465 | 2.4944 | 5.1900 | | 3.9353 | 4.3590 | 1.7471 | 1.7515 | H11 | 2.1764 | 2.8798 | 1.0831 | 2.9268 | 3.0523 | 2.5002 | 3.8728 | 3.2025 | 1.7471 | 3.9353 | | 1.7517 | 2.3992 | 3.1739 | H12 | 2.1663 | 2.8138 | 1.0851 | 3.5268 | 2.5137 | 3.0546 | 3.7624 | 2.5973 | 1.7515 | 4.3590 | 1.7517 | | 3.1739 | 4.1396 | H13 | 2.8798 | 2.1764 | 2.9268 | 1.0831 | 3.8728 | 3.2025 | 3.0523 | 2.5002 | 3.9353 | 1.7471 | 2.3992 | 3.1739 | | 1.7517 | H14 | 2.8138 | 2.1663 | 3.5268 | 1.0851 | 3.7624 | 2.5973 | 2.5137 | 3.0546 | 4.3590 | 1.7515 | 3.1739 | 4.1396 | 1.7517 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C4 |
114.548 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.504 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.166 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.790 |
| C1 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.930 |
|
C1 |
C3 |
H12 |
110.987 |
| C2 |
C1 |
C3 |
114.548 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.504 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.166 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H10 |
110.790 |
| C2 |
C4 |
H13 |
111.930 |
|
C2 |
C4 |
H14 |
110.987 |
| C3 |
C1 |
H5 |
108.706 |
|
C3 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.357 |
| C4 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.706 |
|
C4 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.357 |
| H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
106.230 |
|
H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.230 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.460 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.702 |
| H10 |
C4 |
H13 |
107.460 |
|
H10 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.702 |
| H11 |
C3 |
H12 |
107.787 |
|
H13 |
C4 |
H14 |
107.787 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/Def2TZVPP
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.031 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.031 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.187 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
C |
-0.187 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.039 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.023 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.039 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.023 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.060 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.060 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.049 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
H |
0.047 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
H |
0.049 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
H |
0.047 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
0.000 |
0.000 |
0.101 |
0.101 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.369 |
0.096 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.096 |
-28.956 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-28.814 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
0.517 |
0.096 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.096 |
-0.365 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-0.152 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | -0.304 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | 0.587 |
|---|
| xy | 0.096 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
6.676 |
-0.083 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.083 |
7.781 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
6.981 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
107.020 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.345 |
