Jump to
S1C2
Energy calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -577.247356 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -577.255220 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 158.864316 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A' |
3229 |
2939 |
44.87 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A' |
3222 |
2933 |
32.44 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A' |
3179 |
2893 |
12.52 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A' |
3155 |
2871 |
31.23 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A' |
1628 |
1482 |
5.37 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A' |
1615 |
1470 |
1.04 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A' |
1610 |
1465 |
2.00 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A' |
1539 |
1400 |
0.66 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A' |
1502 |
1367 |
9.36 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A' |
1399 |
1273 |
31.87 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A' |
1202 |
1094 |
0.57 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A' |
1101 |
1002 |
1.53 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A' |
965 |
878 |
9.98 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A' |
785 |
715 |
56.21 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A' |
385 |
350 |
4.11 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A' |
254 |
231 |
2.25 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A" |
3285 |
2990 |
23.16 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A" |
3222 |
2933 |
52.97 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A" |
3197 |
2910 |
4.40 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A" |
1615 |
1470 |
6.63 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A" |
1428 |
1300 |
0.00 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A" |
1352 |
1231 |
0.28 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A" |
1189 |
1082 |
0.59 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A" |
937 |
853 |
0.05 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A" |
804 |
731 |
2.12 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A" |
251 |
228 |
0.01 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A" |
126 |
114 |
1.85 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22087.4 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9101) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20101.7 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is Cs
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.000 |
0.587 |
0.000 |
| C2 |
0.901 |
-0.633 |
0.000 |
| C3 |
2.375 |
-0.236 |
0.000 |
| Cl4 |
-1.739 |
0.129 |
0.000 |
| H5 |
0.150 |
1.195 |
0.878 |
| H6 |
0.150 |
1.195 |
-0.878 |
| H7 |
0.678 |
-1.238 |
-0.871 |
| H8 |
0.678 |
-1.238 |
0.871 |
| H9 |
3.006 |
-1.116 |
0.000 |
| H10 |
2.626 |
0.351 |
-0.877 |
| H11 |
2.626 |
0.351 |
0.877 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
Cl4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 1.5164 | 2.5135 | 1.7986 | 1.0781 | 1.0781 | 2.1328 | 2.1328 | 3.4549 | 2.7787 | 2.7787 |
C2 | 1.5164 | | 1.5266 | 2.7473 | 2.1620 | 2.1620 | 1.0833 | 1.0833 | 2.1600 | 2.1710 | 2.1710 | C3 | 2.5135 | 1.5266 | | 4.1301 | 2.7872 | 2.7872 | 2.1541 | 2.1541 | 1.0829 | 1.0846 | 1.0846 | Cl4 | 1.7986 | 2.7473 | 4.1301 | | 2.3401 | 2.3401 | 2.9100 | 2.9100 | 4.9055 | 4.4580 | 4.4580 | H5 | 1.0781 | 2.1620 | 2.7872 | 2.3401 | | 1.7559 | 3.0421 | 2.4895 | 3.7773 | 3.1501 | 2.6162 | H6 | 1.0781 | 2.1620 | 2.7872 | 2.3401 | 1.7559 | | 2.4895 | 3.0421 | 3.7773 | 2.6162 | 3.1501 | H7 | 2.1328 | 1.0833 | 2.1541 | 2.9100 | 3.0421 | 2.4895 | | 1.7410 | 2.4881 | 2.5137 | 3.0613 | H8 | 2.1328 | 1.0833 | 2.1541 | 2.9100 | 2.4895 | 3.0421 | 1.7410 | | 2.4881 | 3.0613 | 2.5137 | H9 | 3.4549 | 2.1600 | 1.0829 | 4.9055 | 3.7773 | 3.7773 | 2.4881 | 2.4881 | | 1.7507 | 1.7507 | H10 | 2.7787 | 2.1710 | 1.0846 | 4.4580 | 3.1501 | 2.6162 | 2.5137 | 3.0613 | 1.7507 | | 1.7535 | H11 | 2.7787 | 2.1710 | 1.0846 | 4.4580 | 2.6162 | 3.1501 | 3.0613 | 2.5137 | 1.7507 | 1.7535 | |
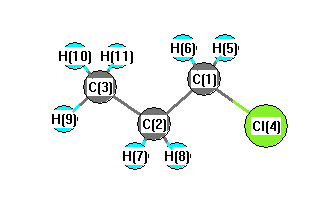 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
111.378 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.116 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.116 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
Cl4 |
111.659 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.766 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.766 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.581 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
111.368 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.368 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
110.087 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.087 |
|
Cl4 |
C1 |
H5 |
106.151 |
| Cl4 |
C1 |
H6 |
106.151 |
|
H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.036 |
| H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.945 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
107.742 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.742 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.880 |
Electronic energy levels
Electronic state
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.064 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.161 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.302 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Cl |
-0.233 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.124 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.109 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.109 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.111 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.093 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
2.401 |
0.320 |
0.000 |
2.423 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-36.348 |
0.153 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.153 |
-32.692 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
-32.801 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-3.602 |
0.153 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.153 |
1.883 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
1.719 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 3.438 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.657 |
|---|
| xy | 0.153 |
|---|
| xz | 0.000 |
|---|
| yz | 0.000 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
8.920 |
0.054 |
0.000 |
| y |
0.054 |
6.163 |
0.000 |
| z |
0.000 |
0.000 |
5.787 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
152.211 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
12.337 |
Jump to
S1C1
Energy calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| | hartrees |
|---|
| Energy at 0K | -577.246832 |
| Energy at 298.15K | -577.254797 |
| Nuclear repulsion energy | 162.555907 |
The energy at 298.15K was derived from the energy at 0K
and an integrated heat capacity that used the calculated vibrational frequencies.
