Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -217.198049 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -217.206098 |
| HF Energy | -217.198049 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 129.011724 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3224 |
2934 |
49.23 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3182 |
2896 |
62.34 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3168 |
2883 |
15.45 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3154 |
2870 |
26.55 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1647 |
1499 |
1.89 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1629 |
1483 |
5.16 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1611 |
1466 |
0.92 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1567 |
1426 |
14.73 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1540 |
1401 |
2.02 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1454 |
1323 |
2.20 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1224 |
1114 |
5.87 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1166 |
1062 |
134.03 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
1097 |
999 |
9.11 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
961 |
875 |
7.06 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
482 |
439 |
7.03 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
291 |
265 |
3.95 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
3234 |
2943 |
119.05 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
3208 |
2919 |
11.13 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A" |
3188 |
2901 |
0.94 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
1616 |
1471 |
5.94 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
1428 |
1300 |
0.03 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
1382 |
1258 |
1.30 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
1300 |
1183 |
2.62 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
963 |
876 |
1.41 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
817 |
743 |
1.00 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
244 |
222 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
139 |
127 |
3.72 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22458.5 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9101) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20439.5 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.134 |
-0.784 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.000 |
0.722 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
-1.460 |
1.164 |
0.000 |
| F4 |
1.453 |
-1.139 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
-0.323 |
-1.221 |
0.880 |
| H6 |
-0.323 |
-1.221 |
-0.880 |
| H7 |
0.511 |
1.116 |
-0.872 |
| H8 |
0.511 |
1.116 |
0.872 |
| H9 |
-1.534 |
2.245 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
-1.984 |
0.798 |
-0.876 |
| H11 |
-1.984 |
0.798 |
0.876 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
F4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 1.5117 | 2.5167 | 1.3667 | 1.0832 | 1.0832 | 2.1241 | 2.1241 | 3.4569 | 2.7845 | 2.7845 |
C2 | 1.5117 | | 1.5251 | 2.3610 | 2.1569 | 2.1569 | 1.0845 | 1.0845 | 2.1610 | 2.1699 | 2.1699 | C3 | 2.5167 | 1.5251 | | 3.7134 | 2.7849 | 2.7849 | 2.1553 | 2.1553 | 1.0826 | 1.0848 | 1.0848 | F4 | 1.3667 | 2.3610 | 3.7134 | | 1.9838 | 1.9838 | 2.5945 | 2.5945 | 4.5131 | 4.0414 | 4.0414 | H5 | 1.0832 | 2.1569 | 2.7849 | 1.9838 | | 1.7602 | 3.0370 | 2.4809 | 3.7746 | 3.1497 | 2.6144 | H6 | 1.0832 | 2.1569 | 2.7849 | 1.9838 | 1.7602 | | 2.4809 | 3.0370 | 3.7746 | 2.6144 | 3.1497 | H7 | 2.1241 | 1.0845 | 2.1553 | 2.5945 | 3.0370 | 2.4809 | | 1.7432 | 2.4928 | 2.5148 | 3.0626 | H8 | 2.1241 | 1.0845 | 2.1553 | 2.5945 | 2.4809 | 3.0370 | 1.7432 | | 2.4928 | 3.0626 | 2.5148 | H9 | 3.4569 | 2.1610 | 1.0826 | 4.5131 | 3.7746 | 3.7746 | 2.4928 | 2.4928 | | 1.7498 | 1.7498 | H10 | 2.7845 | 2.1699 | 1.0848 | 4.0414 | 3.1497 | 2.6144 | 2.5148 | 3.0626 | 1.7498 | | 1.7529 | H11 | 2.7845 | 2.1699 | 1.0848 | 4.0414 | 2.6144 | 3.1497 | 3.0626 | 2.5148 | 1.7498 | 1.7529 | |
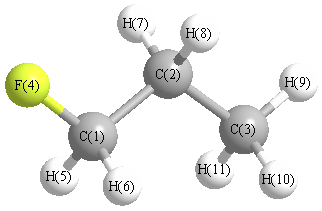 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.932 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.679 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
108.679 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F4 |
110.118 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.372 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.372 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.788 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
111.369 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.369 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
110.217 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.217 |
|
F4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.575 |
| F4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.575 |
|
H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.677 |
| H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.970 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
107.676 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.676 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.792 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.189 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.181 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.309 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.300 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.056 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.056 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.099 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.099 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.109 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.091 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.091 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.850 |
0.789 |
0.000 |
2.011 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-28.775 |
2.390 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.390 |
-25.964 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-24.595 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.495 |
2.390 |
0.000 |
| y |
2.390 |
0.720 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
2.775 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 5.550 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -2.810 |
|---|