Vibrational Frequencies calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
| Mode Number |
Symmetry |
Frequency
(cm-1) |
Scaled Frequency
(cm-1) |
IR Intensities
(km mol-1) |
Raman Act
(Å4/u) |
Dep P |
Dep U |
|---|
| 1 |
A |
3288 |
2992 |
16.58 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
A |
3240 |
2949 |
48.48 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
A |
3233 |
2942 |
29.05 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
A |
3217 |
2928 |
47.19 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
A |
3194 |
2906 |
7.65 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
A |
3161 |
2876 |
24.02 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
A |
3149 |
2865 |
35.93 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
A |
1624 |
1478 |
3.02 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
A |
1619 |
1474 |
7.39 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
A |
1606 |
1462 |
5.19 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
A |
1600 |
1457 |
1.70 |
|
|
|
| 12 |
A |
1544 |
1405 |
4.51 |
|
|
|
| 13 |
A |
1504 |
1368 |
0.61 |
|
|
|
| 14 |
A |
1451 |
1320 |
39.39 |
|
|
|
| 15 |
A |
1393 |
1268 |
3.84 |
|
|
|
| 16 |
A |
1338 |
1218 |
0.69 |
|
|
|
| 17 |
A |
1196 |
1089 |
0.11 |
|
|
|
| 18 |
A |
1172 |
1067 |
0.71 |
|
|
|
| 19 |
A |
1118 |
1017 |
4.01 |
|
|
|
| 20 |
A |
968 |
881 |
4.07 |
|
|
|
| 21 |
A |
916 |
834 |
8.55 |
|
|
|
| 22 |
A |
854 |
777 |
15.97 |
|
|
|
| 23 |
A |
697 |
634 |
33.62 |
|
|
|
| 24 |
A |
450 |
409 |
2.24 |
|
|
|
| 25 |
A |
315 |
287 |
0.80 |
|
|
|
| 26 |
A |
228 |
207 |
1.05 |
|
|
|
| 27 |
A |
138 |
126 |
1.09 |
|
|
|
Unscaled Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 22105.1 cm
-1
Scaled (by 0.9101) Zero Point Vibrational Energy (zpe) 20117.9 cm
-1
See section
III.C.1 List or set vibrational scaling factors
to change the scale factors used here.
See section
III.C.2
Calculate a vibrational scaling factor for a given set of molecules
to determine the least squares best scaling factor.
Geometric Data calculated at HF/cc-pVTZ
Point Group is C1
Cartesians (Å)
| Atom |
x (Å) |
y (Å) |
z (Å) |
|---|
| C1 |
0.184 |
0.871 |
0.312 |
| C2 |
-1.140 |
0.558 |
-0.361 |
| C3 |
-1.823 |
-0.707 |
0.145 |
| Cl4 |
1.457 |
-0.346 |
-0.068 |
| H5 |
0.578 |
1.817 |
-0.019 |
| H6 |
0.094 |
0.882 |
1.387 |
| H7 |
-1.786 |
1.414 |
-0.183 |
| H8 |
-0.987 |
0.500 |
-1.432 |
| H9 |
-2.778 |
-0.844 |
-0.348 |
| H10 |
-1.219 |
-1.584 |
-0.046 |
| H11 |
-2.005 |
-0.650 |
1.213 |
Atom - Atom Distances (Å)
| |
C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
Cl4 |
H5 |
H6 |
H7 |
H8 |
H9 |
H10 |
H11 |
| C1 | | 1.5175 | 2.5579 | 1.8023 | 1.0771 | 1.0784 | 2.1023 | 2.1334 | 3.4851 | 2.8499 | 2.8138 |
C2 | 1.5175 | | 1.5239 | 2.7656 | 2.1572 | 2.1640 | 1.0871 | 1.0836 | 2.1560 | 2.1666 | 2.1649 | C3 | 2.5579 | 1.5239 | | 3.3067 | 3.4872 | 2.7823 | 2.1466 | 2.1542 | 1.0833 | 1.0817 | 1.0849 | Cl4 | 1.8023 | 2.7656 | 3.3067 | | 2.3353 | 2.3414 | 3.6919 | 2.9240 | 4.2734 | 2.9488 | 3.7045 | H5 | 1.0771 | 2.1572 | 3.4872 | 2.3353 | | 1.7565 | 2.4039 | 2.4865 | 4.2954 | 3.8466 | 3.7790 | H6 | 1.0784 | 2.1640 | 2.7823 | 2.3414 | 1.7565 | | 2.5068 | 3.0434 | 3.7729 | 3.1396 | 2.6052 | H7 | 2.1023 | 1.0871 | 2.1466 | 3.6919 | 2.4039 | 2.5068 | | 1.7421 | 2.4716 | 3.0543 | 2.5021 | H8 | 2.1334 | 1.0836 | 2.1542 | 2.9240 | 2.4865 | 3.0434 | 1.7421 | | 2.4874 | 2.5132 | 3.0587 | H9 | 3.4851 | 2.1560 | 1.0833 | 4.2734 | 4.2954 | 3.7729 | 2.4716 | 2.4874 | | 1.7518 | 1.7519 | H10 | 2.8499 | 2.1666 | 1.0817 | 2.9488 | 3.8466 | 3.1396 | 3.0543 | 2.5132 | 1.7518 | | 1.7531 | H11 | 2.8138 | 2.1649 | 1.0849 | 3.7045 | 3.7790 | 2.6052 | 2.5021 | 3.0587 | 1.7519 | 1.7531 | |
 More geometry information
More geometry information
Calculated Bond Angles
| atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
|
atom1 |
atom2 |
atom3 |
angle |
| C1 |
C2 |
C3 |
114.498 |
|
C1 |
C2 |
H7 |
106.467 |
| C1 |
C2 |
H8 |
109.066 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
Cl4 |
112.551 |
| C2 |
C1 |
H5 |
111.356 |
|
C2 |
C1 |
H6 |
111.836 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H9 |
110.429 |
|
C2 |
C3 |
H10 |
111.377 |
| C2 |
C3 |
H11 |
111.046 |
|
C3 |
C2 |
H7 |
109.456 |
| C3 |
C2 |
H8 |
110.262 |
|
Cl4 |
C1 |
H5 |
105.612 |
| Cl4 |
C1 |
H6 |
105.996 |
|
H5 |
C1 |
H6 |
109.153 |
| H7 |
C2 |
H8 |
106.750 |
|
H9 |
C3 |
H10 |
108.029 |
| H9 |
C3 |
H11 |
107.802 |
|
H10 |
C3 |
H11 |
108.023 |
Electronic energy levels
Charges, Dipole, Quadrupole and Polarizability
Charges from optimized geometry at HF/cc-pVTZ
Charges (e)
| Number |
Element |
Mulliken |
CHELPG |
AIM |
ESP |
| 1 |
C |
-0.078 |
|
|
|
| 2 |
C |
-0.169 |
|
|
|
| 3 |
C |
-0.292 |
|
|
|
| 4 |
Cl |
-0.235 |
|
|
|
| 5 |
H |
0.137 |
|
|
|
| 6 |
H |
0.123 |
|
|
|
| 7 |
H |
0.101 |
|
|
|
| 8 |
H |
0.108 |
|
|
|
| 9 |
H |
0.104 |
|
|
|
| 10 |
H |
0.113 |
|
|
|
| 11 |
H |
0.087 |
|
|
|
Electric dipole moments
Electric dipole components in Debye
(What's a Debye? See section
VII.A.3)
| |
x |
y |
z |
Total |
| |
-1.829 |
1.408 |
0.338 |
2.332 |
| CHELPG |
|
|
|
|
| AIM |
|
|
|
|
| ESP |
|
|
|
|
Electric Quadrupole moment
Quadrupole components in D Å
| Primitive |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-35.393 |
0.355 |
0.163 |
| y |
0.355 |
-32.083 |
0.480 |
| z |
0.163 |
0.480 |
-32.888 |
|
| Traceless |
|---|
| | x | y | z |
|---|
| x |
-2.908 |
0.355 |
0.163 |
| y |
0.355 |
2.058 |
0.480 |
| z |
0.163 |
0.480 |
0.850 |
|
| Polar |
|---|
| 3z2-r2 | 1.700 |
|---|
| x2-y2 | -3.310 |
|---|
| xy | 0.355 |
|---|
| xz | 0.163 |
|---|
| yz | 0.480 |
|---|
|
Polarizabilities
Components of the polarizability tensor.
Units are
Å
3 (Angstrom cubed)
Change units.
| |
x |
y |
z |
| x |
7.880 |
-0.519 |
-0.126 |
| y |
-0.519 |
6.824 |
0.133 |
| z |
-0.126 |
0.133 |
5.943 |
<r2> (average value of r
2) Å
2
| <r2> |
131.261 |
| (<r2>)1/2 |
11.457 |