| xy | 2.390 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.543 |
-0.280 |
0.000 |
| y |
-0.280 |
5.459 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
4.978 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
102.374 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
10.118 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -217.198163 |
| Energy at 298.15K | |
| HF Energy | -217.198163 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 131.197920 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3235 |
2944 |
54.89 |
39.28 |
0.70 |
0.82 |
| 2 |
A |
3232 |
2941 |
68.22 |
61.24 |
0.57 |
0.73 |
| 3 |
A |
3214 |
2925 |
61.45 |
46.09 |
0.68 |
0.81 |
| 4 |
A |
3193 |
2906 |
40.92 |
116.92 |
0.12 |
0.22 |
| 5 |
A |
3179 |
2894 |
12.58 |
168.33 |
0.33 |
0.50 |
| 6 |
A |
3159 |
2875 |
18.63 |
179.89 |
0.03 |
0.06 |
| 7 |
A |
3153 |
2870 |
36.14 |
33.23 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 8 |
A |
1644 |
1496 |
0.81 |
3.17 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 9 |
A |
1623 |
1477 |
8.07 |
2.60 |
0.75 |
0.85 |
| 10 |
A |
1613 |
1468 |
6.07 |
8.51 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 11 |
A |
1597 |
1454 |
1.26 |
10.09 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 12 |
A |
1558 |
1418 |
13.79 |
1.37 |
0.07 |
0.13 |
| 13 |
A |
1541 |
1402 |
2.85 |
0.44 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 14 |
A |
1501 |
1366 |
0.90 |
0.77 |
0.74 |
0.85 |
| 15 |
A |
1410 |
1284 |
1.85 |
7.85 |
0.67 |
0.80 |
| 16 |
A |
1385 |
1261 |
2.32 |
3.23 |
0.75 |
0.86 |
| 17 |
A |
1280 |
1165 |
2.29 |
0.78 |
0.05 |
0.09 |
| 18 |
A |
1223 |
1113 |
32.59 |
2.29 |
0.66 |
0.80 |
| 19 |
A |
1168 |
1063 |
60.65 |
4.40 |
0.70 |
0.82 |
| 20 |
A |
1058 |
963 |
40.89 |
4.51 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 21 |
A |
993 |
904 |
3.87 |
0.53 |
0.73 |
0.84 |
| 22 |
A |
922 |
839 |
3.88 |
12.50 |
0.13 |
0.23 |
| 23 |
A |
829 |
755 |
0.95 |
0.88 |
0.27 |
0.42 |
| 24 |
A |
515 |
468 |
5.37 |
0.39 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
| 25 |
A |
337 |
307 |
1.24 |
0.26 |
0.21 |
0.34 |
| 26 |
A |
237 |
215 |
1.69 |
0.06 |
0.40 |
0.57 |
| 27 |
A |
150 |
137 |
2.75 |
0.10 |
0.72 |
0.84 |
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22473.8 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9101) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20453.4 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.802 |
0.495 |
0.300 |
| C2 |
-0.585 |
0.649 |
-0.282 |
| C3 |
-1.538 |
-0.472 |
0.117 |
| F4 |
1.392 |
-0.647 |
-0.173 |
| H5 |
1.439 |
1.326 |
0.024 |
| H6 |
0.773 |
0.419 |
1.380 |
| H7 |
-0.502 |
0.702 |
-1.362 |
| H8 |
-0.975 |
1.607 |
0.051 |
| H9 |
-2.515 |
-0.323 |
-0.327 |
| H10 |
-1.163 |
-1.434 |
-0.210 |
| H11 |
-1.665 |
-0.511 |
1.194 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
F4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 1.5118 | 2.5385 | 1.3692 | 1.0821 | 1.0833 | 2.1229 | 2.1116 | 3.4733 | 2.8004 | 2.8108 |
C2 | 1.5118 | | 1.5249 | 2.3662 | 2.1549 | 2.1581 | 1.0849 | 1.0864 | 2.1617 | 2.1632 | 2.1661 | C3 | 2.5385 | 1.5249 | | 2.9494 | 3.4783 | 2.7799 | 2.1539 | 2.1550 | 1.0833 | 1.0823 | 1.0850 | F4 | 1.3692 | 2.3662 | 2.9494 | | 1.9826 | 1.9827 | 2.6116 | 3.2763 | 3.9231 | 2.6742 | 3.3519 | H5 | 1.0821 | 2.1549 | 3.4783 | 1.9826 | | 1.7619 | 2.4649 | 2.4303 | 4.2975 | 3.7996 | 3.7916 | H6 | 1.0833 | 2.1581 | 2.7799 | 1.9827 | 1.7619 | | 3.0373 | 2.4969 | 3.7778 | 3.1157 | 2.6162 | H7 | 2.1229 | 1.0849 | 2.1539 | 2.6116 | 2.4649 | 3.0373 | | 1.7436 | 2.4845 | 2.5152 | 3.0591 | H8 | 2.1116 | 1.0864 | 2.1550 | 3.2763 | 2.4303 | 2.4969 | 1.7436 | | 2.4977 | 3.0576 | 2.5038 | H9 | 3.4733 | 2.1617 | 1.0833 | 3.9231 | 4.2975 | 3.7778 | 2.4845 | 2.4977 | | 1.7528 | 1.7520 | H10 | 2.8004 | 2.1632 | 1.0823 | 2.6742 | 3.7996 | 3.1157 | 2.5152 | 3.0576 | 1.7528 | | 1.7530 | H11 | 2.8108 | 2.1661 | 1.0850 | 3.3519 | 3.7916 | 2.6162 | 3.0591 | 2.5038 | 1.7520 | 1.7530 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
113.427 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
108.557 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
107.589 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
F4 |
110.338 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.270 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.460 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.813 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
110.994 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.067 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
110.097 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.089 |
|
F4 |
C1 |
H5 |
107.377 |
| F4 |
C1 |
H6 |
107.315 |
|
H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
108.913 |
| H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.838 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.070 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.803 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.960 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
0.174 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.179 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.298 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
F |
-0.308 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.074 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.053 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.097 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.089 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.102 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.111 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.086 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.020 |
1.541 |
0.521 |
1.920 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-27.200 |
1.870 |
0.757 |
| y |
1.870 |
-25.597 |
-0.013 |
| z |
0.757 |
-0.013 |
-24.788 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.008 |
1.870 |
0.757 |
| y |
1.870 |
0.398 |
-0.013 |
| z |
0.757 |
-0.013 |
1.610 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.220 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -1.603 |
|---|
| xy | 1.870 |
|---|
| xz | 0.757 |
|---|
| yz | -0.013 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
5.629 |
0.244 |
0.046 |
| y |
0.244 |
5.269 |
-0.037 |
| z |
0.046 |
-0.037 |
5.080 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
91.251 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
9.553 |
